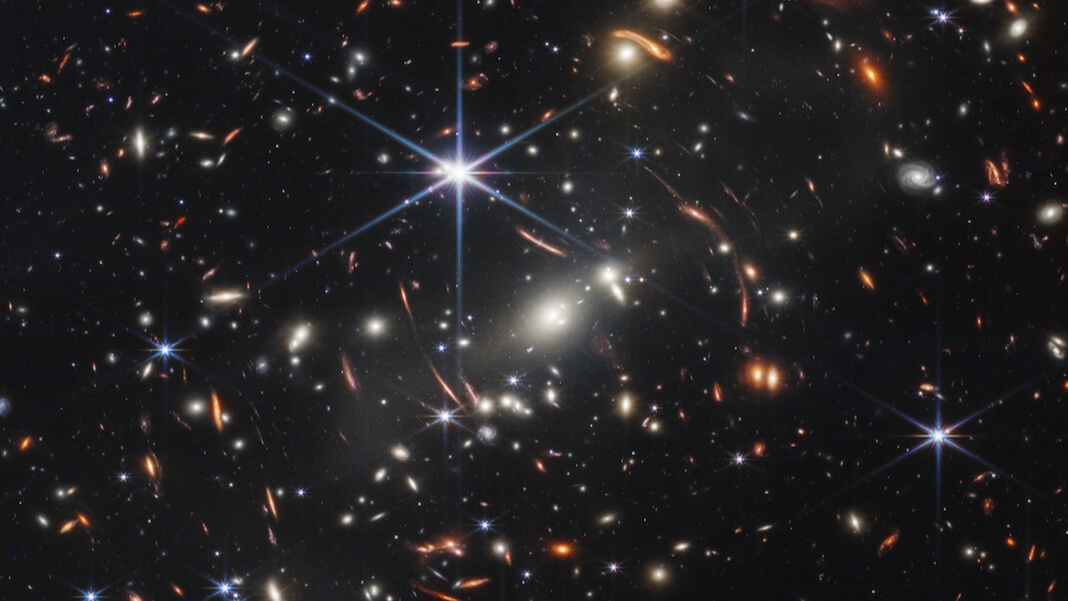
When a bunch of photons struck the almost flawless mirrors of the James Webb House Telescope earlier this yr, they’d been touring the void for 13.4 billion years. The sunshine was emitted from distant galaxies at a time when the delivery of the whole lot we all know and see was nonetheless, in a cosmic sense, latest historical past. Historic doesn’t actually do it justice.
Webb’s first deep area photographs—infrared recordings of minuscule patches of sky, jam-packed with galaxies—sparked a scramble amongst astronomers to search out the oldest galaxies in view. The Hubble House Telescope held the prevailing report with observations of a galaxy from when the universe was simply 400 million years previous. Webb’s bigger mirrors and talent to see into the infrared components of the spectrum had been designed to do higher.
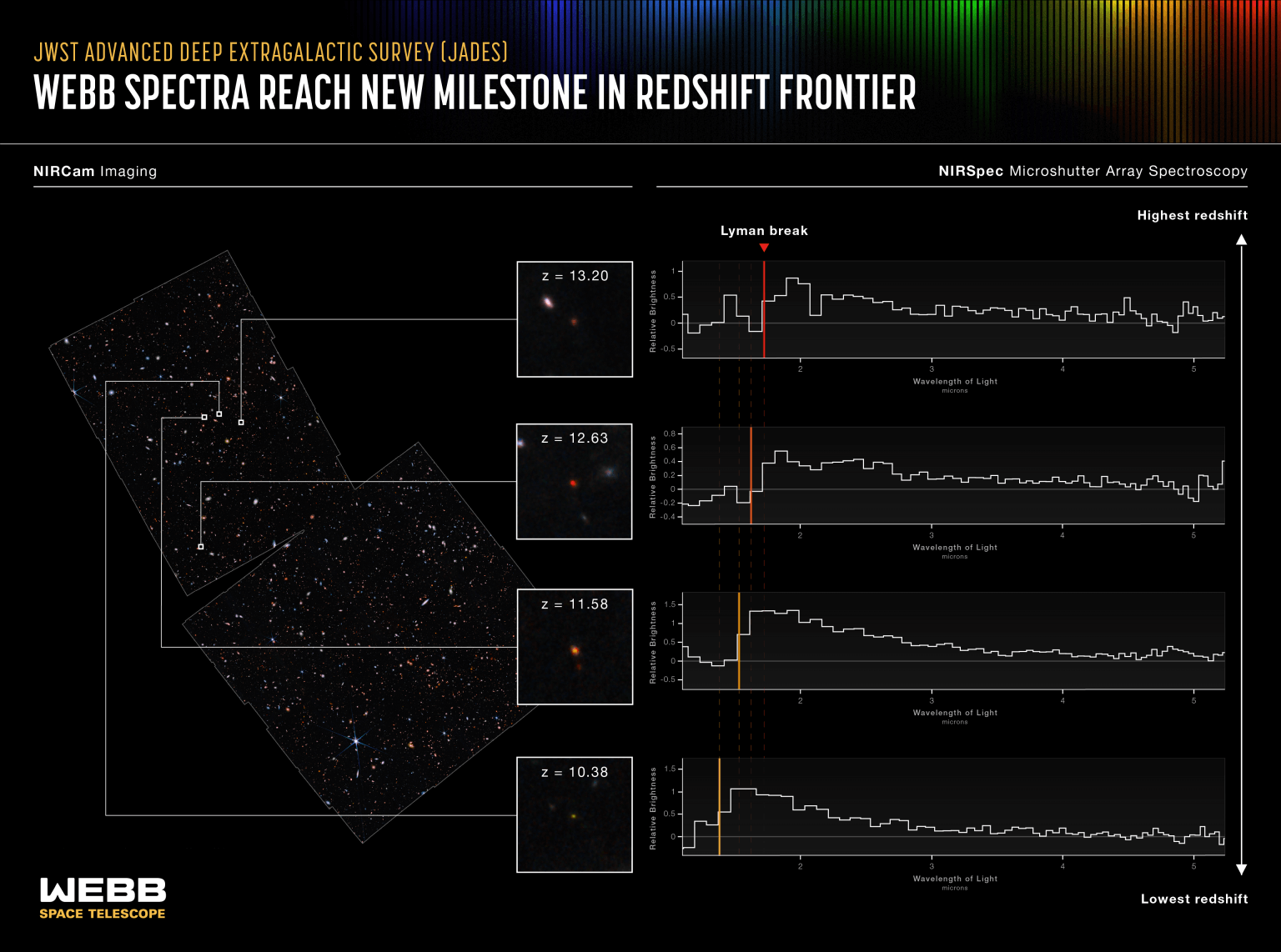
On Friday, the telescope proved its mettle when a crew of scientists—collectively often called JADES, a collaboration between the builders of two of Webb’s devices, NIRcam and NIRspec—introduced they’d confirmed observations of the oldest galaxies but.
“For the primary time, now we have found galaxies solely 350 million years after the Large Bang, and we could be completely assured of their unbelievable distances,” stated Brant Robertson from the College of California Santa Cruz, a member of the NIRCam science crew and coauthor on a latest paper on the work.
Astronomers first started compiling a listing of candidates by analyzing information from Webb’s NIRcam instrument, an exquisitely delicate infrared digital camera. Virtually instantly after Webb’s first photographs went public tales of extraordinarily historic galaxies hit the online.
However whereas NIRcam observations revealed a wealthy inhabitants of targets worthy of a more in-depth look, official affirmation required detailed spectroscopic evaluation.
“It’s very potential for nearer galaxies to masquerade as very distant galaxies,” stated astronomer and coauthor Emma Curtis-Lake from the College of Hertfordshire in the UK.
Due to NIRspec, in two latest research (right here and right here), the groups had been in a position conduct spectroscopic evaluation—the gold customary for confirming the gap and age of those extremely faint early galaxies—for a spread of candidates. Although neither examine has but been peer-reviewed, the findings possible beat Hubble’s report.
The sliver of sky noticed is concerning the measurement of the queen’s eye “on a pound coin held at arm’s size,” Liverpool John Moores College’s Renske Smit advised the BBC. Inside that eye are nearly 100,000 galaxies, every captured at a second billions of years in the past.
