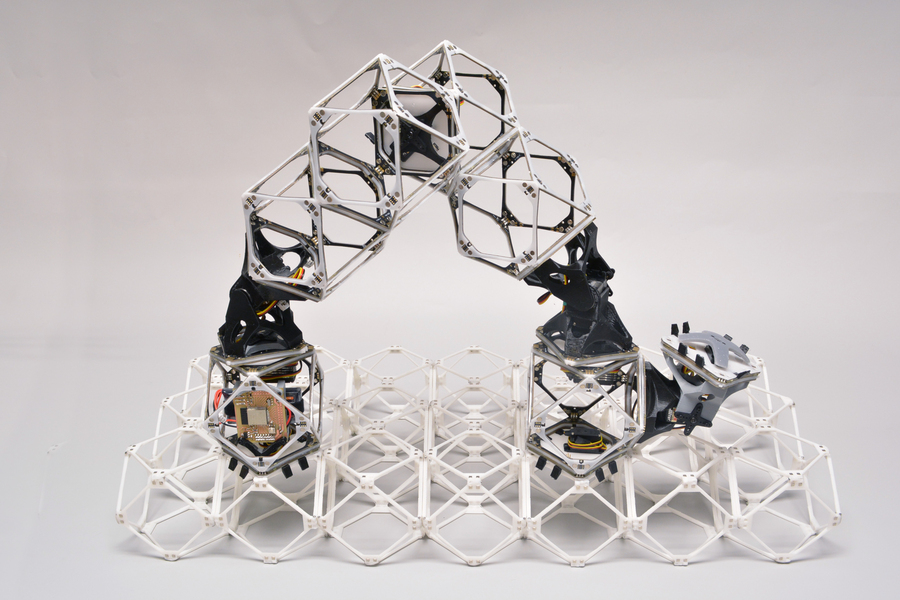
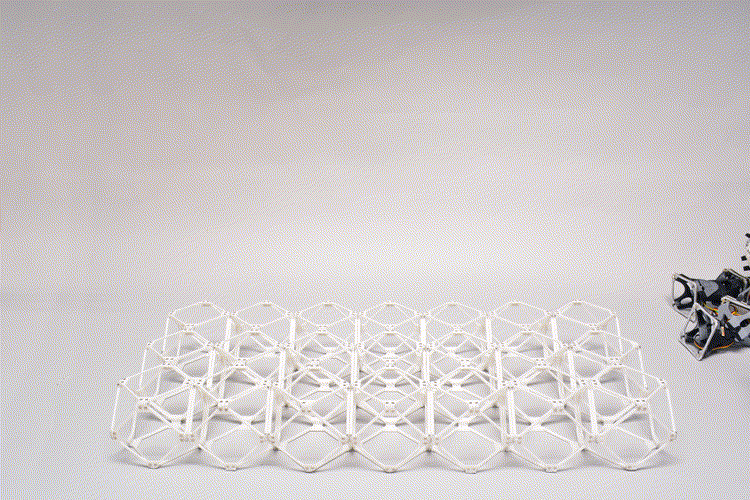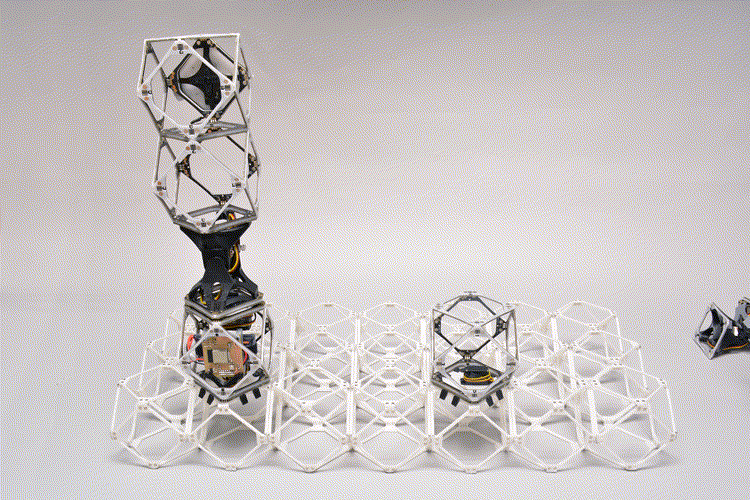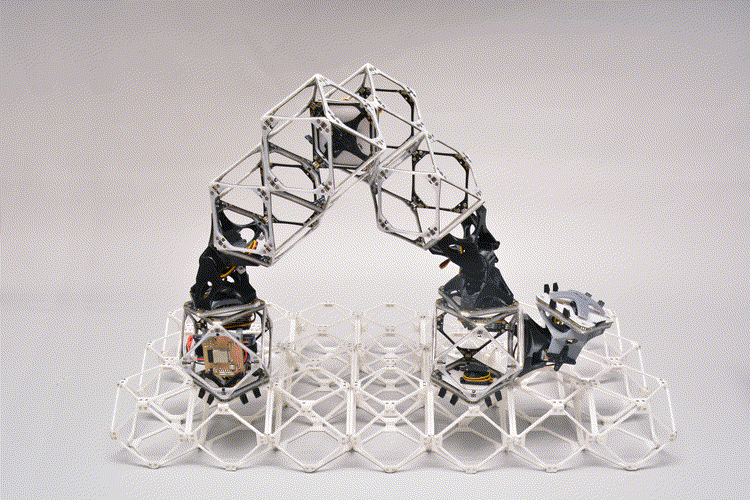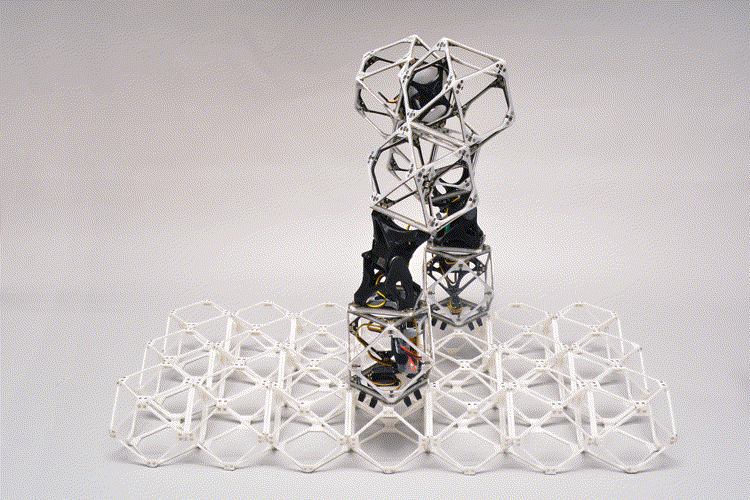
Researchers at MIT have made vital steps towards creating robots that might virtually and economically assemble practically something, together with issues a lot bigger than themselves, from autos to buildings to bigger robots. The brand new system includes giant, usable constructions constructed from an array of tiny similar subunits referred to as voxels (the volumetric equal of a 2-D pixel). Courtesy of the researchers.
By David L. Chandler
Researchers at MIT have made vital steps towards creating robots that might virtually and economically assemble practically something, together with issues a lot bigger than themselves, from autos to buildings to bigger robots.
The brand new work, from MIT’s Heart for Bits and Atoms (CBA), builds on years of analysis, together with current research demonstrating that objects resembling a deformable airplane wing and a practical racing automotive may very well be assembled from tiny similar light-weight items — and that robotic gadgets may very well be constructed to hold out a few of this meeting work. Now, the workforce has proven that each the assembler bots and the elements of the construction being constructed can all be fabricated from the identical subunits, and the robots can transfer independently in giant numbers to perform large-scale assemblies shortly.
