Bayesian optimization (BayesOpt) is a strong software broadly used for world optimization duties, akin to hyperparameter tuning, protein engineering, artificial chemistry, robotic studying, and even baking cookies. BayesOpt is a superb technique for these issues as a result of all of them contain optimizing black-box features which are costly to judge. A black-box operate’s underlying mapping from inputs (configurations of the factor we need to optimize) to outputs (a measure of efficiency) is unknown. Nonetheless, we will try to know its inside workings by evaluating the operate for various mixtures of inputs. As a result of every analysis will be computationally costly, we have to discover the perfect inputs in as few evaluations as attainable. BayesOpt works by repeatedly developing a surrogate mannequin of the black-box operate and strategically evaluating the operate on the most promising or informative enter location, given the knowledge noticed thus far.
Gaussian processes are fashionable surrogate fashions for BayesOpt as a result of they’re simple to make use of, will be up to date with new knowledge, and supply a confidence stage about every of their predictions. The Gaussian course of mannequin constructs a chance distribution over attainable features. This distribution is specified by a imply operate (what these attainable features appear like on common) and a kernel operate (how a lot these features can fluctuate throughout inputs). The efficiency of BayesOpt will depend on whether or not the arrogance intervals predicted by the surrogate mannequin comprise the black-box operate. Historically, consultants use area data to quantitatively outline the imply and kernel parameters (e.g., the vary or smoothness of the black-box operate) to precise their expectations about what the black-box operate ought to appear like. Nonetheless, for a lot of real-world functions like hyperparameter tuning, it is rather obscure the landscapes of the tuning aims. Even for consultants with related expertise, it may be difficult to slim down applicable mannequin parameters.
In “Pre-trained Gaussian processes for Bayesian optimization”, we take into account the problem of hyperparameter optimization for deep neural networks utilizing BayesOpt. We suggest Hyper BayesOpt (HyperBO), a extremely customizable interface with an algorithm that removes the necessity for quantifying mannequin parameters for Gaussian processes in BayesOpt. For brand spanking new optimization issues, consultants can merely choose earlier duties which are related to the present job they’re making an attempt to unravel. HyperBO pre-trains a Gaussian course of mannequin on knowledge from these chosen duties, and routinely defines the mannequin parameters earlier than operating BayesOpt. HyperBO enjoys theoretical ensures on the alignment between the pre-trained mannequin and the bottom fact, in addition to the standard of its options for black-box optimization. We share robust outcomes of HyperBO each on our new tuning benchmarks for close to–state-of-the-art deep studying fashions and basic multi-task black-box optimization benchmarks (HPO-B). We additionally show that HyperBO is strong to the collection of related duties and has low necessities on the quantity of information and duties for pre-training.
Loss features for pre-training
We pre-train a Gaussian course of mannequin by minimizing the Kullback–Leibler divergence (a generally used divergence) between the bottom fact mannequin and the pre-trained mannequin. Because the floor fact mannequin is unknown, we can not immediately compute this loss operate. To unravel for this, we introduce two data-driven approximations: (1) Empirical Kullback–Leibler divergence (EKL), which is the divergence between an empirical estimate of the bottom fact mannequin and the pre-trained mannequin; (2) Unfavorable log probability (NLL), which is the the sum of destructive log likelihoods of the pre-trained mannequin for all coaching features. The computational value of EKL or NLL scales linearly with the variety of coaching features. Furthermore, stochastic gradient–based mostly strategies like Adam will be employed to optimize the loss features, which additional lowers the price of computation. In well-controlled environments, optimizing EKL and NLL result in the identical consequence, however their optimization landscapes will be very totally different. For instance, within the easiest case the place the operate solely has one attainable enter, its Gaussian course of mannequin turns into a Gaussian distribution, described by the imply (m) and variance (s). Therefore the loss operate solely has these two parameters, m and s, and we will visualize EKL and NLL as follows:
Pre-training improves Bayesian optimization
Within the BayesOpt algorithm, choices on the place to judge the black-box operate are made iteratively. The choice standards are based mostly on the arrogance ranges supplied by the Gaussian course of, that are up to date in every iteration by conditioning on earlier knowledge factors acquired by BayesOpt. Intuitively, the up to date confidence ranges must be good: not overly assured or too not sure, since in both of those two circumstances, BayesOpt can not make the selections that may match what an knowledgeable would do.
In HyperBO, we change the hand-specified mannequin in conventional BayesOpt with the pre-trained Gaussian course of. Underneath gentle circumstances and with sufficient coaching features, we will mathematically confirm good theoretical properties of HyperBO: (1) Alignment: the pre-trained Gaussian course of ensures to be near the bottom fact mannequin when each are conditioned on noticed knowledge factors; (2) Optimality: HyperBO ensures to discover a near-optimal resolution to the black-box optimization downside for any features distributed in keeping with the unknown floor fact Gaussian course of.
