
Industrial functions of machine studying are generally composed of varied objects which have differing knowledge modalities or characteristic distributions. Heterogeneous graphs (HGs) supply a unified view of those multimodal knowledge methods by defining a number of sorts of nodes (for every knowledge kind) and edges (for the relation between knowledge objects). As an example, e-commerce networks may need [user, product, review] nodes or video platforms may need [channel, user, video, comment] nodes. Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) study node embeddings summarizing every node’s relationships right into a vector. Nevertheless, in actual world HGs, there may be typically a label imbalance situation between totally different node sorts. Which means that label-scarce node sorts can’t exploit HGNNs, which hampers the broader applicability of HGNNs.
In “Zero-shot Switch Studying inside a Heterogeneous Graph by way of Data Switch Networks”, offered at NeurIPS 2022, we suggest a mannequin referred to as a Data Switch Community (KTN), which transfers data from label-abundant node sorts to zero-labeled node sorts utilizing the wealthy relational data given in a HG. We describe how we pre-train a HGNN mannequin with out the necessity for fine-tuning. KTNs outperform state-of-the-art switch studying baselines by as much as 140% on zero-shot studying duties, and can be utilized to enhance many present HGNN fashions on these duties by 24% (or extra).
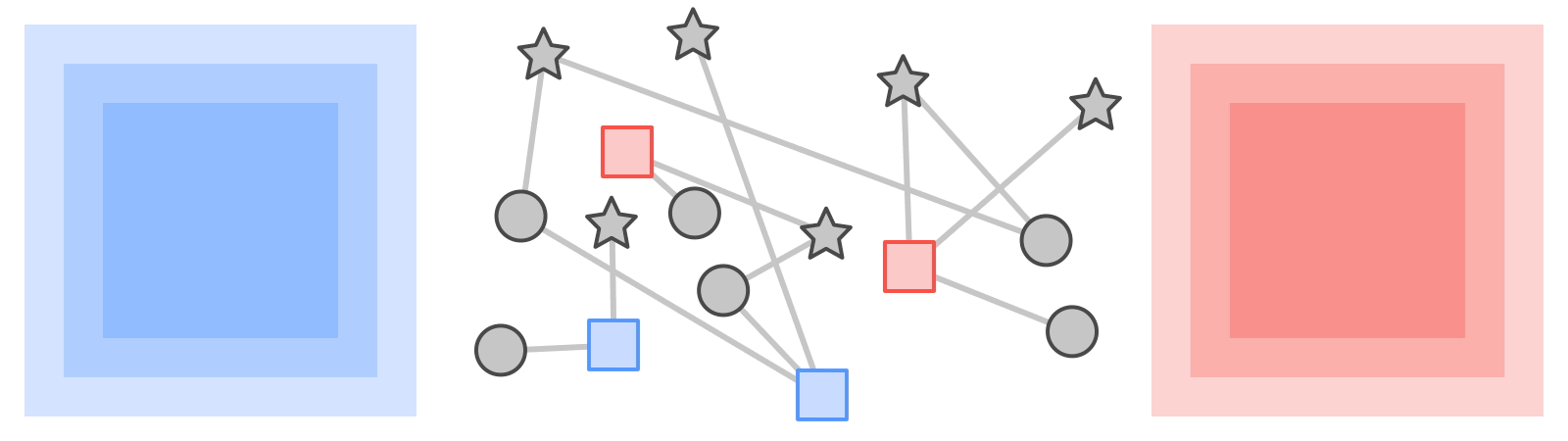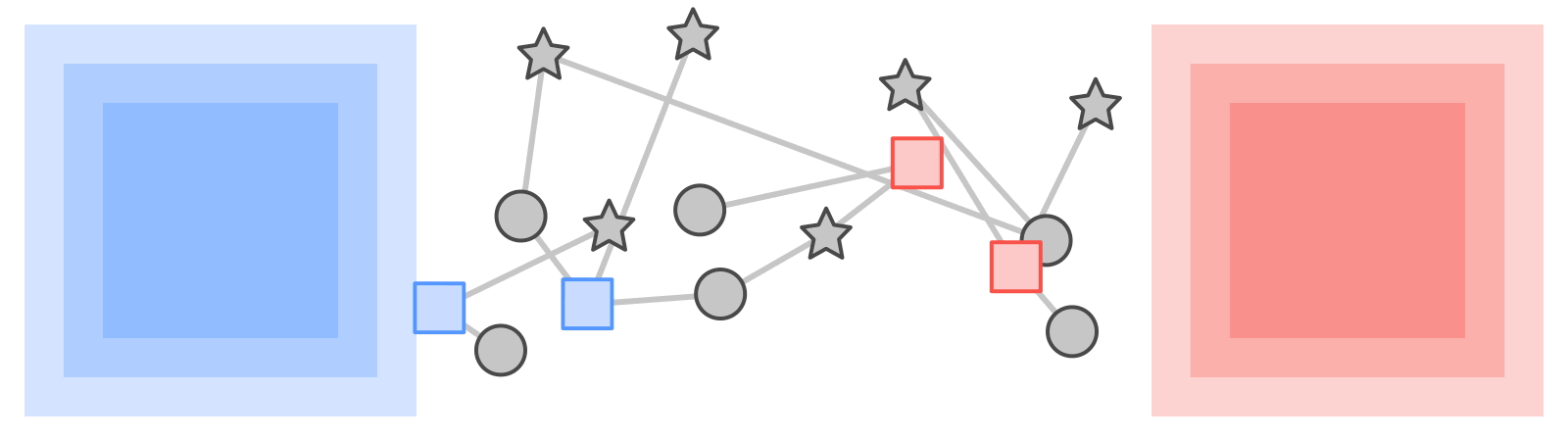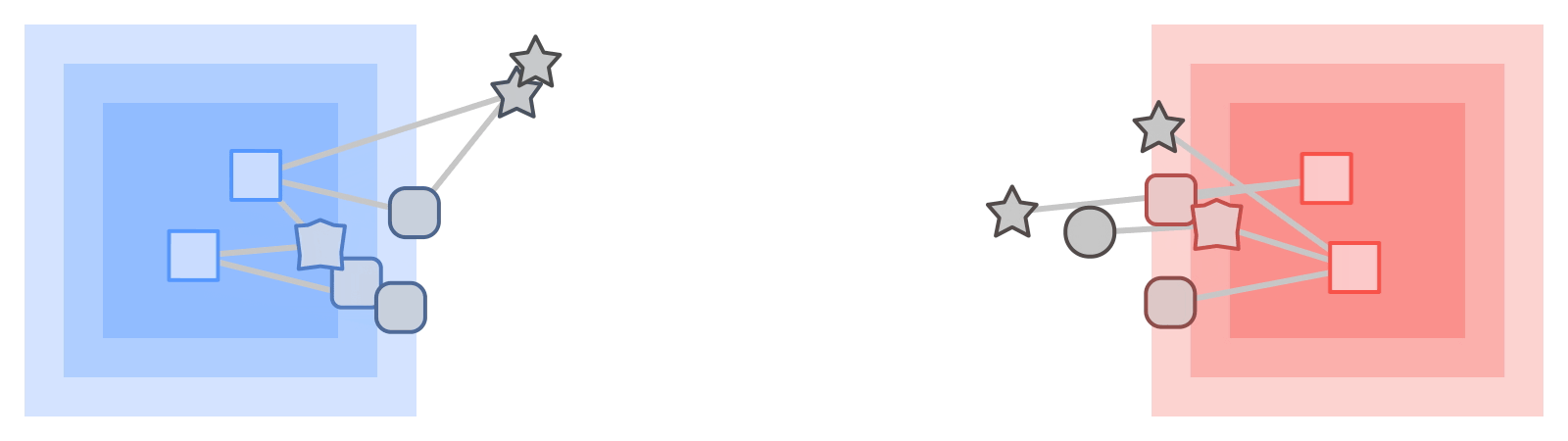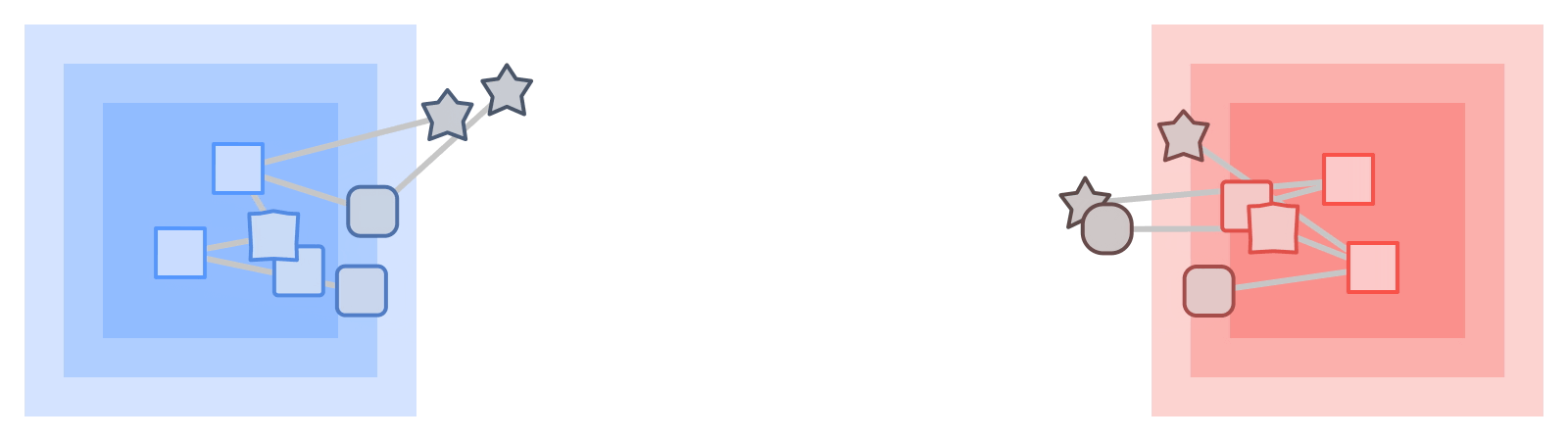 |
| KTNs rework labels from one kind of data (squares) by means of a graph to a different kind (stars). |
What’s a heterogeneous graph?
A HG consists of a number of node and edge sorts. The determine beneath exhibits an e-commerce community offered as a HG. In e-commerce, “customers” buy “merchandise” and