To measure the age of a galaxy close to the start of the universe, scientists measure its “redshift.” As gentle travels, the enlargement of the universe stretches out its wavelength, drawing it into the redder components of the spectrum. A few of the most historic gentle has been stretched out of the seen spectrum and into the infrared—Webb’s specialty.
The oldest galaxies will not be solely seen within the infrared, however their spectrum additionally cuts off at a selected level because of the scattering of intergalactic hydrogen. Faint infrared galaxies exhibiting this cutoff, which strikes with better redshift, crammed out a pool of candidates. The crew then devoted 28 hours’ remark time to 250 of those with NIRspec. This detailed spectroscopic evaluation included particular atomic signatures and nailed down the redshift.
4 galaxies proved exceptionally previous, with redshifts better than 10. Two confirmed redshifts at 13, from a time when the universe was simply 330 million years previous. The crew says these galaxies are small, only a hundred million photo voltaic lots, and made up of younger stars lower than 100 million years previous. The Milky Approach, by comparability, is assumed to have at the very least 100 billion stars, and the solar is a few 4.6 billion years previous. Regardless of their diminutive measurement, the crew says these early galaxies produced stars at a prodigious charge, as a lot as 10 occasions sooner than equally sized galaxies nearer to the current day.
These galaxies now seem to carry the report for oldest ever spectroscopically confirmed, however the title could not final lengthy. Although nonetheless awaiting affirmation, scientists have estimated some galaxies already captured by Webb are even older, and Webb was designed to see gentle from epochs as early as 100 million years after the Large Bang.
By finding out the earliest stars and galaxies, scientists hope to study extra about galaxy formation and to pin down a interval within the universe’s evolution often called reionization, when the sturdy gentle of the primary stars ionized surrounding gasoline by stripping electrons from hydrogen and helium. As the celebs in these 4 galaxies could have begun forming as a lot as 100 million years earlier, this primary technology of stars could date again to as early as round 230 million years after the Large Bang.
“With these measurements, we will know the intrinsic brightness of the galaxies and work out what number of stars they’ve,” Robertson stated. “Now we will begin to actually choose aside how galaxies are put collectively over time.”
Picture Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI

