Reinforcement studying (RL) algorithms can be taught expertise to unravel decision-making duties like enjoying video games, enabling robots to select up objects, and even optimizing microchip designs. Nevertheless, operating RL algorithms in the actual world requires costly lively knowledge assortment. Pre-training on various datasets has confirmed to allow data-efficient fine-tuning for particular person downstream duties in pure language processing (NLP) and imaginative and prescient issues. In the identical means that BERT or GPT-3 fashions present general-purpose initialization for NLP, massive RL–pre-trained fashions may present general-purpose initialization for decision-making. So, we ask the query: Can we allow related pre-training to speed up RL strategies and create a general-purpose “spine” for environment friendly RL throughout numerous duties?
In “Offline Q-learning on Numerous Multi-Process Information Each Scales and Generalizes”, to be revealed at ICLR 2023, we focus on how we scaled offline RL, which can be utilized to coach worth features on beforehand collected static datasets, to offer such a common pre-training methodology. We reveal that Scaled Q-Studying utilizing a various dataset is adequate to be taught representations that facilitate fast switch to novel duties and quick on-line studying on new variations of a process, bettering considerably over present illustration studying approaches and even Transformer-based strategies that use a lot bigger fashions.
 |
Scaled Q-learning: Multi-task pre-training with conservative Q-learning
To supply a general-purpose pre-training strategy, offline RL must be scalable, permitting us to pre-train on knowledge throughout totally different duties and make the most of expressive neural community fashions to accumulate highly effective pre-trained backbones, specialised to particular person downstream duties. We primarily based our offline RL pre-training methodology on conservative Q-learning (CQL), a easy offline RL methodology that mixes customary Q-learning updates with a further regularizer that minimizes the worth of unseen actions. With discrete actions, the CQL regularizer is equal to a regular cross-entropy loss, which is an easy, one-line modification on customary deep Q-learning. Just a few essential design selections made this doable:
- Neural community measurement: We discovered that multi-game Q-learning required massive neural community architectures. Whereas prior strategies typically used comparatively shallow convolutional networks, we discovered that fashions as massive as a ResNet 101 led to vital enhancements over smaller fashions.
- Neural community structure: To be taught pre-trained backbones which are helpful for brand spanking new video games, our ultimate structure makes use of a shared neural community spine, with separate 1-layer heads outputting Q-values of every sport. This design avoids interference between the video games throughout pre-training, whereas nonetheless offering sufficient knowledge sharing to be taught a single shared illustration. Our shared imaginative and prescient spine additionally utilized a realized place embedding (akin to Transformer fashions) to maintain monitor of spatial info within the sport.
- Representational regularization: Current work has noticed that Q-learning tends to undergo from representational collapse points, the place even massive neural networks can fail to be taught efficient representations. To counteract this situation, we leverage our prior work to normalize the final layer options of the shared a part of the Q-network. Moreover, we utilized a categorical distributional RL loss for Q-learning, which is understood to offer richer representations that enhance downstream process efficiency.
