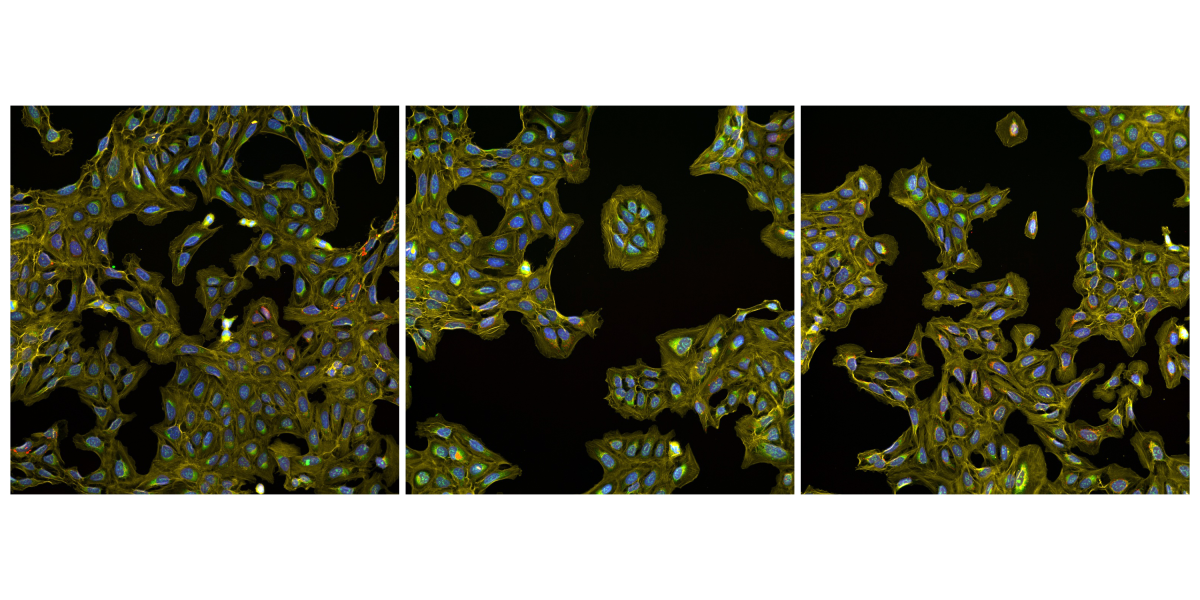
Now some are embracing a brand new paradigm: Measure every little thing, ask questions later. This motto drives a lab at Harvard and MIT’s Broad Institute, the place researchers have developed a way for producing a treasure trove of knowledge on a cell’s internal workings that they will sift for years to return. The strategy, generally known as Cell Portray, impressed scientists at a number of pharmaceutical firms—a lot that they launched a consortium and pooled sources, utilizing the method to create a large information set that they started releasing to the general public in November. The JUMP–Cell Portray Consortium, because it’s known as, hopes the database will speed up drug discovery by serving to researchers determine promising compounds and get a greater sense of what they do and what kinds of unintended effects they could have earlier than the molecules get examined in animals or folks.
Cell Portray makes use of as much as six fluorescent dyes to mild up main parts of the cell, such because the nucleus and mitochondria. A microscope snaps pictures of the varied stains, and software program measures morphological options like measurement, form, depth, and texture, creating an image-based profile of the pattern. It’s “simply concerning the easiest imaging assay you may handle,” says computational biologist Anne Carpenter, who developed the strategy and co-leads the Broad Institute lab with Shantanu Singh. “Our mission was to decide on absolutely the least expensive, best dyes.”
Past ease of use, the facility of Cell Portray lies within the sheer quantity of information that comes from one experiment. The newly launched database accommodates pictures of cells responding to greater than 140,000 perturbations—both a drug remedy or another modification that turns a gene’s exercise up or down. Utilizing this information set, Carpenter and a few of her colleagues discovered a dozen compounds that appear to have an effect on the identical constructions which can be influenced by a key gene concerned in a fast-growing muscle most cancers. Fairly than placing tons of of samples by way of a number of rounds of wet-lab experiments, the Broad researchers got here up with the drug listing a number of years in the past by typing the identify of the gene into the database.
“It’s a completely totally different method that has loads fewer steps and is loads less expensive,” says T.S. Karin Eisinger, a biologist on the College of Pennsylvania who research that specific muscle most cancers. Her group labored with Carpenter’s to validate the compounds in wet-lab assessments, and the 2 scientists are launching an organization to additional develop probably the most promising candidates. Others are a bit additional alongside: Recursion Prescribed drugs, an organization in Salt Lake Metropolis for which Carpenter is an advisor, has already launched 5 scientific trials to check drug candidates recognized utilizing a model of Cell Portray.
Because it wraps up its public launch, consortium members are gearing as much as work with the Well being and Environmental Sciences Institute, primarily based in Washington, DC, to see if they will pair outcomes from Cell Portray with different information to foretell the toxicity of prescribed drugs and agrochemicals.
Esther Landhuis is a science and well being journalist primarily based within the San Francisco Bay Space.