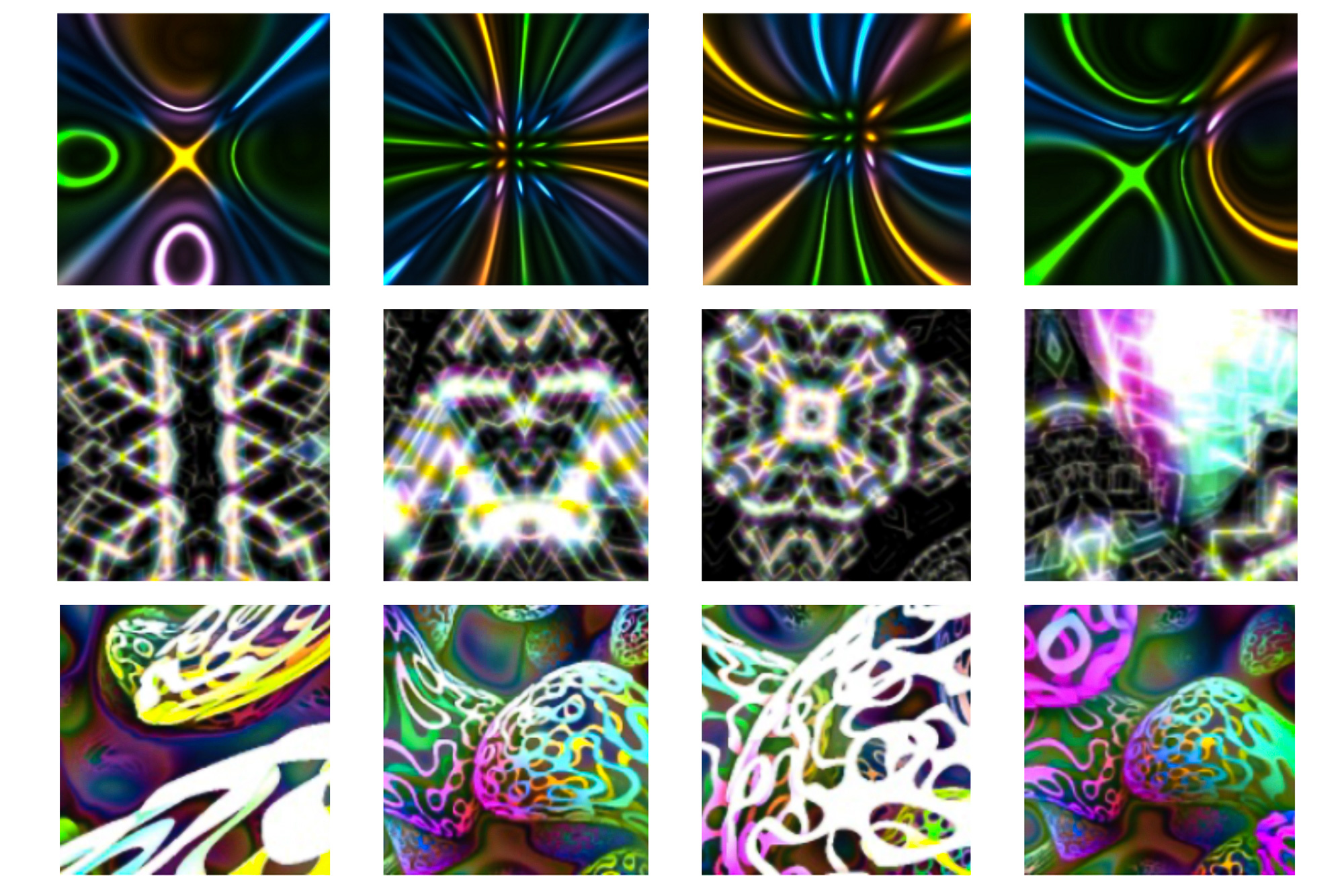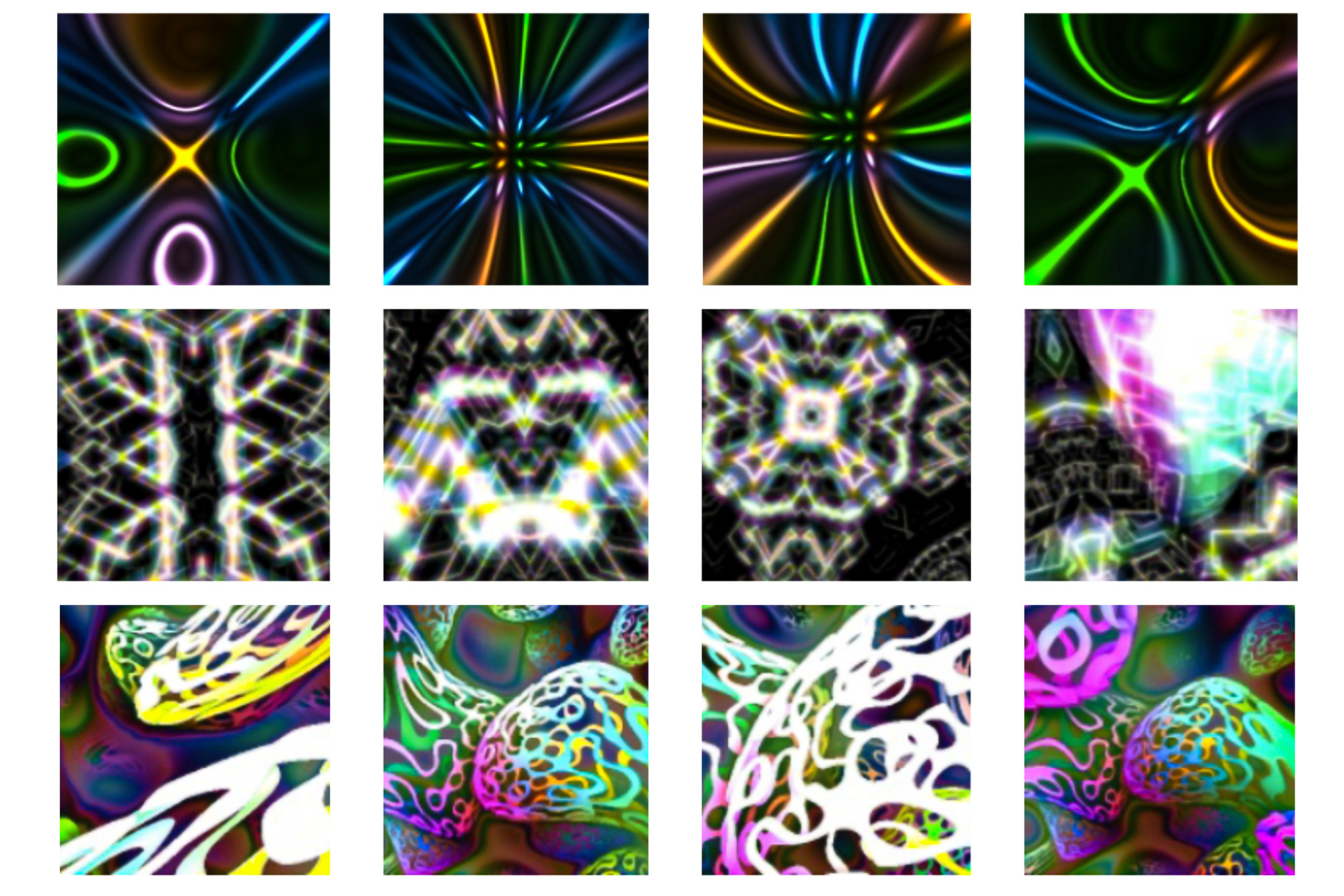
Earlier than a machine-learning mannequin can full a job, equivalent to figuring out most cancers in medical photos, the mannequin should be skilled. Coaching picture classification fashions usually entails exhibiting the mannequin thousands and thousands of instance photos gathered into an enormous dataset.
Nonetheless, utilizing actual picture information can increase sensible and moral issues: The photographs might run afoul of copyright legal guidelines, violate individuals’s privateness, or be biased towards a sure racial or ethnic group. To keep away from these pitfalls, researchers can use picture era applications to create artificial information for mannequin coaching. However these methods are restricted as a result of knowledgeable data is usually wanted to hand-design a picture era program that may create efficient coaching information.