write “opinions”. A HG presents this ecosystem utilizing three node sorts [user, product, review] and three edge sorts [user-buy-product, user-write-review, review-on-product]. Particular person merchandise, customers, and opinions are then offered as nodes and their relationships as edges within the HG with the corresponding node and edge sorts.
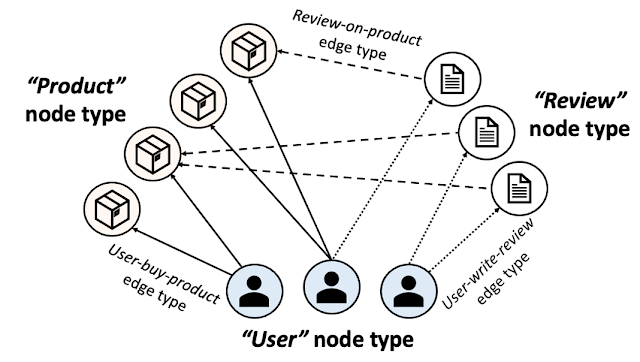 |
| E-commerce heterogeneous graph. |
Along with all connectivity data, HGs are generally given with enter node attributes that summarize every node’s data. Enter node attributes might have totally different modalities throughout totally different node sorts. As an example, photos of merchandise might be given as enter node attributes for the product nodes, whereas textual content might be given as enter attributes to evaluation nodes. Node labels (e.g., the class of every product or the class that the majority pursuits every consumer) are what we need to predict on every node.
