Sturdy algorithm design is the spine of programs throughout Google, notably for our ML and AI fashions. Therefore, creating algorithms with improved effectivity, efficiency and velocity stays a excessive precedence because it empowers providers starting from Search and Adverts to Maps and YouTube. Google Analysis has been on the forefront of this effort, creating many inventions from privacy-safe suggestion programs to scalable options for large-scale ML. In 2022, we continued this journey, and superior the state-of-the-art in a number of associated areas. Right here we spotlight our progress in a subset of those, together with scalability, privateness, market algorithms, and algorithmic foundations.
Scalable algorithms: Graphs, clustering, and optimization
As the necessity to deal with large-scale datasets will increase, scalability and reliability of complicated algorithms that additionally exhibit improved explainability, robustness, and velocity stay a excessive precedence. We continued our efforts in creating new algorithms for dealing with massive datasets in varied areas, together with unsupervised and semi-supervised studying, graph-based studying, clustering, and large-scale optimization.
An essential part of such programs is to construct a similarity graph — a nearest-neighbor graph that represents similarities between objects. For scalability and velocity, this graph must be sparse with out compromising high quality. We proposed a 2-hop spanner approach, known as STAR, as an environment friendly and distributed graph constructing technique, and confirmed the way it considerably decreases the variety of similarity computations in principle and observe, constructing a lot sparser graphs whereas producing high-quality graph studying or clustering outputs. For example, for graphs with 10T edges, we display ~100-fold enhancements in pairwise similarity comparisons and vital operating time speedups with negligible high quality loss. We had beforehand utilized this concept to develop massively parallel algorithms for metric, and minimum-size clustering. Extra broadly within the context of clustering, we developed the primary linear-time hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC) algorithm in addition to DBSCAN, the primary parallel algorithm for HAC with logarithmic depth, which achieves 50x speedup on 100B-edge graphs. We additionally designed improved sublinear algorithms for various flavors of clustering issues corresponding to geometric linkage clustering, constant-round correlation clustering, and absolutely dynamic k-clustering.
Impressed by the success of multi-core processing (e.g., GBBS), we launched into a mission to develop graph mining algorithms that may deal with graphs with 100B edges on a single multi-core machine. The massive problem right here is to realize quick (e.g., sublinear) parallel operating time (i.e., depth). Following our earlier work for neighborhood detection and correlation clustering, we developed an algorithm for HAC, known as ParHAC, which has provable polylogarithmic depth and near-linear work and achieves a 50x speedup. For example, it took ParHAC solely ~10 minutes to search out an approximate affinity hierarchy over a graph of over 100B edges, and ~3 hours to search out the complete HAC on a single machine. Following our earlier work on distributed HAC, we use these multi-core algorithms as a subroutine inside our distributed algorithms in an effort to deal with tera-scale graphs.
We additionally had numerous attention-grabbing outcomes on graph neural networks (GNN) in 2022. We supplied a model-based taxonomy that unified many graph studying strategies. As well as, we found insights for GNN fashions from their efficiency throughout hundreds of graphs with various construction (proven beneath). We additionally proposed a new hybrid structure to beat the depth necessities of current GNNs for fixing basic graph issues, corresponding to shortest paths and the minimal spanning tree.
 |
| Relative efficiency outcomes of three GNN variants (GCN, APPNP, FiLM) throughout 50,000 distinct node classification datasets in GraphWorld. We discover that tutorial GNN benchmark datasets exist in areas the place mannequin rankings don’t change. GraphWorld can uncover beforehand unexplored graphs that reveal new insights about GNN architectures. |
Moreover, to convey a few of these many advances to the broader neighborhood, we had three releases of our flagship modeling library for constructing graph neural networks in TensorFlow (TF-GNN). Highlights embody a mannequin library and mannequin orchestration API to make it simple to compose GNN options. Following our NeurIPS’20 workshop on Mining and Studying with Graphs at Scale, we ran a workshop on graph-based studying at ICML’22, and a tutorial for GNNs in TensorFlow at NeurIPS’22.
In “Sturdy Routing Utilizing Electrical Flows”, we introduced a latest paper that proposed a Google Maps resolution to effectively compute alternate paths in street networks which can be proof against failures (e.g., closures, incidents). We display the way it considerably outperforms the state-of-the-art plateau and penalty strategies on real-world street networks.
