The IMDB dataset
On this instance, we’ll work with the IMDB dataset: a set of fifty,000 extremely polarized critiques from the Web Film Database. They’re cut up into 25,000 critiques for coaching and 25,000 critiques for testing, every set consisting of fifty% damaging and 50% constructive critiques.
Why use separate coaching and check units? Since you ought to by no means check a machine-learning mannequin on the identical information that you just used to coach it! Simply because a mannequin performs nicely on its coaching information doesn’t imply it should carry out nicely on information it has by no means seen; and what you care about is your mannequin’s efficiency on new information (since you already know the labels of your coaching information – clearly
you don’t want your mannequin to foretell these). As an example, it’s attainable that your mannequin may find yourself merely memorizing a mapping between your coaching samples and their targets, which might be ineffective for the duty of predicting targets for information the mannequin has by no means seen earlier than. We’ll go over this level in way more element within the subsequent chapter.
Identical to the MNIST dataset, the IMDB dataset comes packaged with Keras. It has already been preprocessed: the critiques (sequences of phrases) have been became sequences of integers, the place every integer stands for a selected phrase in a dictionary.
The next code will load the dataset (whenever you run it the primary time, about 80 MB of information can be downloaded to your machine).
The argument num_words = 10000 means you’ll solely preserve the highest 10,000 most ceaselessly occurring phrases within the coaching information. Uncommon phrases can be discarded. This lets you work with vector information of manageable measurement.
The variables train_data and test_data are lists of critiques; every evaluate is an inventory of phrase indices (encoding a sequence of phrases). train_labels and test_labels are lists of 0s and 1s, the place 0 stands for damaging and 1 stands for constructive:
int [1:218] 1 14 22 16 43 530 973 1622 1385 65 ...[1] 1Since you’re limiting your self to the highest 10,000 most frequent phrases, no phrase index will exceed 10,000:
[1] 9999For kicks, right here’s how one can rapidly decode one in all these critiques again to English phrases:
# Named checklist mapping phrases to an integer index.
word_index <- dataset_imdb_word_index()
reverse_word_index <- names(word_index)
names(reverse_word_index) <- word_index
# Decodes the evaluate. Notice that the indices are offset by 3 as a result of 0, 1, and
# 2 are reserved indices for "padding," "begin of sequence," and "unknown."
decoded_review <- sapply(train_data[[1]], perform(index) {
phrase <- if (index >= 3) reverse_word_index[[as.character(index - 3)]]
if (!is.null(phrase)) phrase else "?"
})
cat(decoded_review)? this movie was simply sensible casting location surroundings story course
everybody's actually suited the half they performed and you would simply think about
being there robert ? is a tremendous actor and now the identical being director
? father got here from the identical scottish island as myself so i beloved the actual fact
there was an actual reference to this movie the witty remarks all through
the movie have been nice it was simply sensible a lot that i purchased the movie
as quickly because it was launched for ? and would advocate it to everybody to
watch and the fly fishing was wonderful actually cried on the finish it was so
unhappy and you recognize what they are saying for those who cry at a movie it should have been
good and this undoubtedly was additionally ? to the 2 little boy's that performed'
the ? of norman and paul they have been simply sensible kids are sometimes left
out of the ? checklist i believe as a result of the celebrities that play all of them grown up
are such a giant profile for the entire movie however these kids are wonderful
and must be praised for what they've finished do not you assume the entire
story was so pretty as a result of it was true and was somebody's life in spite of everything
that was shared with us allMaking ready the information
You may’t feed lists of integers right into a neural community. You must flip your lists into tensors. There are two methods to try this:
- Pad your lists in order that all of them have the identical size, flip them into an integer tensor of form
(samples, word_indices), after which use as the primary layer in your community a layer able to dealing with such integer tensors (the “embedding” layer, which we’ll cowl intimately later within the e book). - One-hot encode your lists to show them into vectors of 0s and 1s. This could imply, as an illustration, turning the sequence
[3, 5]into a ten,000-dimensional vector that might be all 0s aside from indices 3 and 5, which might be 1s. Then you would use as the primary layer in your community a dense layer, able to dealing with floating-point vector information.