HGNNs and label shortage points
HGNNs compute node embeddings that summarize every node’s native buildings (together with the node and its neighbor’s data). These node embeddings are utilized by a classifier to foretell every node’s label. To coach a HGNN mannequin and a classifier to foretell labels for a selected node kind, we require a very good quantity of labels for the kind.
A standard situation in industrial functions of deep studying is label shortage, and with their numerous node sorts, HGNNs are much more more likely to face this problem. As an example, publicly accessible content material node sorts (e.g., product nodes) are abundantly labeled, whereas labels for consumer or account nodes might not be accessible as a result of privateness restrictions. Which means that in most traditional coaching settings, HGNN fashions can solely study to make good inferences for just a few label-abundant node sorts and might normally not make any inferences for any remaining node sorts (given the absence of any labels for them).
Switch studying on heterogeneous graphs
Zero-shot switch studying is a way used to enhance the efficiency of a mannequin on a goal area with no labels by utilizing the data discovered by the mannequin from one other associated supply area with adequately labeled knowledge. To use switch studying to resolve this label shortage situation for sure node sorts in HGs, the goal area could be the zero-labeled node sorts. Then what could be the supply area? Earlier work generally units the supply area as the identical kind of nodes situated in a unique HG, assuming these nodes are abundantly labeled. This graph-to-graph switch studying method pre-trains a HGNN mannequin on the exterior HG after which runs the mannequin on the unique (label-scarce) HG.
Nevertheless, these approaches will not be relevant in lots of real-world situations for 3 causes. First, any exterior HG that might be utilized in a graph-to-graph switch studying setting would nearly certainly be proprietary, thus, doubtless unavailable. Second, even when practitioners might acquire entry to an exterior HG, it’s unlikely the distribution of that supply HG would match their goal HG nicely sufficient to use switch studying. Lastly, node sorts affected by label shortage are more likely to endure the identical situation on different HGs (e.g., privateness points on consumer nodes).
Our method: Switch studying between node sorts inside a heterogeneous graph
Right here, we make clear a extra sensible supply area, different node sorts with considerable labels situated on the identical HG. As a substitute of utilizing additional HGs, we switch data inside a single HG (assumed to be totally owned by the practitioners) throughout various kinds of nodes. Extra particularly, we pre-train a HGNN mannequin and a classifier on a label-abundant (supply) node kind, then reuse the fashions on the zero-labeled (goal) node sorts situated in the identical HG with out extra fine-tuning. The one requirement is that the supply and goal node sorts share the identical label set (e.g., within the e-commerce HG, product nodes have a label set describing product classes, and consumer nodes share the identical label set describing their favourite purchasing classes).
Why is it difficult?
Sadly, we can’t immediately reuse the pre-trained HGNN and classifier on the goal node kind. One essential attribute of HGNN architectures is that they’re composed of modules specialised to every node kind to totally study the multiplicity of HGs. HGNNs use distinct units of modules to compute embeddings for every node kind. Within the determine beneath, blue- and red-colored modules are used to compute node embeddings for the supply and goal node sorts, respectively.
 |
| HGNNs are composed of modules specialised to every node kind and use distinct units of modules to compute embeddings of various node sorts. Extra particulars might be discovered within the paper. |
Whereas pre-training HGNNs on the supply node kind, source-specific modules within the HGNNs are nicely skilled, nonetheless target-specific modules are under-trained as they’ve solely a small quantity of gradients flowing into them. That is proven beneath, the place we see that the L2 norm of gradients for goal node sorts (i.e., Mtt) are a lot decrease than for supply sorts (i.e., Mss). On this case a HGNN mannequin outputs poor node embeddings for the goal node kind, which leads to poor activity efficiency.