The brand new work is reported within the journal Nature Communications Engineering, in a paper by CBA doctoral pupil Amira Abdel-Rahman, Professor and CBA Director Neil Gershenfeld, and three others.
A completely autonomous self-replicating robotic meeting system able to each assembling bigger constructions, together with bigger robots, and planning the most effective building sequence remains to be years away, Gershenfeld says. However the brand new work makes necessary strides towards that purpose, together with understanding the advanced duties of when to construct extra robots and the way massive to make them, in addition to methods to set up swarms of bots of various sizes to construct a construction effectively with out crashing into one another.
As in earlier experiments, the brand new system includes giant, usable constructions constructed from an array of tiny similar subunits referred to as voxels (the volumetric equal of a 2-D pixel). However whereas earlier voxels had been purely mechanical structural items, the workforce has now developed advanced voxels that every can carry each energy and information from one unit to the subsequent. This might allow the constructing of constructions that may not solely bear hundreds but additionally perform work, resembling lifting, shifting and manipulating supplies — together with the voxels themselves.
“After we’re constructing these constructions, it’s a must to construct in intelligence,” Gershenfeld says. Whereas earlier variations of assembler bots had been linked by bundles of wires to their energy supply and management methods, “what emerged was the concept of structural electronics — of constructing voxels that transmit energy and information in addition to drive.” Trying on the new system in operation, he factors out, “There’s no wires. There’s simply the construction.”
The robots themselves encompass a string of a number of voxels joined end-to-end. These can seize one other voxel utilizing attachment factors on one finish, then transfer inchworm-like to the specified place, the place the voxel may be connected to the rising construction and launched there.
Gershenfeld explains that whereas the sooner system demonstrated by members of his group might in precept construct arbitrarily giant constructions, as the scale of these constructions reached a sure level in relation to the scale of the assembler robotic, the method would turn out to be more and more inefficient due to the ever-longer paths every bot must journey to convey each bit to its vacation spot. At that time, with the brand new system, the bots might determine it was time to construct a bigger model of themselves that might attain longer distances and cut back the journey time. A good larger construction would possibly require yet one more such step, with the brand new bigger robots creating but bigger ones, whereas components of a construction that embrace plenty of wonderful element might require extra of the smallest robots.
Credit score: Amira Abdel-Rahman/MIT Heart for Bits and Atoms
As these robotic gadgets work on assembling one thing, Abdel-Rahman says, they face selections at each step alongside the best way: “It might construct a construction, or it might construct one other robotic of the identical dimension, or it might construct an even bigger robotic.” A part of the work the researchers have been specializing in is creating the algorithms for such decision-making.
“For instance, if you wish to construct a cone or a half-sphere,” she says, “how do you begin the trail planning, and the way do you divide this form” into completely different areas that completely different bots can work on? The software program they developed permits somebody to enter a form and get an output that exhibits the place to position the primary block, and every one after that, primarily based on the distances that should be traversed.
There are millions of papers revealed on route-planning for robots, Gershenfeld says. “However the step after that, of the robotic having to make the choice to construct one other robotic or a distinct form of robotic — that’s new. There’s actually nothing prior on that.”
Whereas the experimental system can perform the meeting and consists of the ability and information hyperlinks, within the present variations the connectors between the tiny subunits usually are not sturdy sufficient to bear the mandatory hundreds. The workforce, together with graduate pupil Miana Smith, is now specializing in growing stronger connectors. “These robots can stroll and may place components,” Gershenfeld says, “however we’re virtually — however not fairly — on the level the place certainly one of these robots makes one other one and it walks away. And that’s right down to fine-tuning of issues, just like the drive of actuators and the power of joints. … However it’s far sufficient alongside that these are the components that may result in it.”