Let’s go together with the latter resolution to vectorize the information, which you’ll do manually for optimum readability.
vectorize_sequences <- perform(sequences, dimension = 10000) {
# Creates an all-zero matrix of form (size(sequences), dimension)
outcomes <- matrix(0, nrow = size(sequences), ncol = dimension)
for (i in 1:size(sequences))
# Units particular indices of outcomes[i] to 1s
outcomes[i, sequences[[i]]] <- 1
outcomes
}
x_train <- vectorize_sequences(train_data)
x_test <- vectorize_sequences(test_data)Right here’s what the samples appear like now:
num [1:10000] 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 ...You must also convert your labels from integer to numeric, which is simple:
Now the information is able to be fed right into a neural community.
Constructing your community
The enter information is vectors, and the labels are scalars (1s and 0s): that is the simplest setup you’ll ever encounter. A sort of community that performs nicely on such an issue is a straightforward stack of totally related (“dense”) layers with relu activations: layer_dense(models = 16, activation = "relu").
The argument being handed to every dense layer (16) is the variety of hidden models of the layer. A hidden unit is a dimension within the illustration house of the layer. It’s possible you’ll keep in mind from chapter 2 that every such dense layer with a relu activation implements the next chain of tensor operations:
output = relu(dot(W, enter) + b)
Having 16 hidden models means the burden matrix W could have form (input_dimension, 16): the dot product with W will undertaking the enter information onto a 16-dimensional illustration house (and you then’ll add the bias vector b and apply the relu operation). You may intuitively perceive the dimensionality of your illustration house as “how a lot freedom you’re permitting the community to have when studying inside representations.” Having extra hidden models (a higher-dimensional illustration house) permits your community to study more-complex representations, however it makes the community extra computationally costly and will result in studying undesirable patterns (patterns that
will enhance efficiency on the coaching information however not on the check information).
There are two key structure choices to be made about such stack of dense layers:
- What number of layers to make use of
- What number of hidden models to decide on for every layer
In chapter 4, you’ll study formal ideas to information you in making these decisions. In the intervening time, you’ll must belief me with the next structure selection:
- Two intermediate layers with 16 hidden models every
- A 3rd layer that may output the scalar prediction relating to the sentiment of the present evaluate
The intermediate layers will use relu as their activation perform, and the ultimate layer will use a sigmoid activation in order to output a likelihood (a rating between 0 and 1, indicating how doubtless the pattern is to have the goal “1”: how doubtless the evaluate is to be constructive). A relu (rectified linear unit) is a perform meant to zero out damaging values.

A sigmoid “squashes” arbitrary values into the [0, 1] interval, outputting one thing that may be interpreted as a likelihood.

Right here’s what the community appears like.

Right here’s the Keras implementation, much like the MNIST instance you noticed beforehand.
Activation Features
Notice that with out an activation perform like relu (additionally known as a non-linearity), the dense layer would encompass two linear operations – a dot product and an addition:
output = dot(W, enter) + b
So the layer may solely study linear transformations (affine transformations) of the enter information: the speculation house of the layer can be the set of all attainable linear transformations of the enter information right into a 16-dimensional house. Such a speculation house is simply too restricted and wouldn’t profit from a number of layers of representations, as a result of a deep stack of linear layers would nonetheless implement a linear operation: including extra layers wouldn’t prolong the speculation house.
As a way to get entry to a a lot richer speculation house that might profit from deep representations, you want a non-linearity, or activation perform. relu is the preferred activation perform in deep studying, however there are a lot of different candidates, which all include equally unusual names: prelu, elu, and so forth.
Loss Operate and Optimizer
Lastly, you must select a loss perform and an optimizer. Since you’re dealing with a binary classification downside and the output of your community is a likelihood (you finish your community with a single-unit layer with a sigmoid activation), it’s greatest to make use of the binary_crossentropy loss. It isn’t the one viable selection: you would use, as an illustration, mean_squared_error. However crossentropy is often your best option whenever you’re coping with fashions that output possibilities. Crossentropy is a amount from the sector of Info Concept that measures the space between likelihood distributions or, on this case, between the ground-truth distribution and your predictions.
Right here’s the step the place you configure the mannequin with the rmsprop optimizer and the binary_crossentropy loss perform. Notice that you just’ll additionally monitor accuracy throughout coaching.
