When quantum computer systems had been first proposed, they had been hoped to be a approach to higher perceive the quantum world. With a so-called “quantum simulator,” one might engineer a quantum pc to research how numerous quantum phenomena come up, together with these which can be intractable to simulate with a classical pc.
However making a helpful quantum simulator has been a problem. Till now, quantum simulations with superconducting qubits have predominantly been used to confirm pre-existing theoretical predictions and have not often explored or found new phenomena. Just a few experiments with trapped ions or chilly atoms have revealed new insights. Superconducting qubits, though they’re one of many essential candidates for common quantum computing and have demonstrated computational capabilities past classical attain, have up to now not delivered on their potential for discovery.
In “Formation of Sturdy Certain States of Interacting Photons”, printed in Nature, we describe a beforehand unpredicted phenomenon first found via experimental investigation. First, we current the experimental affirmation of the theoretical prediction of the existence of a composite particle of interacting photons, or a certain state, utilizing the Google Sycamore quantum processor. Second, whereas learning this technique, we found that though one may guess the certain states to be fragile, they continue to be strong to perturbations that we anticipated to have in any other case destroyed them. Not solely does this open the potential of designing programs that leverage interactions between photons, it additionally marks a step ahead in the usage of superconducting quantum processors to make new scientific discoveries by simulating non-equilibrium quantum dynamics.
Overview
Photons, or quanta of electromagnetic radiation like mild and microwaves, usually don’t work together. For instance, two intersecting flashlight beams will cross via each other undisturbed. In lots of purposes, like telecommunications, the weak interactions of photons is a beneficial function. For different purposes, resembling computer systems primarily based on mild, the dearth of interactions between photons is a shortcoming.
In a quantum processor, the qubits host microwave photons, which may be made to work together via two-qubit operations. This enables us to simulate the XXZ mannequin, which describes the conduct of interacting photons. Importantly, this is among the few examples of integrable fashions, i.e., one with a excessive diploma of symmetry, which significantly reduces its complexity. Once we implement the XXZ mannequin on the Sycamore processor, we observe one thing placing: the interactions pressure the photons into bundles referred to as certain states.
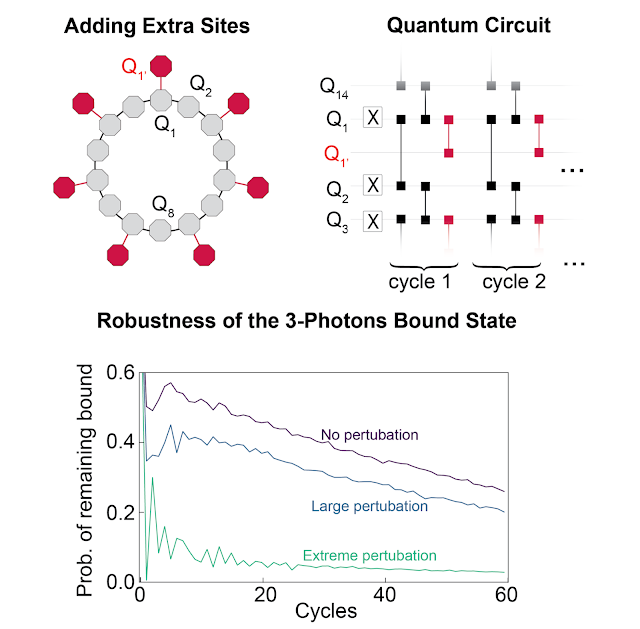
Utilizing this well-understood mannequin as a place to begin, we then push the examine right into a less-understood regime. We break the excessive degree of symmetries displayed within the XXZ mannequin by including further websites that may be occupied by the photons, making the system now not integrable. Whereas this nonintegrable regime is anticipated to exhibit chaotic conduct the place certain states dissolve into their standard, solitary selves, we as a substitute discover that they survive!
Certain Photons
To engineer a system that may assist the formation of certain states, we examine a hoop of superconducting qubits that host microwave photons. If a photon is current, the worth of the qubit is “1”, and if not, the worth is “0”. By the so-called “fSim” quantum gate, we join neighboring websites, permitting the photons to hop round and work together with different photons on the nearest-neighboring websites.