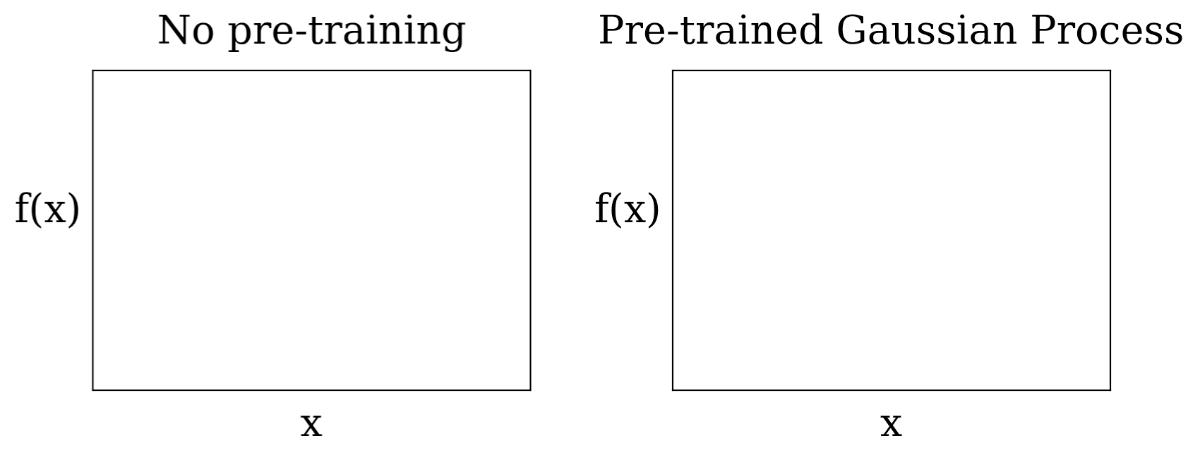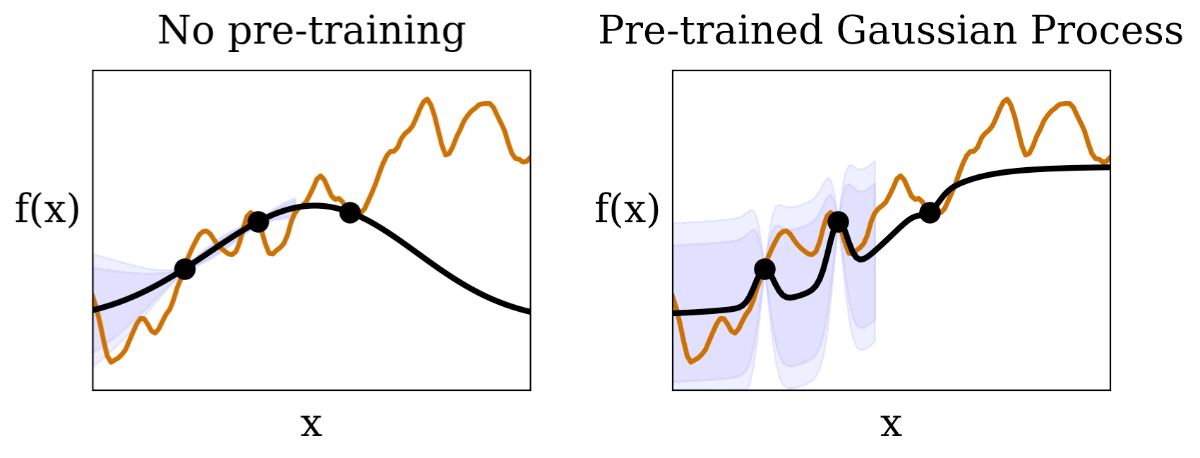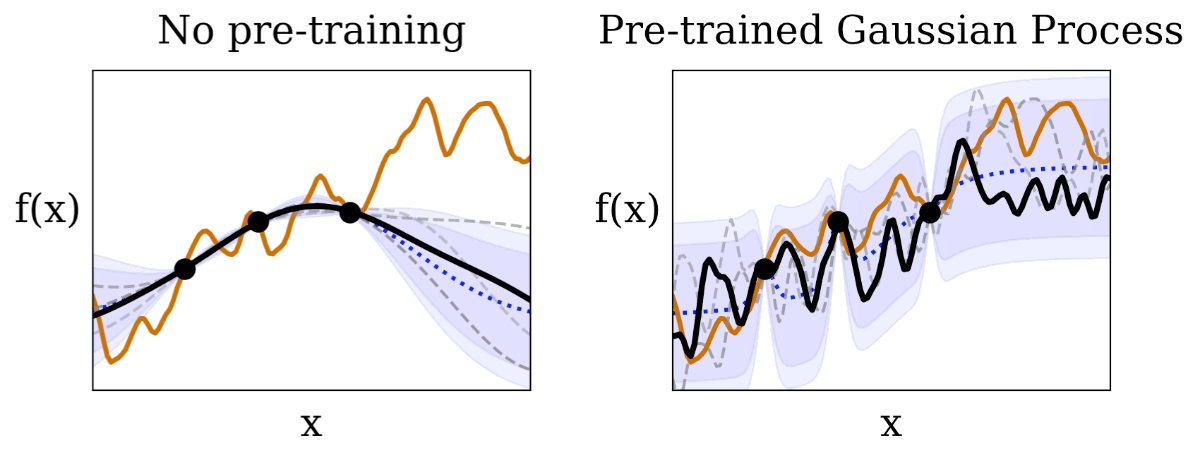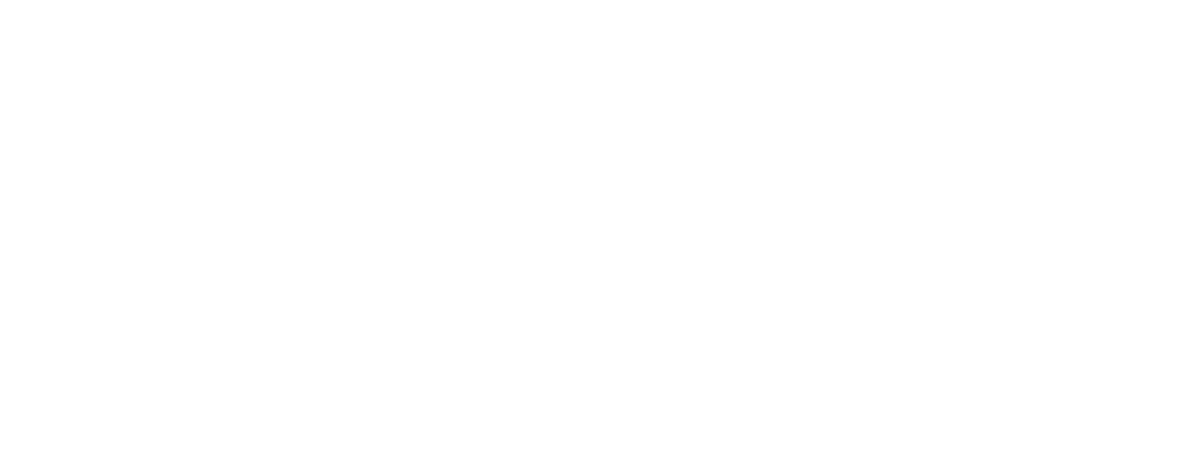 |
| We visualize the Gaussian course of (areas shaded in purple are 95% and 99% confidence intervals) conditional on observations (black dots) from an unknown check operate (orange line). In comparison with the normal BayesOpt with out pre-training, the anticipated confidence ranges in HyperBO captures the unknown check operate significantly better, which is a important prerequisite for Bayesian optimization. |
Empirically, to outline the construction of pre-trained Gaussian processes, we select to make use of very expressive imply features modeled by neural networks, and apply well-defined kernel features on inputs encoded to the next dimensional house with neural networks.
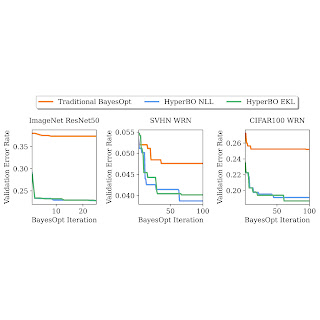
To guage HyperBO on difficult and sensible black-box optimization issues, we created the PD1 benchmark, which incorporates a dataset for multi-task hyperparameter optimization for deep neural networks. PD1 was developed by coaching tens of 1000’s of configurations of close to–state-of-the-art deep studying fashions on fashionable picture and textual content datasets, in addition to a protein sequence dataset. PD1 incorporates roughly 50,000 hyperparameter evaluations from 24 totally different duties (e.g., tuning Large ResNet on CIFAR100) with roughly 12,000 machine days of computation.
We show that when pre-training for only some hours on a single CPU, HyperBO can considerably outperform BayesOpt with fastidiously hand-tuned fashions on unseen difficult duties, together with tuning ResNet50 on ImageNet. Even with solely ~100 knowledge factors per coaching operate, HyperBO can carry out competitively in opposition to baselines.