On the optimization entrance, we open-sourced Vizier, our flagship blackbox optimization and hyperparameter tuning library at Google. We additionally developed new strategies for linear programming (LP) solvers that deal with scalability limits attributable to their reliance on matrix factorizations, which restricts the chance for parallelism and distributed approaches. To this finish, we open-sourced a primal-dual hybrid gradient (PDHG) resolution for LP known as primal-dual linear programming (PDLP), a brand new first-order solver for large-scale LP issues. PDLP has been used to resolve real-world issues with as many as 12B non-zeros (and an inside distributed model scaled to 92B non-zeros). PDLP’s effectiveness is because of a mixture of theoretical developments and algorithm engineering.
 |
| With OSS Vizier, a number of shoppers every ship a “Recommend” request to the Service API, which produces Options for the shoppers utilizing Pythia insurance policies. The shoppers consider these options and return measurements. All transactions are saved to permit fault-tolerance. |
Privateness and federated studying
Respecting person privateness whereas offering high-quality providers stays a prime precedence for all Google programs. Analysis on this space spans many merchandise and makes use of ideas from differential privateness (DP) and federated studying.
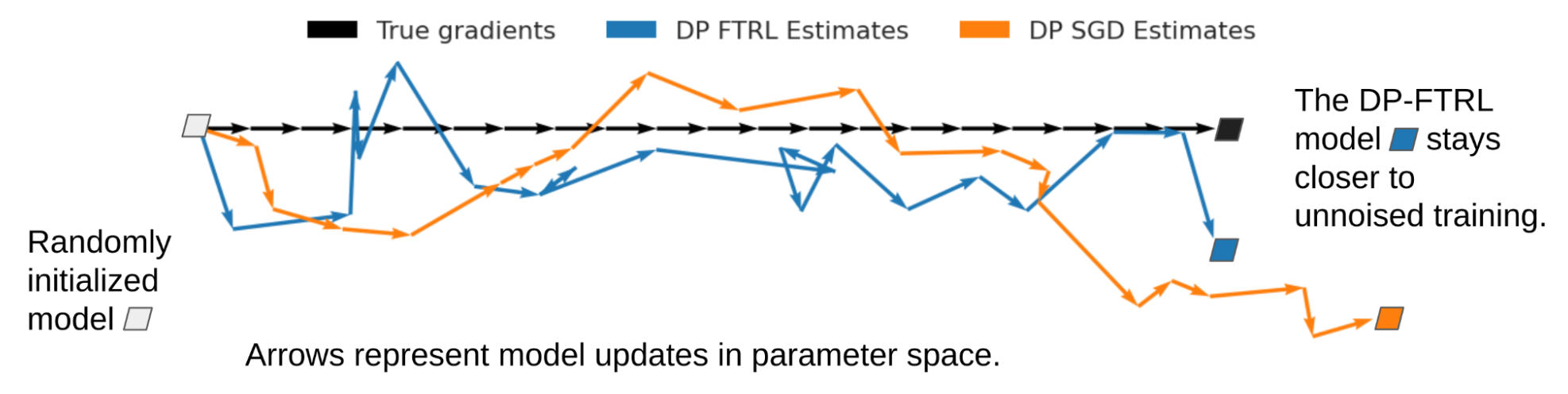
Initially, now we have made quite a lot of algorithmic advances to deal with the issue of coaching massive neural networks with DP. Constructing on our earlier work, which enabled us to launch a DP neural community primarily based on the DP-FTRL algorithm, we developed the matrix factorization DP-FTRL method. This work demonstrates that one can design a mathematical program to optimize over a big set of potential DP mechanisms to search out these greatest suited to particular studying issues. We additionally set up margin ensures which can be impartial of the enter characteristic dimension for DP studying of neural networks and kernel-based strategies. We additional prolong this idea to a broader vary of ML duties, matching baseline efficiency with 300x much less computation. For fine-tuning of enormous fashions, we argued that after pre-trained, these fashions (even with DP) basically function over a low-dimensional subspace, therefore circumventing the curse of dimensionality that DP imposes.
On the algorithmic entrance, for estimating the entropy of a high-dimensional distribution, we obtained native DP mechanisms (that work even when as little as one bit per pattern is obtainable) and environment friendly shuffle DP mechanisms. We proposed a extra correct methodology to concurrently estimate the top-ok hottest gadgets within the database in a non-public method, which we employed within the Plume library. Furthermore, we confirmed a near-optimal approximation algorithm for DP clustering within the massively parallel computing (MPC) mannequin, which additional improves on our earlier work for scalable and distributed settings.
