Clever assistants on cellular gadgets have considerably superior language-based interactions for performing easy every day duties, reminiscent of setting a timer or turning on a flashlight. Regardless of the progress, these assistants nonetheless face limitations in supporting conversational interactions in cellular person interfaces (UIs), the place many person duties are carried out. For instance, they can’t reply a person’s query about particular info displayed on a display screen. An agent would wish to have a computational understanding of graphical person interfaces (GUIs) to realize such capabilities.
Prior analysis has investigated a number of essential technical constructing blocks to allow conversational interplay with cellular UIs, together with summarizing a cellular display screen for customers to shortly perceive its function, mapping language directions to UI actions and modeling GUIs in order that they’re extra amenable for language-based interplay. Nevertheless, every of those solely addresses a restricted facet of conversational interplay and requires appreciable effort in curating large-scale datasets and coaching devoted fashions. Moreover, there’s a broad spectrum of conversational interactions that may happen on cellular UIs. Due to this fact, it’s crucial to develop a light-weight and generalizable method to understand conversational interplay.
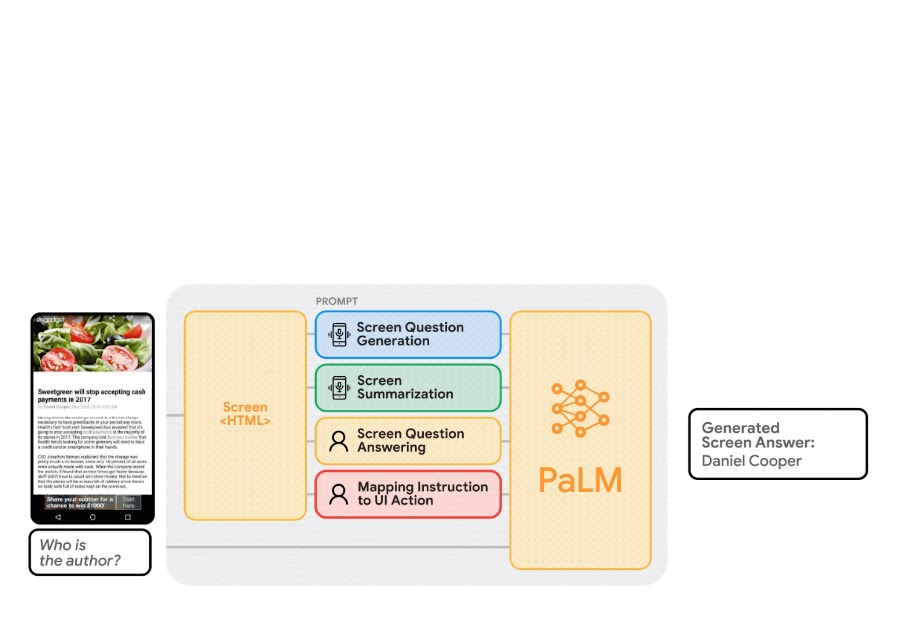
In “Enabling Conversational Interplay with Cell UI utilizing Giant Language Fashions”, introduced at CHI 2023, we examine the viability of using giant language fashions (LLMs) to allow various language-based interactions with cellular UIs. Latest pre-trained LLMs, reminiscent of PaLM, have demonstrated talents to adapt themselves to varied downstream language duties when being prompted with a handful of examples of the goal job. We current a set of prompting methods that allow interplay designers and builders to shortly prototype and check novel language interactions with customers, which saves time and assets earlier than investing in devoted datasets and fashions. Since LLMs solely take textual content tokens as enter, we contribute a novel algorithm that generates the textual content illustration of cellular UIs. Our outcomes present that this method achieves aggressive efficiency utilizing solely two knowledge examples per job. Extra broadly, we show LLMs’ potential to essentially remodel the longer term workflow of conversational interplay design.
 |
| Animation exhibiting our work on enabling numerous conversational interactions with cellular UI utilizing LLMs. |
Prompting LLMs with UIs
LLMs help in-context few-shot studying by way of prompting — as a substitute of fine-tuning or re-training fashions for every new job, one can immediate an LLM with just a few enter and output knowledge exemplars from the goal job. For a lot of pure language processing duties, reminiscent of question-answering or translation, few-shot prompting performs competitively with benchmark approaches that prepare a mannequin particular to every job. Nevertheless, language fashions can solely take textual content enter, whereas cellular UIs are multimodal, containing textual content, picture, and structural info of their view hierarchy knowledge (i.e., the structural knowledge containing detailed properties of UI components) and screenshots. Furthermore, instantly inputting the view hierarchy knowledge of a cellular display screen into LLMs is just not possible because it accommodates extreme info, reminiscent of detailed properties of every UI component, which might exceed the enter size limits of LLMs.