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = "rmsprop",
loss = "binary_crossentropy",
metrics = c("accuracy")
)You’re passing your optimizer, loss perform, and metrics as strings, which is feasible as a result of rmsprop, binary_crossentropy, and accuracy are packaged as a part of Keras. Typically you might wish to configure the parameters of your optimizer or move a customized loss perform or metric perform. The previous could be finished by passing an optimizer occasion because the optimizer argument:
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(lr=0.001),
loss = "binary_crossentropy",
metrics = c("accuracy")
) Customized loss and metrics capabilities could be offered by passing perform objects because the loss and/or metrics arguments
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(lr = 0.001),
loss = loss_binary_crossentropy,
metrics = metric_binary_accuracy
) Validating your method
As a way to monitor throughout coaching the accuracy of the mannequin on information it has by no means seen earlier than, you’ll create a validation set by isolating 10,000 samples from the unique coaching information.
val_indices <- 1:10000
x_val <- x_train[val_indices,]
partial_x_train <- x_train[-val_indices,]
y_val <- y_train[val_indices]
partial_y_train <- y_train[-val_indices]You’ll now prepare the mannequin for 20 epochs (20 iterations over all samples within the x_train and y_train tensors), in mini-batches of 512 samples. On the identical time, you’ll monitor loss and accuracy on the ten,000 samples that you just set aside. You accomplish that by passing the validation information because the validation_data argument.
On CPU, this can take lower than 2 seconds per epoch – coaching is over in 20 seconds. On the finish of each epoch, there’s a slight pause because the mannequin computes its loss and accuracy on the ten,000 samples of the validation information.
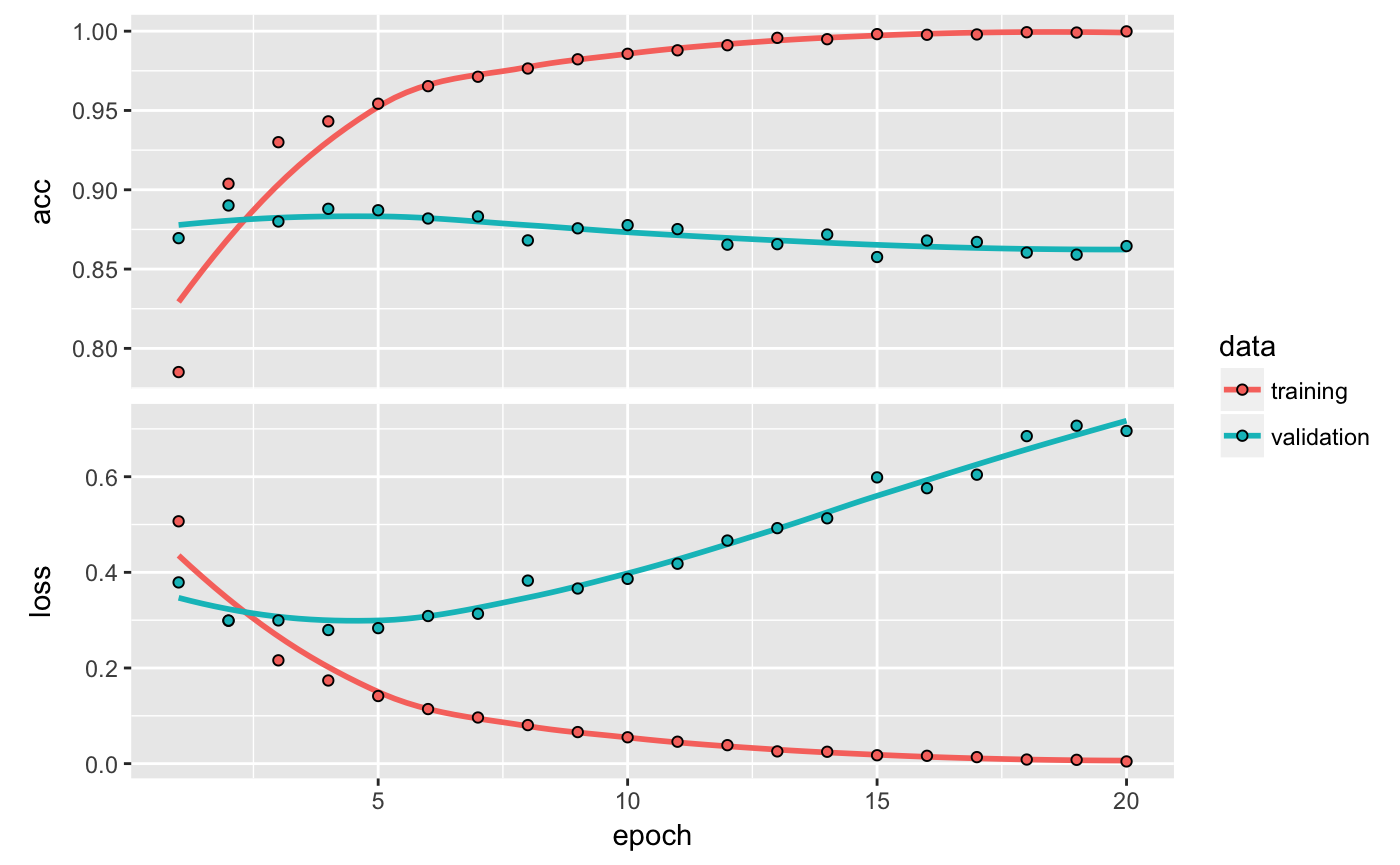
Notice that the decision to match() returns a historical past object. The historical past object has a plot() methodology that permits us to visualise the coaching and validation metrics by epoch:

The accuracy is plotted on the highest panel and the loss on the underside panel. Notice that your individual outcomes might range barely on account of a distinct random initialization of your community.