 |
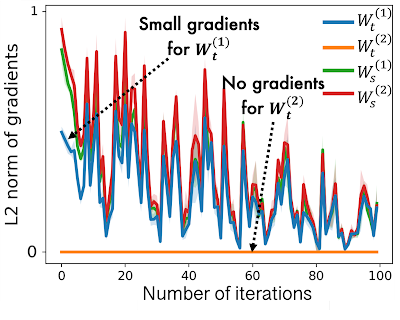 |
| In HGNNs, goal type-specific modules obtain zero or solely a small quantity of gradients throughout pre-training on the supply node kind, resulting in poor efficiency on the goal node kind. |
KTN: Trainable cross-type switch studying for HGNNs
Our work focuses on reworking the (poor) goal node embeddings computed by a pre-trained HGNN mannequin to observe the distribution of the supply node embeddings. Then the classifier, pre-trained on the supply node kind, might be reused for the goal node kind. How can we map the goal node embeddings to the supply area? To reply this query, we examine how HGNNs compute node embeddings to study the connection between supply and goal distributions.
HGNNs combination linked node embeddings to enhance a goal node’s embeddings in every layer. In different phrases, the node embeddings for each supply and goal node sorts are up to date utilizing the identical enter — the earlier layer’s node embeddings of any linked node sorts. Which means that they are often represented by one another. We show this relationship theoretically and discover there’s a mapping matrix (outlined by HGNN parameters) from the goal area to the supply area (extra particulars in Theorem 1 within the paper). Based mostly on this theorem, we introduce an auxiliary neural community, which we consult with as a Data Switch Community (KTN), that receives the goal node embeddings after which transforms them by multiplying them with a (trainable) mapping matrix. We then outline a regularizer that’s minimized together with the efficiency loss within the pre-training section to coach the KTN. At check time, we map the goal embeddings computed from the pre-trained HGNN to the supply area utilizing the skilled KTN for classification.
Experimental outcomes
To look at the effectiveness of KTNs, we ran 18 totally different zero-shot switch studying duties on two public heterogeneous graphs, Open Tutorial Graph and Pubmed. We examine KTN with eight state-of-the-art switch studying strategies (DAN, JAN, DANN, CDAN, CDAN-E, WDGRL, LP, EP). Proven beneath, KTN persistently outperforms all baselines on all duties, beating switch studying baselines by as much as 140% (as measured by Normalized Discounted Cumulative Acquire, a rating metric).
 |
 |
| Zero-shot switch studying on Open Tutorial Graph (OAG-CS) and Pubmed datasets. The colours symbolize totally different classes of switch studying baselines towards which the outcomes are in contrast. Yellow: Use statistical properties (e.g., imply, variance) of distributions. Inexperienced: Use adversarial fashions to switch data. Orange: Switch data immediately by way of graph construction utilizing label propagation. |
Most significantly, KTN might be utilized to nearly all HGNN fashions which have node and edge type-specific parameters and enhance their zero-shot efficiency on the right track domains. As proven beneath, KTN improves accuracy on zero-labeled node sorts throughout six totally different HGNN fashions(R-GCN, HAN, HGT, MAGNN, MPNN, H-MPNN) by as much as 190%.
 |
| KTN might be utilized to 6 totally different HGNN fashions and enhance their zero-shot efficiency on the right track domains. |
Takeaways
Numerous ecosystems in business might be offered as heterogeneous graphs. HGNNs summarize heterogeneous graph data into efficient representations. Nevertheless, label shortage points on sure sorts of nodes stop the broader software of HGNNs. On this publish, we launched KTN, the primary cross-type switch studying technique designed for HGNNs. With KTN, we are able to totally exploit the richness of heterogeneous graphs by way of HGNNs no matter label shortage. See the paper for extra particulars.
Acknowledgements
This paper is joint work with our co-authors John Palowitch (Google Analysis), Dustin Zelle (Google Analysis), Ziniu Hu (Intern, Google Analysis), and Russ Salakhutdinov (CMU). We thank Tom Small for creating the animated determine on this weblog publish.