To deal with these challenges, we developed a set of methods to immediate LLMs with cellular UIs. We contribute an algorithm that generates the textual content illustration of cellular UIs utilizing depth-first search traversal to transform the Android UI’s view hierarchy into HTML syntax. We additionally make the most of chain of thought prompting, which includes producing intermediate outcomes and chaining them collectively to reach on the closing output, to elicit the reasoning skill of the LLM.
 |
| Animation exhibiting the method of few-shot prompting LLMs with cellular UIs. |
Our immediate design begins with a preamble that explains the immediate’s function. The preamble is adopted by a number of exemplars consisting of the enter, a series of thought (if relevant), and the output for every job. Every exemplar’s enter is a cellular display screen within the HTML syntax. Following the enter, chains of thought may be offered to elicit logical reasoning from LLMs. This step is just not proven within the animation above as it’s non-compulsory. The duty output is the specified consequence for the goal duties, e.g., a display screen abstract or a solution to a person query. Few-shot prompting may be achieved with a couple of exemplar included within the immediate. Throughout prediction, we feed the mannequin the immediate with a brand new enter display screen appended on the finish.
Experiments
We carried out complete experiments with 4 pivotal modeling duties: (1) display screen question-generation, (2) display screen summarization, (3) display screen question-answering, and (4) mapping instruction to UI motion. Experimental outcomes present that our method achieves aggressive efficiency utilizing solely two knowledge examples per job.
 |
Job 1: Display screen query era
Given a cellular UI display screen, the aim of display screen question-generation is to synthesize coherent, grammatically appropriate pure language questions related to the UI components requiring person enter.
We discovered that LLMs can leverage the UI context to generate questions for related info. LLMs considerably outperformed the heuristic method (template-based era) relating to query high quality.
We additionally revealed LLMs’ skill to mix related enter fields right into a single query for environment friendly communication. For instance, the filters asking for the minimal and most worth had been mixed right into a single query: “What’s the worth vary?
 |
| We noticed that the LLM may use its prior data to mix a number of associated enter fields to ask a single query. |
In an analysis, we solicited human rankings on whether or not the questions had been grammatically appropriate (Grammar) and related to the enter fields for which they had been generated (Relevance). Along with the human-labeled language high quality, we mechanically examined how effectively LLMs can cowl all the weather that have to generate questions (Protection F1). We discovered that the questions generated by LLM had nearly excellent grammar (4.98/5) and had been extremely related to the enter fields displayed on the display screen (92.8%). Moreover, LLM carried out effectively by way of overlaying the enter fields comprehensively (95.8%).
| Template | 2-shot LLM | |||||||
| Grammar | 3.6 (out of 5) | 4.98 (out of 5) | ||||||
| Relevance | 84.1% | 92.8% | ||||||
| Protection F1 | 100% | 95.8% |
Job 2: Display screen summarization
Display screen summarization is the automated era of descriptive language overviews that cowl important functionalities of cellular screens. The duty helps customers shortly perceive the aim of a cellular UI, which is especially helpful when the UI is just not visually accessible.
Our outcomes confirmed that LLMs can successfully summarize the important functionalities of a cellular UI. They’ll generate extra correct summaries than the Screen2Words benchmark mannequin that we beforehand launched utilizing UI-specific textual content, as highlighted within the coloured textual content and containers under.
 |
| Instance abstract generated by 2-shot LLM. We discovered the LLM is ready to use particular textual content on the display screen to compose extra correct summaries. |
Curiously, we noticed LLMs utilizing their prior data to infer info not introduced within the UI when creating summaries. Within the instance under, the LLM inferred the subway stations belong to the London Tube system, whereas the enter UI doesn’t include this info.
