
The mix of the atmosphere a person experiences and their genetic predispositions determines the vast majority of their threat for numerous ailments. Giant nationwide efforts, corresponding to the UK Biobank, have created massive, public sources to higher perceive the hyperlinks between atmosphere, genetics, and illness. This has the potential to assist people higher perceive how you can keep wholesome, clinicians to deal with diseases, and scientists to develop new medicines.
One problem on this course of is how we make sense of the huge quantity of scientific measurements — the UK Biobank has many petabytes of imaging, metabolic checks, and medical data spanning 500,000 people. To greatest use this knowledge, we want to have the ability to signify the knowledge current as succinct, informative labels about significant ailments and traits, a course of referred to as phenotyping. That’s the place we are able to use the power of ML fashions to choose up on delicate intricate patterns in massive quantities of information.
We’ve beforehand demonstrated the power to make use of ML fashions to rapidly phenotype at scale for retinal ailments. Nonetheless, these fashions have been educated utilizing labels from clinician judgment, and entry to clinical-grade labels is a limiting issue as a result of time and expense wanted to create them.
In “Inference of continual obstructive pulmonary illness with deep studying on uncooked spirograms identifies new genetic loci and improves threat fashions”, revealed in Nature Genetics, we’re excited to spotlight a way for coaching correct ML fashions for genetic discovery of ailments, even when utilizing noisy and unreliable labels. We show the power to coach ML fashions that may phenotype straight from uncooked scientific measurement and unreliable medical document data. This diminished reliance on medical area consultants for labeling drastically expands the vary of functions for our method to a panoply of ailments and has the potential to enhance their prevention, analysis, and remedy. We showcase this technique with ML fashions that may higher characterize lung operate and continual obstructive pulmonary illness (COPD). Moreover, we present the usefulness of those fashions by demonstrating a greater potential to determine genetic variants related to COPD, improved understanding of the biology behind the illness, and profitable prediction of outcomes related to COPD.
ML for deeper understanding of exhalation
For this demonstration, we targeted on COPD, the third main reason behind worldwide loss of life in 2019, during which airway irritation and impeded airflow can progressively scale back lung operate. Lung operate for COPD and different ailments is measured by recording a person’s exhalation quantity over time (the document is known as a spirogram; see an instance under). Though there are pointers (referred to as GOLD) for figuring out COPD standing from exhalation, these use only some, particular knowledge factors within the curve and apply mounted thresholds to these values. A lot of the wealthy knowledge from these spirograms is discarded on this evaluation of lung operate.
We reasoned that ML fashions educated to categorise spirograms would be capable of use the wealthy knowledge current extra fully and end in extra correct and complete measures of lung operate and illness, much like what we now have seen in different classification duties like mammography or histology. We educated ML fashions to foretell whether or not a person has COPD utilizing the complete spirograms as inputs.
The frequent technique of coaching fashions for this downside, supervised studying, requires samples to be related to labels. Figuring out these labels can require the trouble of very time-constrained consultants. For this work, to indicate that we don’t essentially want medically graded labels, we determined to make use of quite a lot of extensively out there sources of medical document data to create these labels with out medical professional assessment. These labels are much less dependable and noisy for 2 causes. First, there are gaps within the medical data of people as a result of they use a number of well being companies. Second, COPD is commonly undiagnosed, that means many with the illness is not going to be labeled as having it even when we compile the entire medical data. Nonetheless, we educated a mannequin to foretell these noisy labels from the spirogram curves and deal with the mannequin predictions as a quantitative COPD legal responsibility or threat rating.
Predicting COPD outcomes
We then investigated whether or not the chance scores produced by our mannequin might higher predict quite a lot of binary COPD outcomes (for instance, a person’s COPD standing, whether or not they have been hospitalized for COPD or died from it). For comparability, we benchmarked the mannequin relative to expert-defined measurements required to diagnose COPD, particularly FEV1/FVC, which compares particular factors on the spirogram curve with a easy mathematical ratio. We noticed an enchancment within the potential to foretell these outcomes as seen within the precision-recall curves under.