The multi-task Atari benchmark
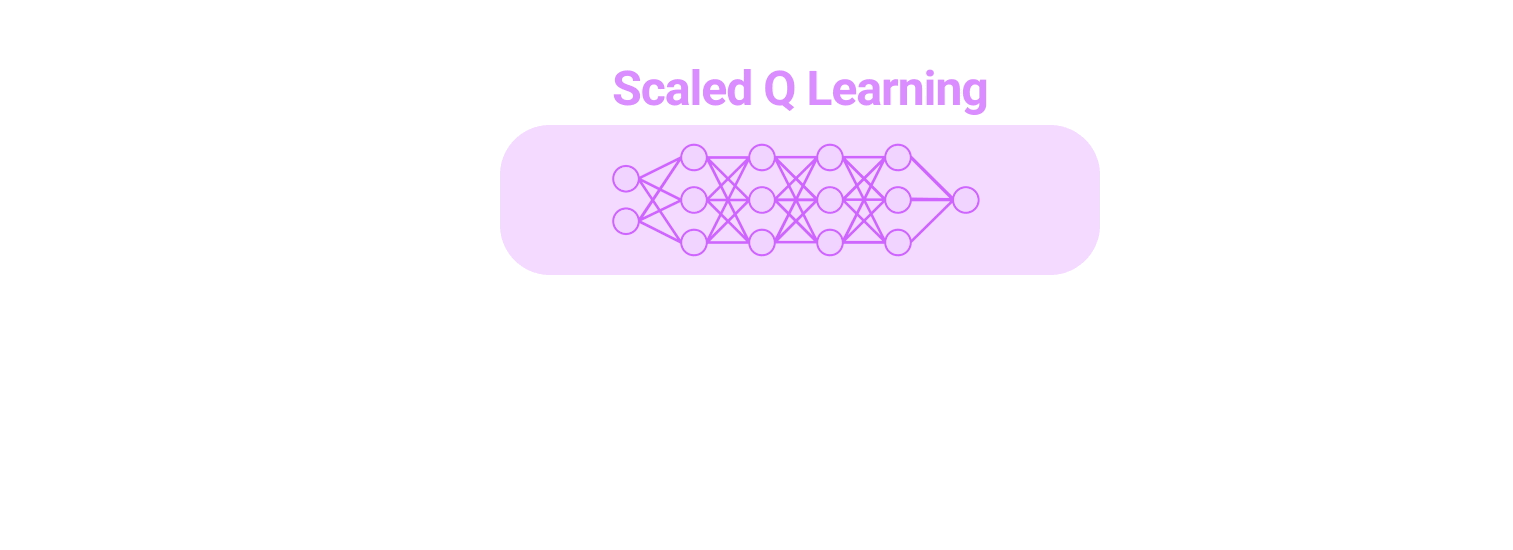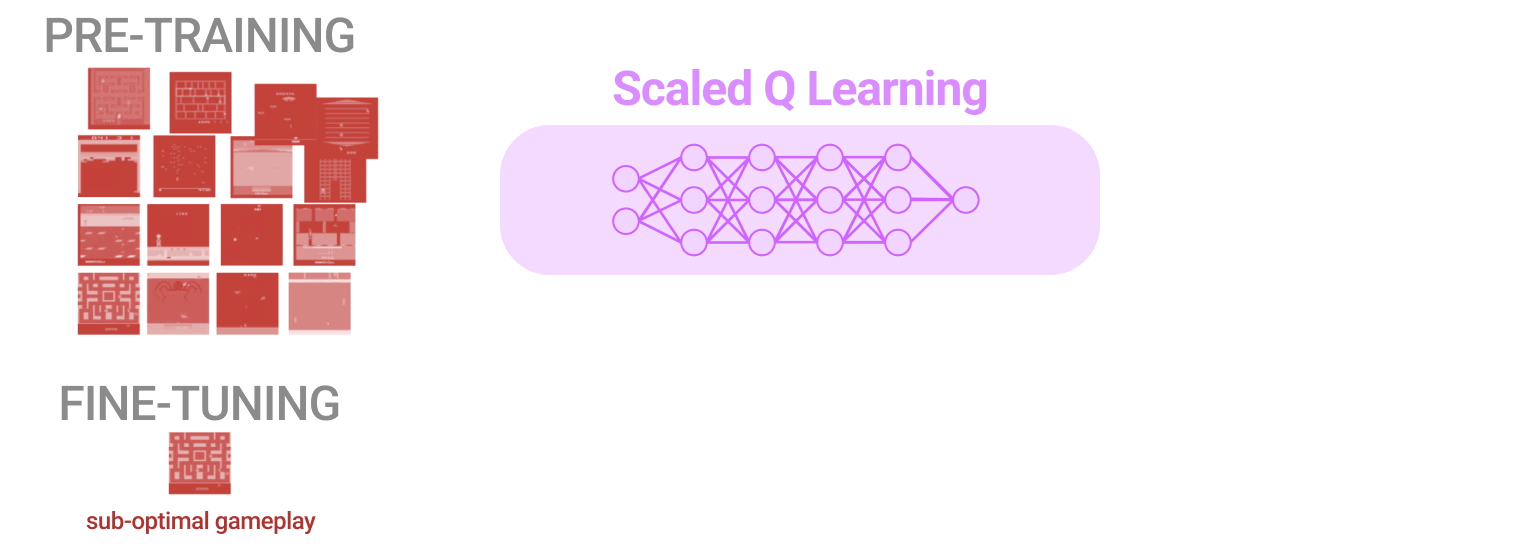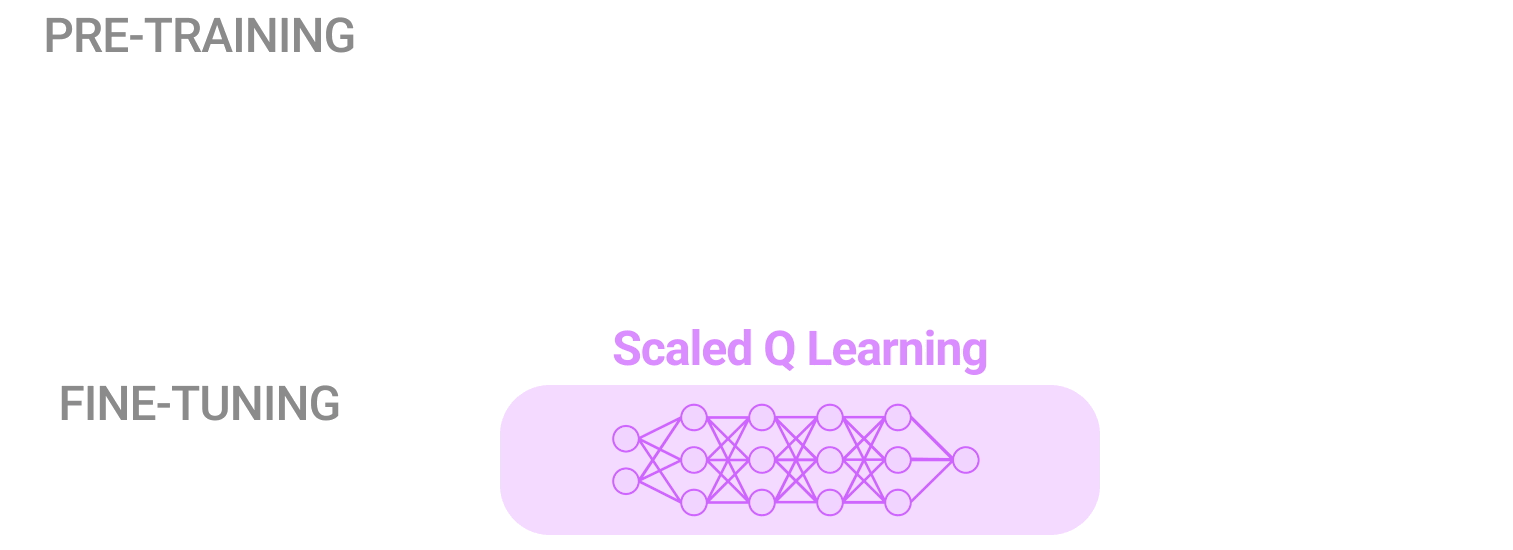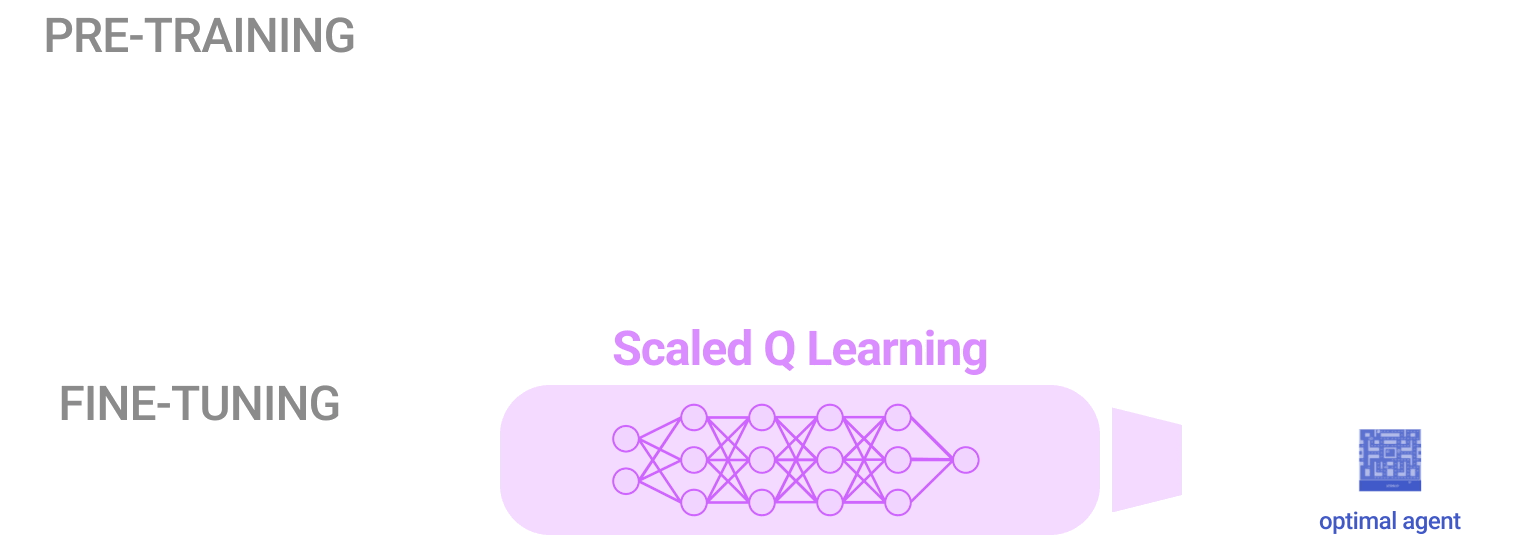
We consider our strategy for scalable offline RL on a collection of Atari video games, the place the aim is to coach a single RL agent to play a set of video games utilizing heterogeneous knowledge from low-quality (i.e., suboptimal) gamers, after which use the ensuing community spine to rapidly be taught new variations in pre-training video games or fully new video games. Coaching a single coverage that may play many alternative Atari video games is troublesome sufficient even with customary on-line deep RL strategies, as every sport requires