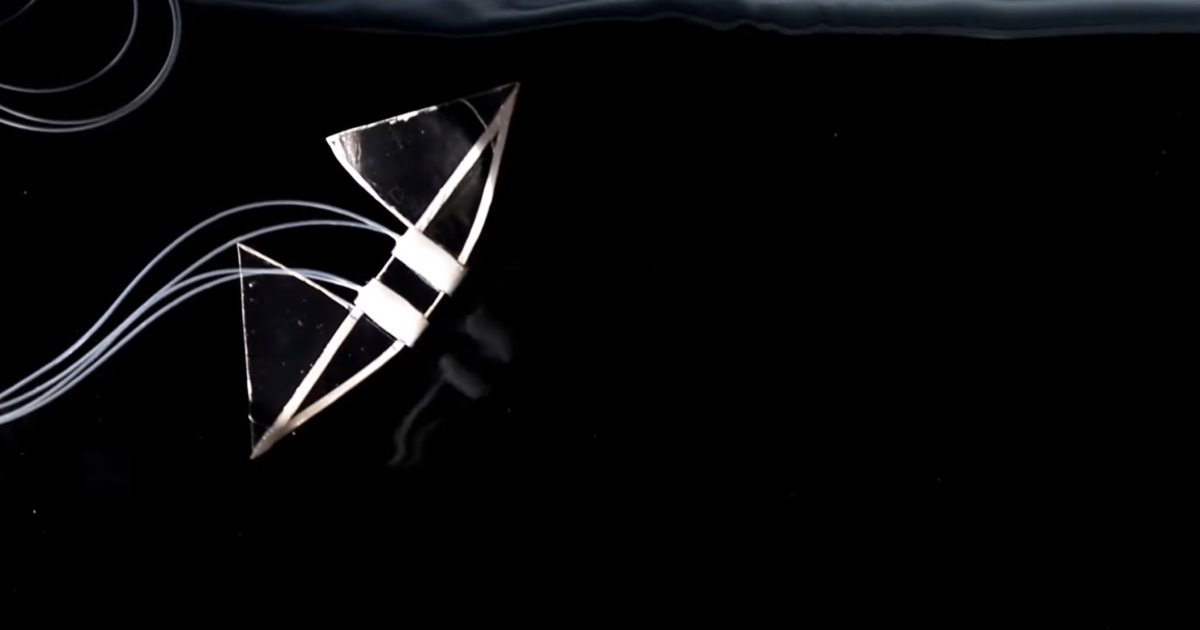
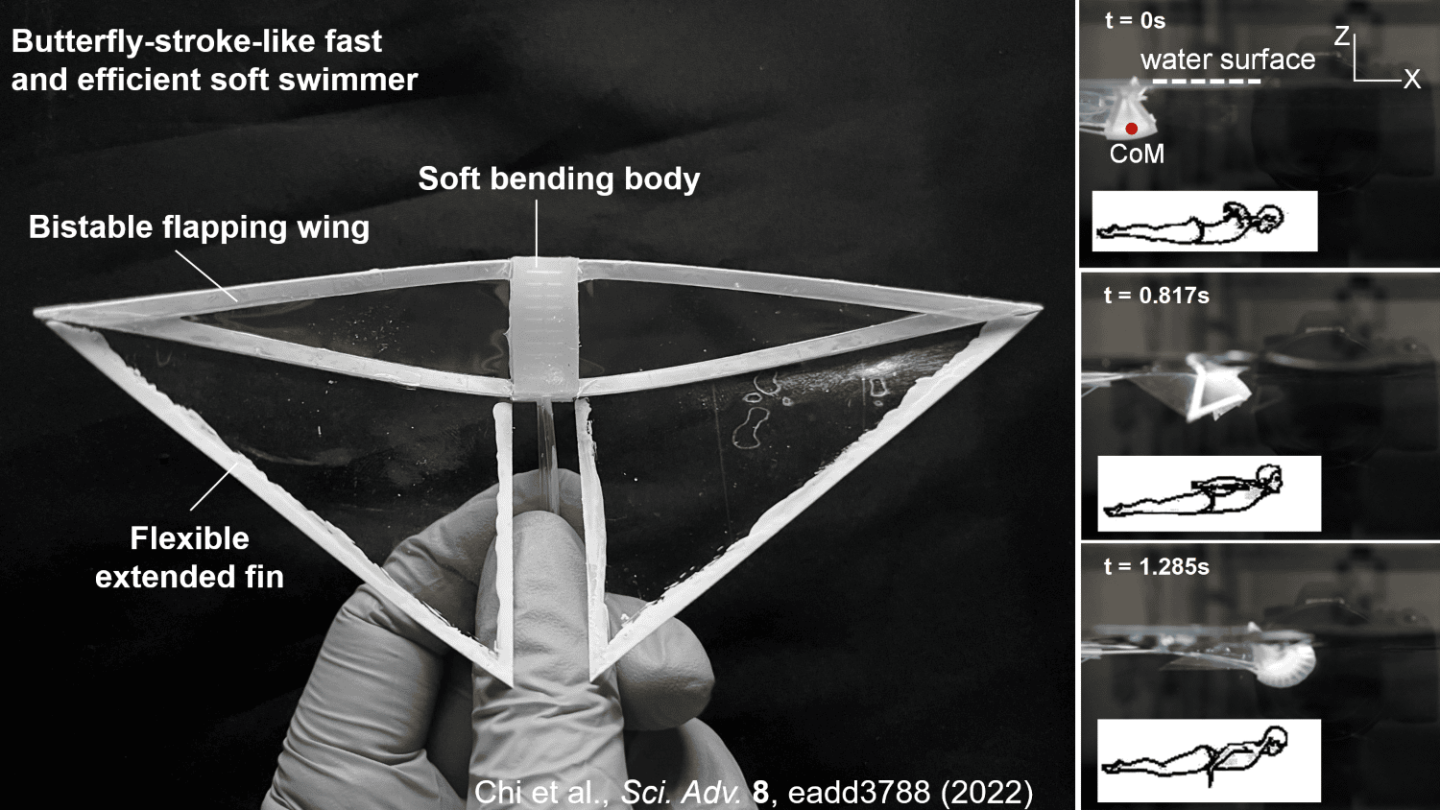
Scientists repeatedly draw concepts from the pure world in a bid to enhance robotic efficiency, and with regards to comfortable robots that swim, movement within the ocean is a wealthy supply of inspiration. The most recent creation to emerge on this house is a comfortable robotic modeled on the manta ray that mimics butterfly stroke in people to maneuver by the water with unparalleled pace.
Jellyfish, turtles, tuna and lots of different marine creatures have impressed comfortable robots that carry completely different capabilities to aquatic environments, however scientists at North Carolina (NC) State College have approached their work with a necessity for pace.
“So far, swimming comfortable robots haven’t been in a position to swim quicker than one physique size per second, however marine animals – equivalent to manta rays – are in a position to swim a lot quicker, and rather more effectively,” says Jie Yin, research creator and affiliate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State. “We needed to attract on the biomechanics of those animals to see if we might develop quicker, extra energy-efficient comfortable robots. The prototypes we’ve developed work exceptionally nicely.”
We have seen comfortable robots modeled on the manta ray earlier than, with some utilizing flapping mechanisms to imitate their environment friendly propulsion, and others counting on passive methods with versatile fins to maneuver extra naturally with the water. The NC State workforce truly constructed two variations of their robotic, each of that are designed round a comfortable silicone physique that may be inflated and deflated with a change.
North Carolina State College
