The capability of a neural community to soak up data is proscribed by the variety of its parameters, and as a consequence, discovering simpler methods to extend mannequin parameters has develop into a pattern in deep studying analysis. Combination-of-experts (MoE), a kind of conditional computation the place elements of the community are activated on a per-example foundation, has been proposed as a method of dramatically growing mannequin capability with no proportional improve in computation. In sparsely-activated variants of MoE fashions (e.g., Swap Transformer, GLaM, V-MoE), a subset of consultants is chosen on a per-token or per-example foundation, thus creating sparsity within the community. Such fashions have demonstrated higher scaling in a number of domains and higher retention functionality in a continuing studying setting (e.g., Knowledgeable Gate). Nonetheless, a poor knowledgeable routing technique may cause sure consultants to be under-trained, resulting in an knowledgeable being below or over-specialized.
In “Combination-of-Consultants with Knowledgeable Selection Routing”, introduced at NeurIPS 2022, we introduce a novel MoE routing algorithm known as Knowledgeable Selection (EC). We focus on how this novel strategy can obtain optimum load balancing in an MoE system whereas permitting heterogeneity in token-to-expert mapping. In comparison with token-based routing and different routing strategies in conventional MoE networks, EC demonstrates very robust coaching effectivity and downstream activity scores. Our methodology resonates with one of many imaginative and prescient for Pathways, which is to allow heterogeneous mixture-of-experts through Pathways MPMD (multi program, multi knowledge) assist.
Overview of MoE Routing
MoE operates by adopting quite a few consultants, every as a sub-network, and activating just one or a number of consultants for every enter token. A gating community have to be chosen and optimized with a purpose to route every token to probably the most suited knowledgeable(s). Relying on how tokens are mapped to consultants, MoE may be sparse or dense. Sparse MoE solely selects a subset of consultants when routing every token, decreasing computational price as in comparison with a dense MoE. For instance, latest work has carried out sparse routing through k-means clustering, linear project to maximise token-expert affinities, or hashing. Google additionally not too long ago introduced GLaM and V-MoE, each of which advance the cutting-edge in pure language processing and pc imaginative and prescient through sparsely gated MoE with top-okay token routing, demonstrating higher efficiency scaling with sparsely activated MoE layers. Many of those prior works used a token alternative routing technique during which the routing algorithm picks the perfect one or two consultants for every token.
 |
| Token Selection Routing. The routing algorithm picks the top-1 or top-2 consultants with highest affinity scores for every token. The affinity scores may be educated along with mannequin parameters. |
The unbiased token alternative strategy usually results in an imbalanced load of consultants and under-utilization. In an effort to mitigate this, earlier sparsely gated networks launched extra auxiliary losses as regularization to stop too many tokens being routed to a single knowledgeable, however the effectiveness was restricted. In consequence, token alternative routings must overprovision knowledgeable capability by a big margin (2x–8x of the calculated capability) to keep away from dropping tokens when there’s a buffer overflow.
Along with load imbalance, most prior works allocate a set variety of consultants to every token utilizing a top-okay operate, whatever the relative significance of various tokens. We argue that completely different tokens needs to be obtained by a variable variety of consultants, conditioned on token significance or problem.
Knowledgeable Selection Routing
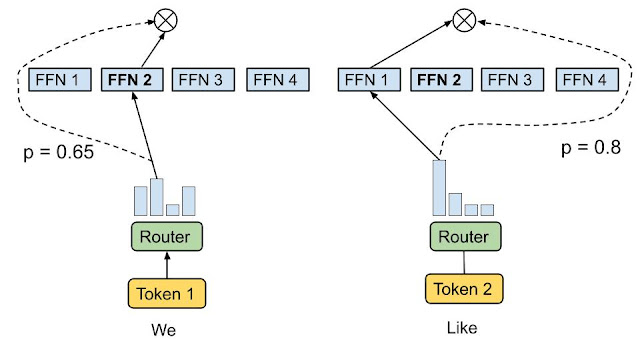
To handle the above points, we suggest a heterogeneous MoE that employs the knowledgeable alternative routing methodology illustrated beneath. As a substitute of getting tokens choose the top-okay consultants, the consultants with predetermined buffer capability are assigned to the top-okay tokens. This methodology ensures even load balancing, permits a variable variety of consultants for every token, and achieves substantial features in coaching effectivity and downstream efficiency. EC routing quickens coaching convergence by over 2x in an 8B/64E (8 billion activated parameters, 64 consultants) mannequin, in comparison with the top-1 and top-2 gating counterparts in Swap Transformer, GShard, and GLaM.
In EC routing, we set knowledgeable capability okay as the common tokens per knowledgeable in a batch of enter sequences multiplied by a capability issue, which determines the common variety of consultants that may be obtained by every token. To be taught the token-to-expert affinity, our methodology produces a token-to-expert rating matrix that’s used to make routing choices. The rating matrix signifies the probability of a given token in a batch of enter sequences being routed to a given knowledgeable.