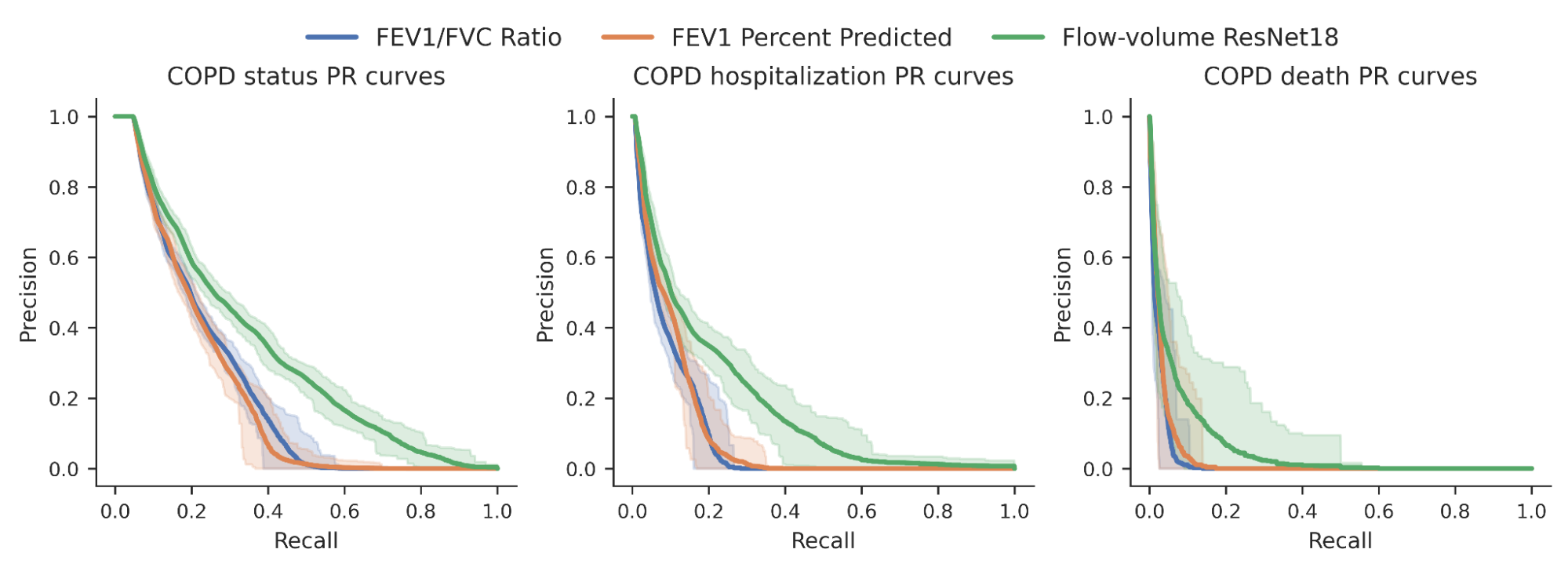 |
| Precision-recall curves for COPD standing and outcomes for our ML mannequin (inexperienced) in comparison with conventional measures. Confidence intervals are proven by lighter shading. |
We additionally noticed that separating populations by their COPD mannequin rating was predictive of all-cause mortality. This plot means that people with larger COPD threat usually tend to die earlier from any causes and the chance in all probability has implications past simply COPD.
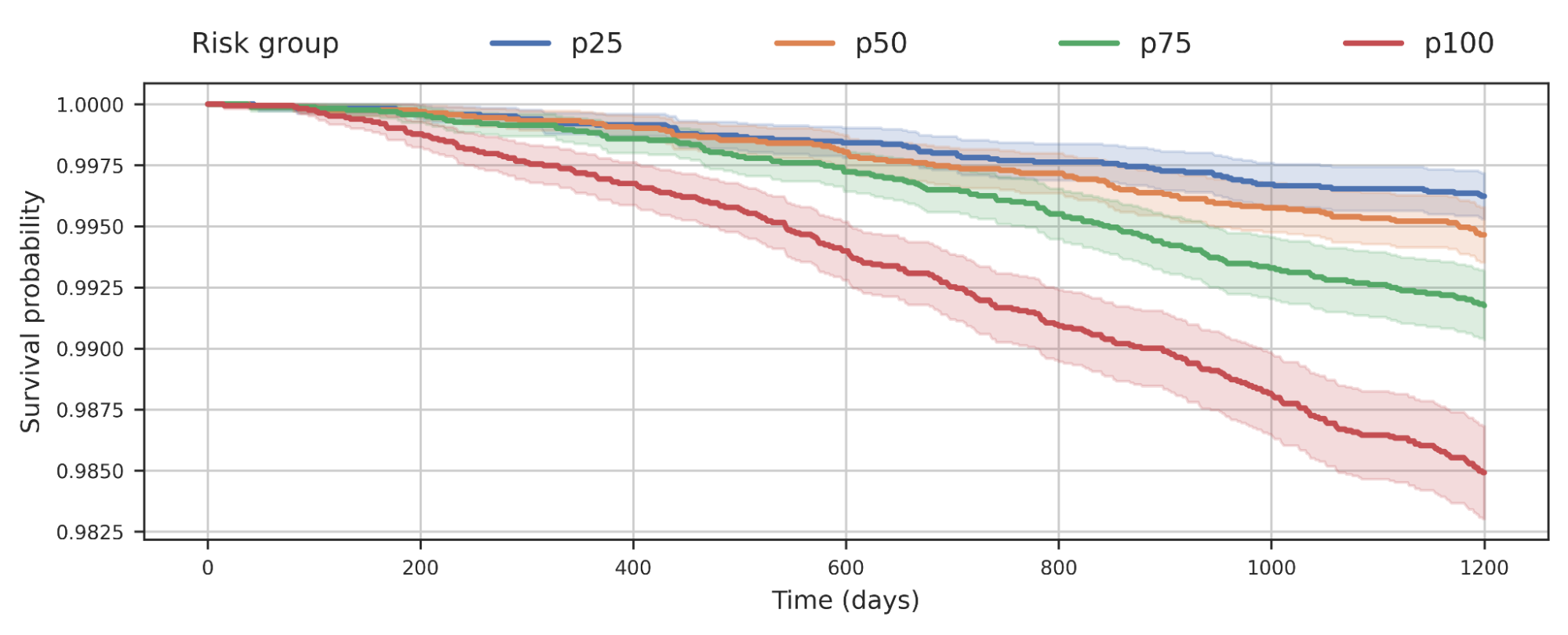 |
| Survival evaluation of a cohort of UK Biobank people stratified by their COPD mannequin’s predicted threat quartile. The lower of the curve signifies people within the cohort dying over time. For instance, p100 represents the 25% of the cohort with biggest predicted threat, whereas p50 represents the 2nd quartile. |
Figuring out the genetic hyperlinks with COPD
Because the objective of enormous scale biobanks is to convey collectively massive quantities of each phenotype and genetic knowledge, we additionally carried out a check referred to as a genome-wide affiliation research (GWAS) to determine the genetic hyperlinks with COPD and genetic predisposition. A GWAS measures the power of the statistical affiliation between a given genetic variant — a change in a selected place of DNA — and the observations (e.g., COPD) throughout a cohort of instances and controls. Genetic associations found on this method can inform drug growth that modifies the exercise or merchandise of a gene, in addition to develop our understanding of the biology for a illness.
We confirmed with our ML-phenotyping technique that not solely will we rediscover nearly all recognized COPD variants discovered by guide phenotyping, however we additionally discover many novel genetic variants considerably related to COPD. As well as, we see good settlement on the impact sizes for the variants found by each our ML strategy and the guide one (R2=0.93), which supplies robust proof for validity of the newly discovered variants.