Researchers from MIT, the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, and elsewhere took a unique method. As an alternative of designing custom-made picture era applications for a selected coaching job, they gathered a dataset of 21,000 publicly out there applications from the web. Then they used this huge assortment of primary picture era applications to coach a pc imaginative and prescient mannequin.
These applications produce various photos that show easy colours and textures. The researchers didn’t curate or alter the applications, which every comprised only a few traces of code.
The fashions they skilled with this huge dataset of applications categorized photos extra precisely than different synthetically skilled fashions. And, whereas their fashions underperformed these skilled with actual information, the researchers confirmed that growing the variety of picture applications within the dataset additionally elevated mannequin efficiency, revealing a path to attaining increased accuracy.
“It seems that utilizing numerous applications which can be uncurated is definitely higher than utilizing a small set of applications that folks want to govern. Knowledge are necessary, however we have now proven that you would be able to go fairly far with out actual information,” says Manel Baradad, {an electrical} engineering and laptop science (EECS) graduate pupil working within the Pc Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and lead creator of the paper describing this system.
Co-authors embrace Tongzhou Wang, an EECS grad pupil in CSAIL; Rogerio Feris, principal scientist and supervisor on the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab; Antonio Torralba, the Delta Electronics Professor of Electrical Engineering and Pc Science and a member of CSAIL; and senior creator Phillip Isola, an affiliate professor in EECS and CSAIL; together with others at JPMorgan Chase Financial institution and Xyla, Inc. The analysis might be offered on the Convention on Neural Data Processing Techniques.
Rethinking pretraining
Machine-learning fashions are usually pretrained, which suggests they’re skilled on one dataset first to assist them construct parameters that can be utilized to sort out a unique job. A mannequin for classifying X-rays is likely to be pretrained utilizing an enormous dataset of synthetically generated photos earlier than it’s skilled for its precise job utilizing a a lot smaller dataset of actual X-rays.
These researchers beforehand confirmed that they might use a handful of picture era applications to create artificial information for mannequin pretraining, however the applications wanted to be fastidiously designed so the artificial photos matched up with sure properties of actual photos. This made the method troublesome to scale up.
Within the new work, they used an infinite dataset of uncurated picture era applications as a substitute.
They started by gathering a group of 21,000 photos era applications from the web. All of the applications are written in a easy programming language and comprise only a few snippets of code, so that they generate photos quickly.
“These applications have been designed by builders all around the world to supply photos which have a number of the properties we’re taken with. They produce photos that look type of like summary artwork,” Baradad explains.
These easy applications can run so shortly that the researchers didn’t want to supply photos upfront to coach the mannequin. The researchers discovered they might generate photos and prepare the mannequin concurrently, which streamlines the method.
They used their large dataset of picture era applications to pretrain laptop imaginative and prescient fashions for each supervised and unsupervised picture classification duties. In supervised studying, the picture information are labeled, whereas in unsupervised studying the mannequin learns to categorize photos with out labels.
Enhancing accuracy
Once they in contrast their pretrained fashions to state-of-the-art laptop imaginative and prescient fashions that had been pretrained utilizing artificial information, their fashions have been extra correct, that means they put photos into the proper classes extra typically. Whereas the accuracy ranges have been nonetheless lower than fashions skilled on actual information, their method narrowed the efficiency hole between fashions skilled on actual information and people skilled on artificial information by 38 p.c.
“Importantly, we present that for the variety of applications you gather, efficiency scales logarithmically. We don’t saturate efficiency, so if we gather extra applications, the mannequin would carry out even higher. So, there’s a solution to prolong our method,” Manel says.
The researchers additionally used every particular person picture era program for pretraining, in an effort to uncover components that contribute to mannequin accuracy. They discovered that when a program generates a extra various set of photos, the mannequin performs higher. Additionally they discovered that colourful photos with scenes that fill all the canvas have a tendency to enhance mannequin efficiency probably the most.
Now that they’ve demonstrated the success of this pretraining method, the researchers wish to prolong their method to different sorts of information, equivalent to multimodal information that embrace textual content and pictures. Additionally they wish to proceed exploring methods to enhance picture classification efficiency.
“There may be nonetheless a spot to shut with fashions skilled on actual information. This offers our analysis a course that we hope others will comply with,” he says.