a special technique and totally different representations. Within the offline setting, some prior works, akin to multi-game choice transformers, proposed to dispense with RL totally, and as a substitute make the most of conditional imitation studying in an try and scale with massive neural community architectures, akin to transformers. Nevertheless, on this work, we present that this sort of multi-game pre-training could be finished successfully by way of RL by using CQL together with just a few cautious design selections, which we describe under.
Scalability on coaching video games
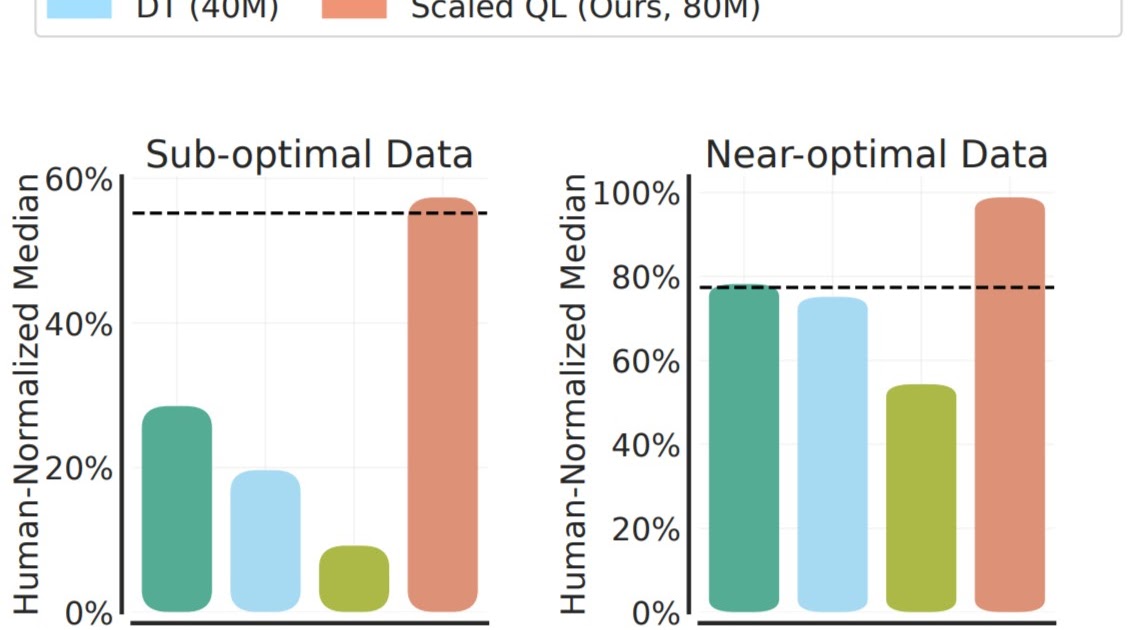
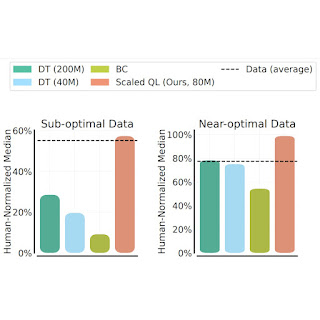