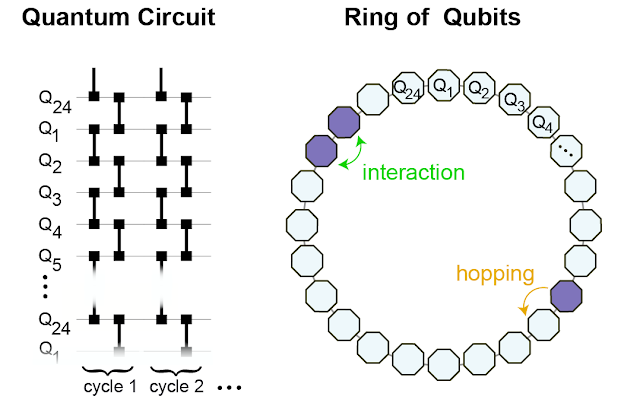 |
| We implement the fSim gate between neighboring qubits (left) to successfully kind a hoop of 24 interconnected qubits on which we simulate the conduct of the interacting photons (proper). |
The interactions between the photons have an effect on their so-called “part.” This part retains observe of the oscillation of the photon’s wavefunction. When the photons are non-interacting, their part accumulation is fairly uninteresting. Like a well-rehearsed choir, they’re all in sync with each other. On this case, a photon that was initially subsequent to a different photon can hop away from its neighbor with out getting out of sync. Simply as each particular person within the choir contributes to the tune, each attainable path the photon can take contributes to the photon’s general wavefunction. A gaggle of photons initially clustered on neighboring websites will evolve right into a superposition of all attainable paths every photon might need taken.
When photons work together with their neighbors, that is now not the case. If one photon hops away from its neighbor, its fee of part accumulation adjustments, changing into out of sync with its neighbors. All paths by which the photons break up aside overlap, resulting in harmful interference. It could be like every choir member singing at their very own tempo — the tune itself will get washed out, changing into unimaginable to discern via the din of the person singers. Amongst all of the attainable configuration paths, the one attainable situation that survives is the configuration by which all photons stay clustered collectively in a certain state. Because of this interplay can improve and result in the formation of a certain state: by suppressing all different potentialities by which photons should not certain collectively.
In our processor, we begin by placing two to 5 photons on adjoining websites (i.e., initializing two to 5 adjoining qubits in “1”, and the remaining qubits in “0”), after which examine how they propagate. First, we discover that within the theoretically predicted parameter regime, they continue to be caught collectively. Subsequent, we discover that the bigger certain states transfer extra slowly across the ring, in keeping with the truth that they’re “heavier”. This may be seen within the plot above the place the lattice websites closest to Web site 12, the preliminary place of the photons, stay darker than the others with growing variety of photons (nph) within the certain state, indicating that with extra photons certain collectively there’s much less propagation across the ring.
Certain States Behave Like Single Composite Particles
To extra rigorously present that the certain states certainly behave as single particles with well-defined bodily properties, we devise a way to measure how the vitality of the particles adjustments with momentum, i.e., the energy-momentum dispersion relation.
To measure the vitality of the certain state, we use the truth that the vitality distinction between two states determines how briskly their relative part grows with time. Therefore, we put together the certain state in a superposition with the state that has no photons, and measure their part distinction as a perform of time and house. Then, to transform the results of this measurement to a dispersion relation, we make the most of a Fourier rework, which interprets place and time into momentum and vitality, respectively. We’re left with the acquainted energy-momentum relationship of excitations in a lattice.
 |
| Spectroscopy of certain states. We evaluate the part accumulation of an n-photon certain state with that of the vacuum (no photons) as a perform of lattice web site and time. A 2D Fourier rework yields the dispersion relation of the bound-state quasiparticle. |
Breaking Integrability
The above system is “integrable,” that means that it has a enough variety of conserved portions that its dynamics are constrained to a small a part of the obtainable computational house. In such integrable regimes, the looks of certain states isn’t that shocking. Actually, certain states in comparable programs had been predicted in 2012, then noticed in 2013. Nevertheless, these certain states are fragile and their existence is often thought to derive from integrability. For extra complicated programs, there’s much less symmetry and integrability is rapidly misplaced. Our preliminary concept was to probe how these certain states disappear as we break integrability to raised perceive their rigidity.
To interrupt integrability, we modify which qubits are related with fSim gates. We add qubits in order that at alternating websites, along with hopping to every of its two nearest-neighboring websites, a photon also can hop to a 3rd web site oriented radially outward from the ring.
Whereas a certain state is constrained to a really small a part of part house, we anticipated that the chaotic conduct related to integrability breaking would permit the system to discover the part house extra freely. This could trigger the certain states to interrupt aside. We discover that this isn’t the case. Even when the integrability breaking is so sturdy that the photons are equally more likely to hop to the third web site as they’re to hop to both of the 2 adjoining ring websites, the certain state stays intact, as much as the decoherence impact that makes them slowly decay (see paper for particulars).
Conclusion
We don’t but have a satisfying clarification for this sudden resilience. We speculate that it might be associated to a phenomenon known as prethermalization, the place incommensurate vitality scales within the system can forestall a system from reaching thermal equilibrium as rapidly because it in any other case would. We consider additional investigations will hopefully result in new insights into many-body quantum physics, together with the interaction of prethermalization and integrability.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank our Quantum Science Communicator Katherine McCormick for her assist penning this weblog publish.