One other thrilling analysis route is the intersection of privateness and streaming. We obtained a near-optimal approximation-space trade-off for the non-public frequency moments and a brand new algorithm for privately counting distinct components within the sliding window streaming mannequin. We additionally introduced a normal hybrid framework for learning adversarial streaming.
Addressing functions on the intersection of safety and privateness, we developed new algorithms which can be safe, non-public, and communication-efficient, for measuring cross-publisher attain and frequency. The World Federation of Advertisers has adopted these algorithms as a part of their measurement system. In subsequent work, we developed new protocols which can be safe and personal for computing sparse histograms within the two-server mannequin of DP. These protocols are environment friendly from each computation and communication factors of view, are considerably higher than what normal strategies would yield, and mix instruments and strategies from sketching, cryptography and multiparty computation, and DP.
Whereas now we have educated BERT and transformers with DP, understanding coaching instance memorization in massive language fashions (LLMs) is a heuristic solution to consider their privateness. Particularly, we investigated when and why LLMs neglect (doubtlessly memorized) coaching examples throughout coaching. Our findings recommend that earlier-seen examples could observe privateness advantages on the expense of examples seen later. We additionally quantified the diploma to which LLMs emit memorized coaching information.
Market algorithms and causal inference
We additionally continued our analysis in bettering on-line marketplaces in 2022. For instance, an essential latest space in advert public sale analysis is the examine of auto-bidding internet marketing the place nearly all of bidding occurs through proxy bidders that optimize higher-level targets on behalf of advertisers. The complicated dynamics of customers, advertisers, bidders, and advert platforms results in non-trivial issues on this area. Following our earlier work in analyzing and bettering mechanisms below auto-bidding auctions, we continued our analysis in bettering on-line marketplaces within the context of automation whereas taking totally different points into consideration, corresponding to person expertise and advertiser budgets. Our findings recommend that correctly incorporating ML recommendation and randomization strategies, even in non-truthful auctions, can robustly enhance the general welfare at equilibria amongst auto-bidding algorithms.
 |
| Construction of auto-bidding on-line adverts system. |
Past auto-bidding programs, we additionally studied public sale enhancements in complicated environments, e.g., settings the place patrons are represented by intermediaries, and with Wealthy Adverts the place every advert might be proven in one among a number of potential variants. We summarize our work on this space in a latest survey. Past auctions, we additionally examine using contracts in multi-agent and adversarial settings.
On-line stochastic optimization stays an essential a part of internet marketing programs with utility in optimum bidding and finances pacing. Constructing on our long-term analysis in on-line allocation, we lately blogged about twin mirror descent, a brand new algorithm for on-line allocation issues that’s easy, strong, and versatile. This state-of-the-art algorithm is strong towards a variety of adversarial and stochastic enter distributions and might optimize essential targets past financial effectivity, corresponding to equity. We additionally present that by tailoring twin mirror descent to the particular construction of the more and more in style return-on-spend constraints, we are able to optimize advertiser worth. Twin mirror descent has a variety of functions and has been used over time to assist advertisers acquire extra worth by means of higher algorithmic determination making.
 |
| An outline of the twin mirror descent algorithm. |
Moreover, following our latest work on the interaction of ML, mechanism design and markets, we investigated transformers for uneven public sale design, designed utility-maximizing methods for no-regret studying patrons, and developed new studying algorithms to bid or to worth in auctions.