We consider the Scaled Q-Studying methodology’s efficiency and scalability utilizing two knowledge compositions: (1) close to optimum knowledge, consisting of all of the coaching knowledge showing in replay buffers of earlier RL runs, and (2) low high quality knowledge, consisting of information from the primary 20% of the trials within the replay buffer (i.e., solely knowledge from extremely suboptimal insurance policies). In our outcomes under, we evaluate Scaled Q-Studying with an 80-million parameter mannequin to multi-game choice transformers (DT) with both 40-million or 80-million parameter fashions, and a behavioral cloning (imitation studying) baseline (BC). We observe that Scaled Q-Studying is the one strategy that improves over the offline knowledge, attaining about 80% of human normalized efficiency.
 |
Additional, as proven under, Scaled Q-Studying improves by way of efficiency, but it surely additionally enjoys favorable scaling properties: simply as how the efficiency of pre-trained language and imaginative and prescient fashions improves as community sizes get greater, having fun with what is often referred as “power-law scaling”, we present that the efficiency of Scaled Q-learning enjoys related scaling properties. Whereas this can be unsurprising, this sort of scaling has been elusive in RL, with efficiency typically deteriorating with bigger mannequin sizes. This means that Scaled Q-Studying together with the above design selections higher unlocks the flexibility of offline RL to make the most of massive fashions.