 |
| LLM makes use of its prior data to assist summarize the screens. |
Human analysis rated LLM summaries as extra correct than the benchmark, but they scored decrease on metrics like BLEU. The mismatch between perceived high quality and metric scores echoes latest work exhibiting LLMs write higher summaries regardless of automated metrics not reflecting it.
 |
 |
| Left: Display screen summarization efficiency on automated metrics. Proper: Display screen summarization accuracy voted by human evaluators. |
Job 3: Display screen question-answering
Given a cellular UI and an open-ended query asking for info relating to the UI, the mannequin ought to present the right reply. We concentrate on factual questions, which require solutions based mostly on info introduced on the display screen.
 |
| Instance outcomes from the display screen QA experiment. The LLM considerably outperforms the off-the-shelf QA baseline mannequin. |
We report efficiency utilizing 4 metrics: Precise Matches (similar predicted reply to floor fact), Incorporates GT (reply absolutely containing floor fact), Sub-String of GT (reply is a sub-string of floor fact), and the Micro-F1 rating based mostly on shared phrases between the anticipated reply and floor fact throughout your complete dataset.
Our outcomes confirmed that LLMs can accurately reply UI-related questions, reminiscent of “what is the headline?”. The LLM carried out considerably higher than baseline QA mannequin DistillBERT, reaching a 66.7% absolutely appropriate reply price. Notably, the 0-shot LLM achieved an actual match rating of 30.7%, indicating the mannequin’s intrinsic query answering functionality.
| Fashions | Precise Matches | Incorporates GT | Sub-String of GT | Micro-F1 | ||||||||||
| 0-shot LLM | 30.7% | 6.5% | 5.6% | 31.2% | ||||||||||
| 1-shot LLM | 65.8% | 10.0% | 7.8% | 62.9% | ||||||||||
| 2-shot LLM | 66.7% | 12.6% | 5.2% | 64.8% | ||||||||||
| DistillBERT | 36.0% | 8.5% | 9.9% | 37.2% |
Job 4: Mapping instruction to UI motion
Given a cellular UI display screen and pure language instruction to manage the UI, the mannequin must predict the ID of the item to carry out the instructed motion. For instance, when instructed with “Open Gmail,” the mannequin ought to accurately determine the Gmail icon on the house display screen. This job is beneficial for controlling cellular apps utilizing language enter reminiscent of voice entry. We launched this benchmark job beforehand.