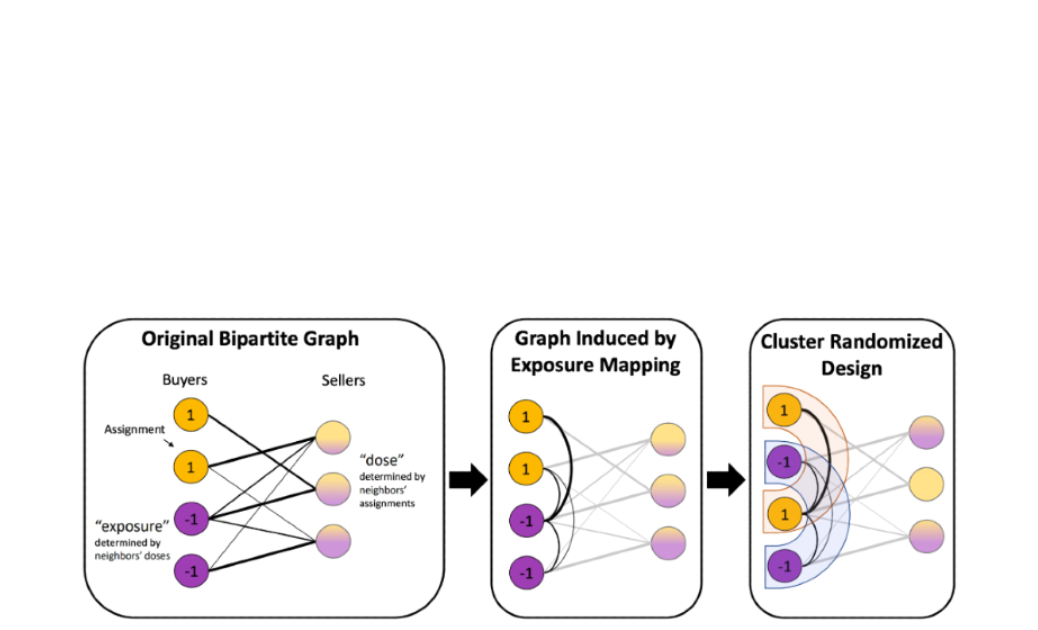
A crucial part of any refined on-line service is the flexibility to experimentally measure the response of customers and different gamers to new interventions. A significant problem of estimating these causal results precisely is dealing with complicated interactions — or interference — between the management and therapy models of those experiments. We mixed our graph clustering and causal inference experience to develop the outcomes of our earlier work on this space, with improved outcomes below a versatile response mannequin and a brand new experimental design that’s simpler at decreasing these interactions when therapy assignments and metric measurements happen on the identical aspect of a bipartite platform. We additionally confirmed how artificial management and optimization strategies might be mixed to design extra highly effective experiments, particularly in small information regimes.
Algorithmic foundations and principle
Lastly, we continued our basic algorithmic analysis by tackling long-standing open issues. A surprisingly concise paper affirmatively resolved a four-decade previous open query on whether or not there’s a mechanism that ensures a continuing fraction of the gains-from-trade attainable each time purchaser’s worth weakly exceeds vendor’s value. One other latest paper obtained the state-of-the-art approximation for the basic and highly-studied k-means drawback. We additionally improved the perfect approximation for correlation clustering breaking the barrier approximation issue of two. Lastly, our work on dynamic information buildings to resolve min-cost and different community circulate issues has contributed to a breakthrough line of labor in adapting steady optimization strategies to resolve basic discrete optimization issues.
Concluding ideas
Designing efficient algorithms and mechanisms is a crucial part of many Google programs that have to deal with tera-scale information robustly with crucial privateness and security issues. Our method is to develop algorithms with strong theoretical foundations that may be deployed successfully in our product programs. As well as, we’re bringing many of those advances to the broader neighborhood by open-sourcing a few of our most novel developments and by publishing the superior algorithms behind them. On this publish, we coated a subset of algorithmic advances in privateness, market algorithms, scalable algorithms, graph-based studying, and optimization. As we transfer towards an AI-first Google with additional automation, creating strong, scalable, and privacy-safe ML algorithms stays a excessive precedence. We’re enthusiastic about creating new algorithms and deploying them extra broadly.
Acknowledgements
This publish summarizes analysis from a lot of groups and benefited from enter from a number of researchers together with Gagan Aggarwal, Amr Ahmed, David Applegate, Santiago Balseiro, Vincent Cohen-addad, Yuan Deng, Alessandro Epasto, Matthew Fahrbach, Badih Ghazi, Sreenivas Gollapudi, Rajesh Jayaram, Ravi Kumar, Sanjiv Kumar, Silvio Lattanzi, Kuba Lacki, Brendan McMahan, Aranyak Mehta, Bryan Perozzi, Daniel Ramage, Ananda Theertha Suresh, Andreas Terzis, Sergei Vassilvitskii, Di Wang, and Music Zuo. Particular due to Ravi Kumar for his contributions to this publish.
Google Analysis, 2022 & past
This was the fifth weblog publish within the “Google Analysis, 2022 & Past” sequence. Different posts on this sequence are listed within the desk beneath:
| * Articles will probably be linked as they’re launched. |