As an information scientist, among the best issues about working with DataRobot clients is the sheer number of extremely fascinating questions that come up. Lately, a potential buyer requested me how I reconcile the truth that DataRobot has a number of very profitable funding banks utilizing DataRobot to reinforce the P&L of their buying and selling companies with my feedback that machine studying fashions aren’t all the time nice at predicting monetary asset costs. Peek into our dialog to be taught when machine studying does—and doesn’t—work properly in monetary markets use instances.
Why is machine studying capable of carry out properly in excessive frequency buying and selling functions, however is so dangerous at predicting asset costs longer-term?
Whereas there have been some successes within the trade utilizing machine studying for value prediction, they’ve been few and much between. As a rule of thumb, the shorter the prediction time horizon, the higher the percentages of success.
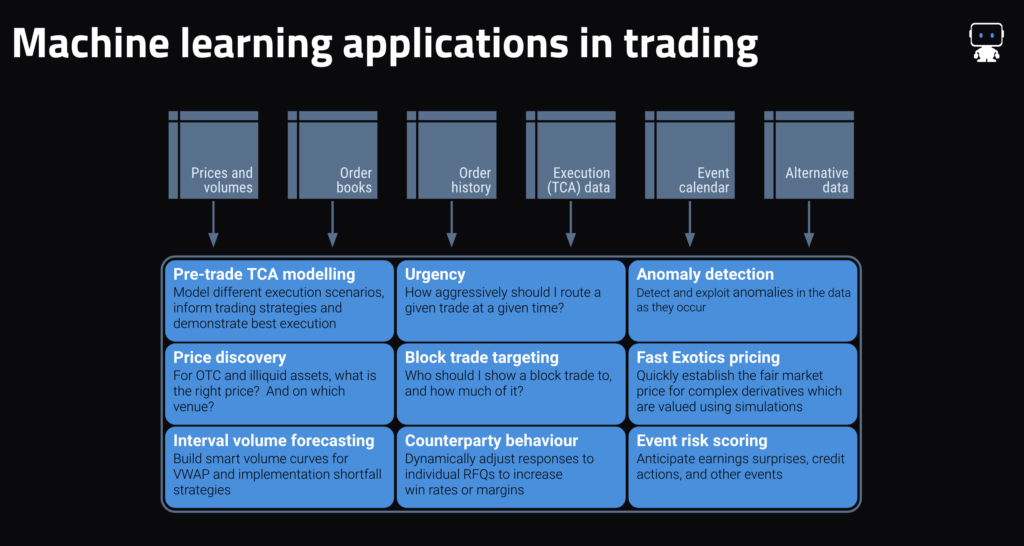
Typically talking, market making use instances that DataRobot (and different machine studying approaches) excel at share a number of of the next traits:
- For ahead value prediction: a really quick prediction horizon (sometimes inside the subsequent one to 10 seconds), the supply of fine order e book knowledge, and an acknowledgment that even a mannequin that’s 55%–60% correct is beneficial—it’s in the end a proportion recreation.
- For value discovery (e.g., establishing an applicable value illiquid securities, predicting the place liquidity shall be positioned, and figuring out applicable hedge ratios) in addition to extra typically: the existence of fine historic commerce knowledge on the property to be priced (e.g., TRACE, Asian bond market reporting, ECNs’ commerce historical past) in addition to a transparent set of extra liquid property which can be utilized as predictors (e.g., extra liquid credit, bond futures, swaps markets, and many others.).
- For counterparty conduct prediction: some type of structured knowledge which incorporates not solely gained trades but in addition unsuccessful requests/responses.
- Throughout functions: an data edge, as an example from commanding a big share of the circulation in that asset class, or from having buyer conduct knowledge that can be utilized.
Areas the place any type of machine studying will wrestle are sometimes characterised by a number of of those facets:
- Quickly altering regimes, behaviors and drivers: a key cause why longer-term predictions are so exhausting. We fairly often discover that the important thing mannequin drivers change very recurrently in most monetary markets, with a variable that’s a helpful indicator for one week or month having little data content material within the subsequent. Even in profitable functions, fashions are re-trained and re-deployed very recurrently (sometimes not less than weekly).
- Rare knowledge: a traditional instance right here is month-to-month or much less frequent knowledge. In such instances, the conduct being modeled sometimes adjustments so typically that by the point that sufficient coaching knowledge for machine studying has accrued (24 months or above), the market is in a distinct regime. For what it’s price, a number of of our clients have certainly had some success at, as an example, inventory choice utilizing predictions on a one-month horizon, however they’re (understandably) not telling us how they’re doing it.
- Sparse knowledge: the place there’s inadequate knowledge accessible to get an excellent image of the market in mixture, similar to sure OTC markets the place there aren’t any good ECNs.
- An absence of predictors: typically, knowledge on previous conduct of the variable being predicted (e.g., costs) isn’t sufficient. You additionally want knowledge describing the drivers of that variable (e.g., order books, flows, expectations, positioning). Previous efficiency isn’t indicative of future outcomes… .
- Restricted historical past of comparable regimes: as a result of machine studying fashions are all about recognising patterns in historic knowledge, new markets or property could be very tough for ML fashions. That is recognized in academia because the “chilly begin drawback.” There are numerous methods to take care of it, however none of them are excellent.
- Not really being a machine studying drawback: Worth-at-Threat modeling is the traditional instance right here—VaR isn’t a prediction of something, it’s a statistical summation of simulation outcomes. That mentioned, predicting the end result of a simulation is an ML drawback, and there are some good ML functions in pricing advanced, path-dependent derivatives.
Lastly, and apart from the above, a essential success consider any machine studying use case which shouldn’t be underestimated is the involvement of succesful and motivated individuals (sometimes quants and typically knowledge scientists) who perceive the info (and how one can manipulate it), enterprise processes, and worth levers. Success is normally pushed by such individuals finishing up many iterative experiments on the issue at hand, which is in the end the place our platform is available in. As mentioned, we massively speed up that means of experimentation. There’s quite a bit that may be automated in machine studying, however area information can’t be.
To summarize: it’s honest to say that the chance of success in buying and selling use instances is positively correlated with the frequency of the buying and selling (or not less than negatively with the holding interval/horizon) with a number of exceptions to show the rule. It’s additionally price taking into consideration that machine studying is commonly higher at second-order use instances similar to predicting the drivers of markets, as an example, occasion danger and, to some extent, volumes, fairly than first-order value predictions— topic to the above caveats.
Concerning the writer

Managing Director, Monetary Markets Information Science
Peter leads DataRobot’s monetary markets knowledge science apply and works carefully with fintech, banking, and asset administration purchasers on quite a few high-ROI use instances for the DataRobot AI Platform. Previous to becoming a member of DataRobot, he gained twenty-five years’ expertise in senior quantitative analysis, portfolio administration, buying and selling, danger administration and knowledge science roles at funding banks and asset managers together with Morgan Stanley, Warburg Pincus, Goldman Sachs, Credit score Suisse, Lansdowne Companions and Invesco, in addition to spending a number of years as a accomplice at a start-up international equities hedge fund. Peter has an M.Sc. in Information Science from Metropolis, College of London, an MBA from Cranfield College Faculty of Administration, and a B.Sc. in Accounting and Monetary Evaluation from the College of Warwick. His paper, “Searching Excessive and Low: Visualising Shifting Correlations in Monetary Markets”, was printed within the July 2018 concern of Laptop Graphics Discussion board.