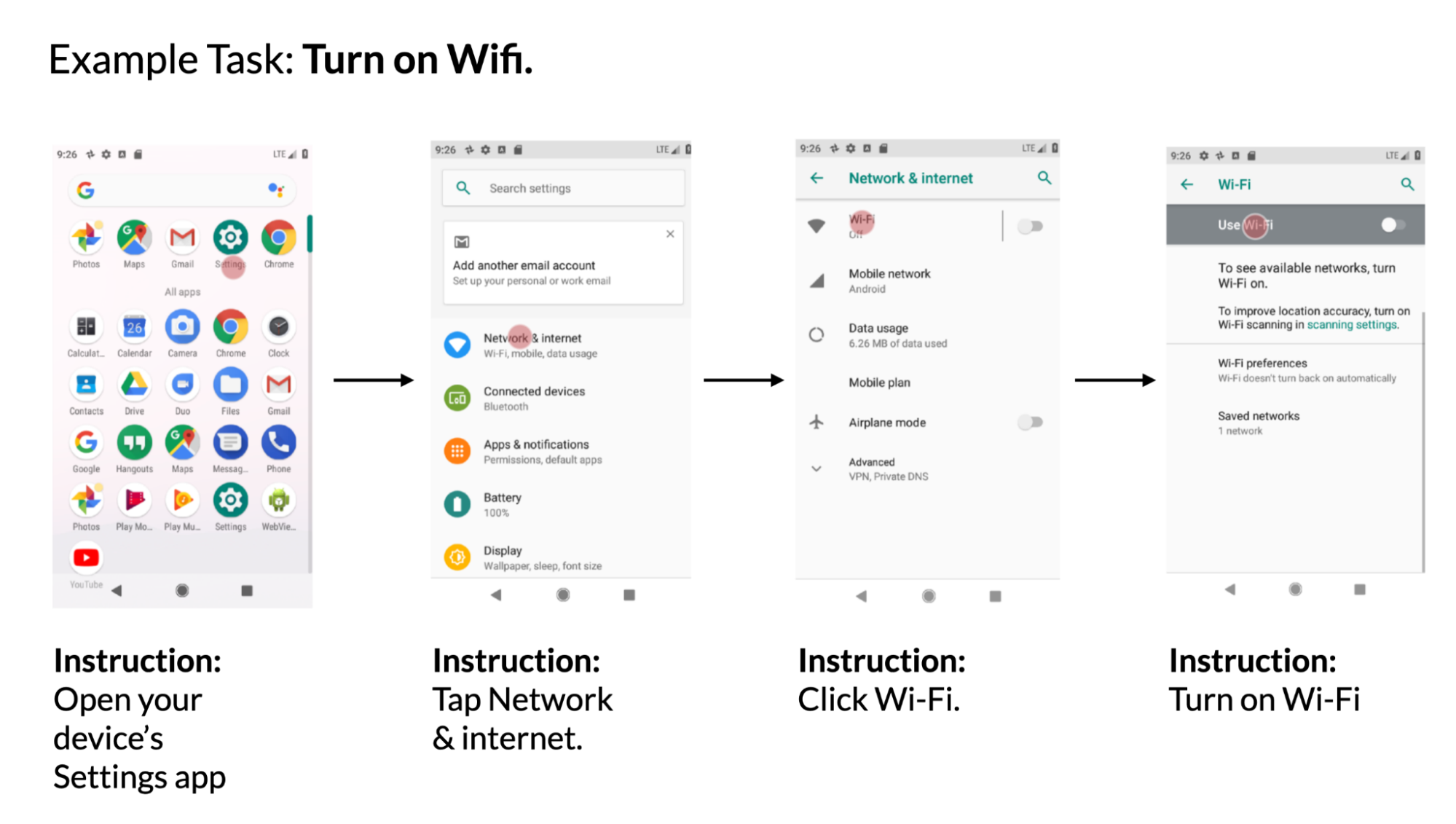 |
| Instance utilizing knowledge from the PixelHelp dataset. The dataset accommodates interplay traces for widespread UI duties reminiscent of turning on wifi. Every hint accommodates a number of steps and corresponding directions. |
We assessed the efficiency of our method utilizing the Partial and Full metrics from the Seq2Act paper. Partial refers back to the proportion of accurately predicted particular person steps, whereas Full measures the portion of precisely predicted complete interplay traces. Though our LLM-based technique didn’t surpass the benchmark skilled on huge datasets, it nonetheless achieved outstanding efficiency with simply two prompted knowledge examples.
| Fashions | Partial | Full | ||||||
| 0-shot LLM | 1.29 | 0.00 | ||||||
| 1-shot LLM (cross-app) | 74.69 | 31.67 | ||||||
| 2-shot LLM (cross-app) | 75.28 | 34.44 | ||||||
| 1-shot LLM (in-app) | 78.35 | 40.00 | ||||||
| 2-shot LLM (in-app) | 80.36 | 45.00 | ||||||
| Seq2Act | 89.21 | 70.59 |
Takeaways and conclusion
Our examine reveals that prototyping novel language interactions on cellular UIs may be as simple as designing a knowledge exemplar. In consequence, an interplay designer can quickly create functioning mock-ups to check new concepts with finish customers. Furthermore, builders and researchers can discover completely different prospects of a goal job earlier than investing vital efforts into growing new datasets and fashions.
We investigated the feasibility of prompting LLMs to allow numerous conversational interactions on cellular UIs. We proposed a set of prompting methods for adapting LLMs to cellular UIs. We carried out intensive experiments with the 4 essential modeling duties to guage the effectiveness of our method. The outcomes confirmed that in comparison with conventional machine studying pipelines that consist of pricy knowledge assortment and mannequin coaching, one may quickly understand novel language-based interactions utilizing LLMs whereas reaching aggressive efficiency.
Acknowledgements
We thank our paper co-author Gang Li, and respect the discussions and suggestions from our colleagues Chin-Yi Cheng, Tao Li, Yu Hsiao, Michael Terry and Minsuk Chang. Particular because of Muqthar Mohammad and Ashwin Kakarla for his or her invaluable help in coordinating knowledge assortment. We thank John Guilyard for serving to create animations and graphics within the weblog.