Finally, such methods may be used to assemble all kinds of enormous, high-value constructions. For instance, at the moment the best way airplanes are constructed includes big factories with gantries a lot bigger than the elements they construct, after which “whenever you make a jumbo jet, you want jumbo jets to hold the components of the jumbo jet to make it,” Gershenfeld says. With a system like this constructed up from tiny elements assembled by tiny robots, “The ultimate meeting of the airplane is the one meeting.”
Equally, in producing a brand new automotive, “you possibly can spend a yr on tooling” earlier than the primary automotive will get truly constructed, he says. The brand new system would bypass that entire course of. Such potential efficiencies are why Gershenfeld and his college students have been working intently with automotive corporations, aviation corporations, and NASA. However even the comparatively low-tech constructing building trade might probably additionally profit.
Whereas there was growing curiosity in 3-D-printed homes, as we speak these require printing equipment as giant or bigger than the home being constructed. Once more, the potential for such constructions to as a substitute be assembled by swarms of tiny robots might present advantages. And the Protection Superior Analysis Tasks Company can be within the work for the potential for constructing constructions for coastal safety in opposition to erosion and sea stage rise.
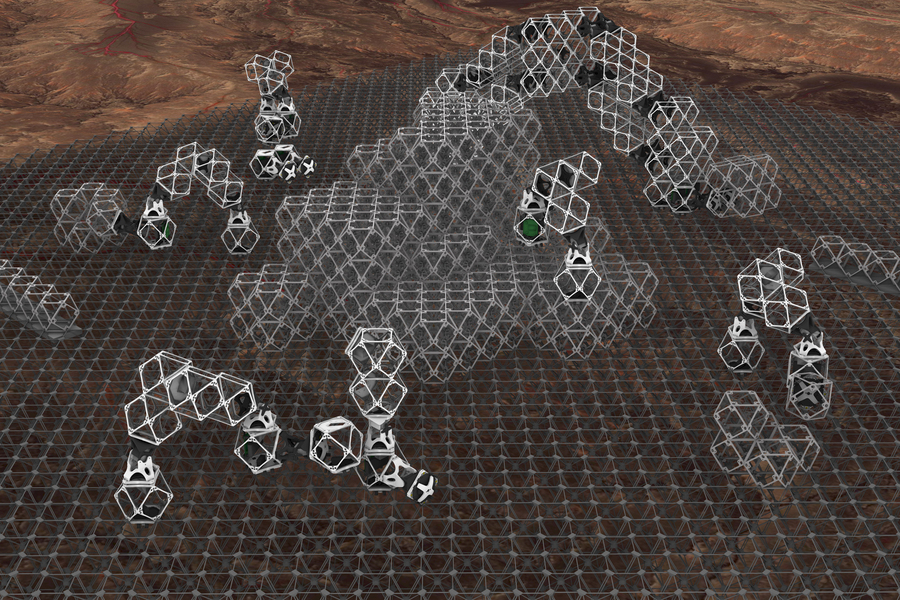
The brand new examine exhibits that each the assembler bots and the elements of the construction being constructed can all be fabricated from the identical subunits, and the robots can transfer independently in giant numbers to perform large-scale assemblies shortly. Courtesy of the researchers.
Aaron Becker, an affiliate professor {of electrical} and pc engineering on the College of Houston, who was not related to this analysis, calls this paper “a house run — [offering] an modern {hardware} system, a brand new method to consider scaling a swarm, and rigorous algorithms.”
Becker provides: “This paper examines a vital space of reconfigurable methods: methods to shortly scale up a robotic workforce and use it to effectively assemble supplies right into a desired construction. … That is the primary work I’ve seen that assaults the issue from a radically new perspective — utilizing a uncooked set of robotic components to construct a set of robots whose sizes are optimized to construct the specified construction (and different robots) as quick as potential.”
The analysis workforce additionally included MIT-CBA pupil Benjamin Jenett and Christopher Cameron, who’s now on the U.S. Military Analysis Laboratory. The work was supported by NASA, the U.S. Military Analysis Laboratory, and CBA consortia funding.

MIT Information