Lastly, our collaborators at Harvard Medical College and Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital additional examined the plausibility of those findings by offering insights into the potential organic function of the novel variants in growth and development of COPD (you’ll be able to see extra dialogue on these insights within the paper).
Conclusion
We demonstrated that our earlier strategies for phenotyping with ML will be expanded to a variety of ailments and might present novel and priceless insights. We made two key observations through the use of this to foretell COPD from spirograms and discovering new genetic insights. First, area data was not essential to make predictions from uncooked medical knowledge. Apparently, we confirmed the uncooked medical knowledge might be underutilized and the ML mannequin can discover patterns in it that aren’t captured by expert-defined measurements. Second, we don’t want medically graded labels; as an alternative, noisy labels outlined from extensively out there medical data can be utilized to generate clinically predictive and genetically informative threat scores. We hope that this work will broadly develop the power of the sphere to make use of noisy labels and can enhance our collective understanding of lung operate and illness.
Acknowledgments
This work is the mixed output of a number of contributors and establishments. We thank all contributors: Justin Cosentino, Babak Alipanahi, Zachary R. McCaw, Cory Y. McLean, Farhad Hormozdiari (Google), Davin Hill (Northeastern College), Tae-Hwi Schwantes-An and Dongbing Lai (Indiana College), Brian D. Hobbs and Michael H. Cho (Brigham and Ladies’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical College). We additionally thank Ted Yun and Nick Furlotte for reviewing the manuscript, Greg Corrado and Shravya Shetty for assist, and Howard Yang, Kavita Kulkarni, and Tammi Huynh for serving to with publication logistics.