As you may see, the coaching loss decreases with each epoch, and the coaching accuracy will increase with each epoch. That’s what you’d anticipate when working a gradient-descent optimization – the amount you’re making an attempt to reduce must be much less with each iteration. However that isn’t the case for the validation loss and accuracy: they appear to peak on the fourth epoch. That is an instance of what we warned towards earlier: a mannequin that performs higher on the coaching information isn’t essentially a mannequin that may do higher on information it has by no means seen earlier than. In exact phrases, what you’re seeing is overfitting: after the second epoch, you’re overoptimizing on the coaching information, and you find yourself studying representations which can be particular to the coaching information and don’t generalize to information outdoors of the coaching set.
On this case, to stop overfitting, you would cease coaching after three epochs. Typically, you should use a variety of methods to mitigate overfitting,which we’ll cowl in chapter 4.
Let’s prepare a brand new community from scratch for 4 epochs after which consider it on the check information.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_dense(models = 16, activation = "relu", input_shape = c(10000)) %>%
layer_dense(models = 16, activation = "relu") %>%
layer_dense(models = 1, activation = "sigmoid")
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = "rmsprop",
loss = "binary_crossentropy",
metrics = c("accuracy")
)
mannequin %>% match(x_train, y_train, epochs = 4, batch_size = 512)
outcomes <- mannequin %>% consider(x_test, y_test)$loss
[1] 0.2900235
$acc
[1] 0.88512This pretty naive method achieves an accuracy of 88%. With state-of-the-art approaches, you need to be capable of get near 95%.
Producing predictions
After having educated a community, you’ll wish to use it in a sensible setting. You may generate the probability of critiques being constructive through the use of the predict methodology:
[1,] 0.92306918
[2,] 0.84061098
[3,] 0.99952853
[4,] 0.67913240
[5,] 0.73874789
[6,] 0.23108074
[7,] 0.01230567
[8,] 0.04898361
[9,] 0.99017477
[10,] 0.72034937As you may see, the community is assured for some samples (0.99 or extra, or 0.01 or much less) however much less assured for others (0.7, 0.2).
Additional experiments
The next experiments will assist persuade you that the structure decisions you’ve made are all pretty cheap, though there’s nonetheless room for enchancment.
- You used two hidden layers. Attempt utilizing one or three hidden layers, and see how doing so impacts validation and check accuracy.
- Attempt utilizing layers with extra hidden models or fewer hidden models: 32 models, 64 models, and so forth.
- Attempt utilizing the
mseloss perform as an alternative ofbinary_crossentropy. - Attempt utilizing the
tanhactivation (an activation that was standard within the early days of neural networks) as an alternative ofrelu.
Wrapping up
Right here’s what you need to take away from this instance:
- You often have to do fairly a little bit of preprocessing in your uncooked information so as to have the ability to feed it – as tensors – right into a neural community. Sequences of phrases could be encoded as binary vectors, however there are different encoding choices, too.
- Stacks of dense layers with
reluactivations can clear up a variety of issues (together with sentiment classification), and also you’ll doubtless use them ceaselessly. - In a binary classification downside (two output lessons), your community ought to finish with a dense layer with one unit and a
sigmoidactivation: the output of your community must be a scalar between 0 and 1, encoding a likelihood. - With such a scalar sigmoid output on a binary classification downside, the loss perform you need to use is
binary_crossentropy. - The
rmspropoptimizer is mostly a ok selection, no matter your downside. That’s one much less factor so that you can fear about. - As they get higher on their coaching information, neural networks ultimately begin overfitting and find yourself acquiring more and more worse outcomes on information they’ve
by no means seen earlier than. Make sure you at all times monitor efficiency on information that’s outdoors of the coaching set.