Because it does so, wings connected to the inflatable physique change between two steady states in a means the scientists liken to how a hair clip snaps between open and closed when sufficient power is utilized to it. Because the physique is inflated and deflated, the wings snap backwards and forwards to generate propulsion in a means the researchers say is much like how an individual’s arms transfer throughout butterfly stroke.
“Most earlier makes an attempt to develop flapping robots have centered on utilizing motors to offer energy on to the wings,” Yin says. “Our strategy makes use of bistable wings which are passively pushed by transferring the central physique. This is a crucial distinction, as a result of it permits for a simplified design, which lowers the burden.”
The quicker model of the “butterfly bot” makes use of the comfortable physique as a single drive unit, controlling each wings directly for optimum pace. This permits it to journey at a median of three.74 physique lengths per second, round 4 instances quicker than what was beforehand doable for comfortable swimming robots, in accordance with the workforce. A second robotic constructed for maneuverability makes use of two drive items for management over both wing, enabling it to make tight turns. This extra agile model, nevertheless, was nonetheless able to touring at 1.7 physique lengths a second.
“This work is an thrilling proof of idea, however it has limitations,” Yin says. “Most clearly, the present prototypes are tethered by slender tubing, which is what we use to pump air into the central our bodies. We’re presently working to develop an untethered, autonomous model.”
You possibly can see the robots in motion within the video beneath, whereas the analysis was revealed within the journal Science Advances.
A butterfly-stroke-like comfortable robotic swimmer that’s quick and environment friendly
Supply: North Carolina State College