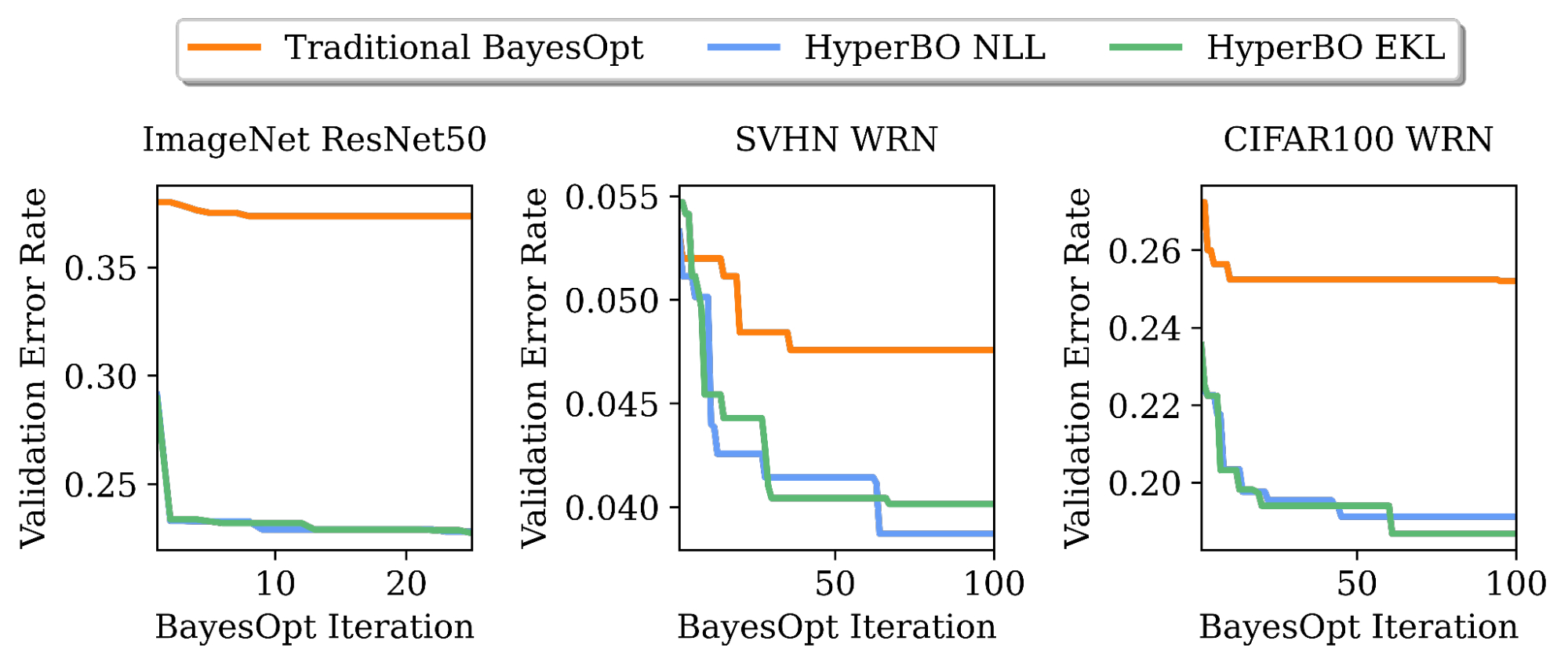 |
| Tuning validation error charges of ResNet50 on ImageNet and Large ResNet (WRN) on the Avenue View Home Numbers (SVHN) dataset and CIFAR100. By pre-training on solely ~20 duties and ~100 knowledge factors per job, HyperBO can considerably outperform conventional BayesOpt (with a fastidiously hand-tuned Gaussian course of) on beforehand unseen duties. |
Conclusion and future work
HyperBO is a framework that pre-trains a Gaussian course of and subsequently performs Bayesian optimization with a pre-trained mannequin. With HyperBO, we now not must hand-specify the precise quantitative parameters in a Gaussian course of. As an alternative, we solely must determine associated duties and their corresponding knowledge for pre-training. This makes BayesOpt each extra accessible and simpler. An vital future route is to allow HyperBO to generalize over heterogeneous search areas, for which we’re growing new algorithms by pre-training a hierarchical probabilistic mannequin.
Acknowledgements
The next members of the Google Analysis Mind Group carried out this analysis: Zi Wang, George E. Dahl, Kevin Swersky, Chansoo Lee, Zachary Nado, Justin Gilmer, Jasper Snoek, and Zoubin Ghahramani. We would wish to thank Zelda Mariet and Matthias Feurer for assist and session on switch studying baselines. We would additionally wish to thank Rif A. Saurous for constructive suggestions, and Rodolphe Jenatton and David Belanger for suggestions on earlier variations of the manuscript. As well as, we thank Sharat Chikkerur, Ben Adlam, Balaji Lakshminarayanan, Fei Sha and Eytan Bakshy for feedback, and Setareh Ariafar and Alexander Terenin for conversations on animation. Lastly, we thank Tom Small for designing the animation for this put up.