 |
Superb-tuning to new video games and variations
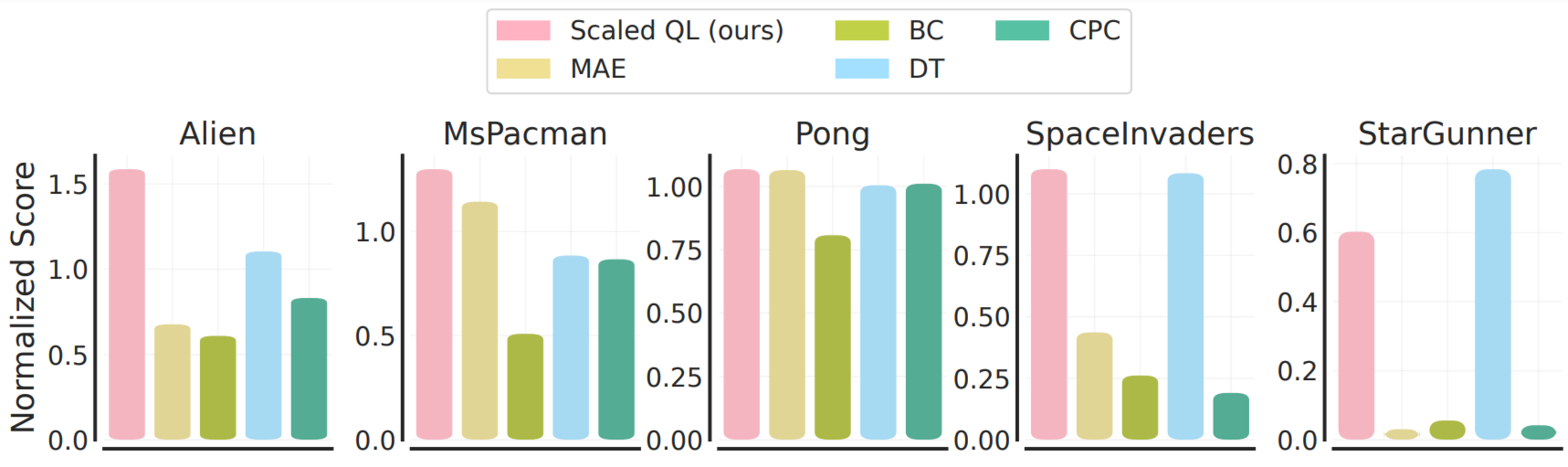
To guage fine-tuning from this offline initialization, we contemplate two settings: (1) fine-tuning to a brand new, totally unseen sport with a small quantity of offline knowledge from that sport, similar to 2M transitions of gameplay, and (2) fine-tuning to a brand new variant of the video games with on-line interplay. The fine-tuning from offline gameplay knowledge is illustrated under. Word that this situation is usually extra favorable to imitation-style strategies, Resolution Transformer and behavioral cloning, for the reason that offline knowledge for the brand new video games is of comparatively high-quality. Nonetheless, we see that generally Scaled Q-learning improves over different approaches (80% on common), in addition to devoted illustration studying strategies, akin to MAE or CPC, which solely use the offline knowledge to be taught visible representations reasonably than worth features.
 |
Within the on-line setting, we see even bigger enhancements from pre-training with Scaled Q-learning. On this case, illustration studying strategies like MAE yield minimal enchancment throughout on-line RL, whereas Scaled Q-Studying can efficiently combine prior information in regards to the pre-training video games to considerably enhance the ultimate rating after 20k on-line interplay steps.
These outcomes reveal that pre-training generalist worth perform backbones with multi-task offline RL can considerably increase efficiency of RL on downstream duties, each in offline and on-line mode. Word that these fine-tuning duties are fairly troublesome: the varied Atari video games, and even variants of the identical sport, differ considerably in look and dynamics. For instance, the goal blocks in Breakout disappear within the variation of the sport as proven under, making management troublesome. Nevertheless, the success of Scaled Q-learning, significantly as in comparison with visible illustration studying strategies, akin to MAE and CPC, means that the mannequin is in actual fact studying some illustration of the sport dynamics, reasonably than merely offering higher visible options.
Conclusion and takeaways
We offered Scaled Q-Studying, a pre-training methodology for scaled offline RL that builds on the CQL algorithm, and demonstrated the way it allows environment friendly offline RL for multi-task coaching. This work made preliminary progress in direction of enabling extra sensible real-world coaching of RL brokers as an alternative choice to pricey and complicated simulation-based pipelines or large-scale experiments. Maybe in the long term, related work will result in usually succesful pre-trained RL brokers that develop broadly relevant exploration and interplay expertise from large-scale offline pre-training. Validating these outcomes on a broader vary of extra sensible duties, in domains akin to robotics (see some preliminary outcomes) and NLP, is a vital course for future analysis. Offline RL pre-training has a whole lot of potential, and we anticipate that we are going to see many advances on this space in future work.
Acknowledgements
This work was finished by Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal, Xinyang Geng, George Tucker, and Sergey Levine. Particular due to Sherry Yang, Ofir Nachum, and Kuang-Huei Lee for assist with the multi-game choice transformer codebase for analysis and the multi-game Atari benchmark, and Tom Small for illustrations and animation.