Just like Swap Transformer and GShard, we apply an MoE and gating operate within the dense feedforward (FFN) layer, as it’s the most computationally costly a part of a Transformer-based community. After producing the token-to-expert rating matrix, a top-okay operate is utilized alongside the token dimension for every knowledgeable to select probably the most related tokens. A permutation operate is then utilized primarily based on the generated indexes of the token, to create a hidden worth with an extra knowledgeable dimension. The info is break up throughout a number of consultants such that every one consultants can execute the identical computational kernel concurrently on a subset of tokens. As a result of a set knowledgeable capability may be decided, we not overprovision knowledgeable capability resulting from load imbalancing, thus considerably decreasing coaching and inference step time by round 20% in comparison with GLaM.
Analysis
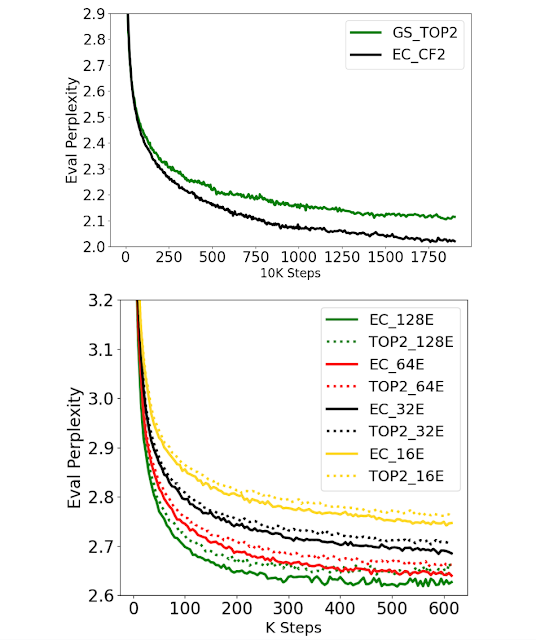
For instance the effectiveness of Knowledgeable Selection routing, we first have a look at coaching effectivity and convergence. We use EC with a capability issue of two (EC-CF2) to match the activated parameter measurement and computational price on a per-token foundation to GShard top-2 gating and run each for a set variety of steps. EC-CF2 reaches the identical perplexity as GShard top-2 in lower than half the steps and, as well as, we discover that every GShard top-2 step is 20% slower than our methodology.
We additionally scale the variety of consultants whereas fixing the knowledgeable measurement to 100M parameters for each EC and GShard top-2 strategies. We discover that each work properly by way of perplexity on the analysis dataset throughout pre-training — having extra consultants persistently improves coaching perplexity.
To validate whether or not improved perplexity straight interprets to raised efficiency in downstream duties, we carry out fine-tuning on 11 chosen duties from GLUE and SuperGLUE. We examine three MoE strategies together with Swap Transformer top-1 gating (ST High-1), GShard top-2 gating (GS High-2) and a model of our methodology (EC-CF2) that matches the activated parameters and computational price of GS High-2. The EC-CF2 methodology persistently outperforms the associated strategies and yields a mean accuracy improve of greater than 2% in a big 8B/64E setting. Evaluating our 8B/64E mannequin towards its dense counterpart, our methodology achieves higher fine-tuning outcomes, growing the common rating by 3.4 factors.
Our empirical outcomes point out that capping the variety of consultants for every token hurts the fine-tuning rating by 1 level on common. This examine confirms that permitting a variable variety of consultants per token is certainly useful. However, we compute statistics on token-to-expert routing, notably on the ratio of tokens which were routed to a sure variety of consultants. We discover {that a} majority of tokens have been routed to 1 or two consultants whereas 23% have been routed to a few or 4 consultants and solely about 3% tokens have been routed to greater than 4 consultants, thus verifying our speculation that knowledgeable alternative routing learns to allocate a variable variety of consultants to tokens.
Last Ideas
We suggest a brand new routing methodology for sparsely activated mixture-of-experts fashions. This methodology addresses load imbalance and under-utilization of consultants in standard MoE strategies, and allows the choice of completely different numbers of consultants for every token. Our mannequin demonstrates greater than 2x coaching effectivity enchancment when in comparison with the state-of-the-art GShard and Swap Transformer fashions, and achieves robust features when fine-tuning on 11 datasets within the GLUE and SuperGLUE benchmark.
Our strategy for knowledgeable alternative routing allows heterogeneous MoE with easy algorithmic improvements. We hope that this will likely result in extra advances on this area at each the applying and system ranges.
Acknowledgements
Many collaborators throughout google analysis supported this work. We notably thank Nan Du, Andrew Dai, Yanping Huang, and Zhifeng Chen for the preliminary floor work on MoE infrastructure and Tarzan datasets. We drastically respect Hanxiao Liu and Quoc Le for contributing the preliminary concepts and discussions. Tao Lei, Vincent Zhao, Da Huang, Chang Lan, Daiyi Peng, and Yifeng Lu contributed considerably on implementations and evaluations. Claire Cui, James Laudon, Martin Abadi, and Jeff Dean offered invaluable suggestions and useful resource assist.