The big technological leap that machine studying fashions have proven in the previous couple of months is getting everybody enthusiastic about the way forward for AI — but additionally nervous about its uncomfortable penalties. After text-to-image instruments from Stability AI and OpenAI turned the discuss of the city, ChatGPT’s potential to carry clever conversations is the brand new obsession in sectors throughout the board.
In China, the place the tech group has at all times watched progress within the West carefully, entrepreneurs, researchers, and traders are in search of methods to make their dent within the generative AI house. Tech corporations are devising instruments constructed on open supply fashions to draw client and enterprise clients. People are cashing in on AI-generated content material. Regulators have responded shortly to outline how textual content, picture, and video synthesis must be used. In the meantime, U.S. tech sanctions are elevating considerations about China’s potential to maintain up with AI development.
As generative AI takes the world by storm in the direction of the tip of 2022, let’s check out how this explosive expertise is shaking out in China.
Chinese language flavors
Due to viral artwork creation platforms like Steady Diffusion and DALL-E 2, generative AI is out of the blue on everybody’s lips. Midway internationally, Chinese language tech giants have additionally captivated the general public with their equal merchandise, including a twist to go well with the nation’s tastes and political local weather.
Baidu, which made its identify in search engines like google and has lately been stepping up its recreation in autonomous driving, operates ERNIE-ViLG, a 10-billion parameter mannequin educated on an information set of 145 million Chinese language image-text pairs. How does it honest in opposition to its American counterpart? Beneath are the outcomes from the immediate “children consuming shumai in New York Chinatown” given to Steady Diffusion, versus the identical immediate in Chinese language (纽约唐人街小孩吃烧卖) for ERNIE-ViLG.
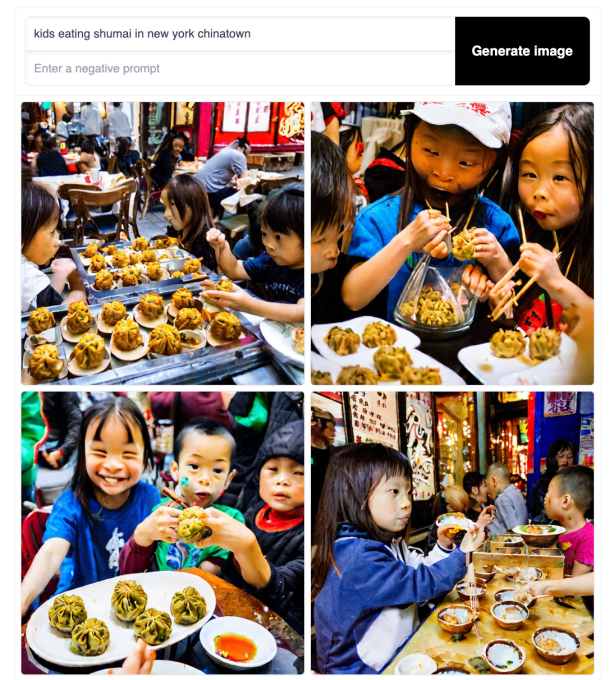
Steady Diffusion
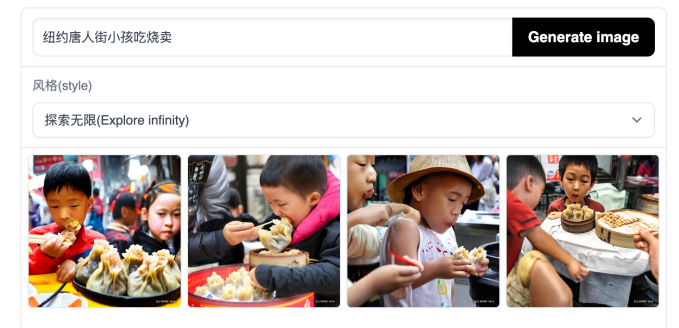
ERNIE-ViLG
As somebody who grew up consuming dim sum in China and Chinatowns, I’d say the outcomes are a tie. Neither acquired the appropriate shumai, which, within the dim sum context, is a kind of succulent, shrimp and pork dumpling in a half-open yellow wrapping. Whereas Steady Diffusion nails the environment of a Chinatown dim sum eatery, its shumai is off (however I see the place the machine goes). And whereas ERNIE-ViLG does generate a sort of shumai, it’s a range extra generally seen in japanese China fairly than the Cantonese model.
The short check displays the problem in capturing cultural nuances when the info units used are inherently biased — assuming Steady Diffusion would have extra knowledge on the Chinese language diaspora and ERNIE-ViLG in all probability is educated on a higher number of shumai pictures which can be rarer exterior China.
One other Chinese language device that has made noise is Tencent’s Totally different Dimension Me, which may flip images of individuals into anime characters. The AI generator reveals its personal bias. Meant for Chinese language customers, it took off unexpectedly in different anime-loving areas like South America. However customers quickly realized the platform did not establish black and plus-size people, teams which can be noticeably lacking in Japanese anime, resulting in offensive AI-generated outcomes.
Apart from ERNIE-ViLG, one other large-scale Chinese language text-to-image mannequin is Taiyi, a brainchild of IDEA, a analysis lab led by famend laptop scientist Harry Shum, who co-founded Microsoft’s largest analysis department exterior the U.S., Microsoft Analysis Asia. The open supply AI mannequin is educated on 20 million filtered Chinese language image-text pairs and has one billion parameters.
Not like Baidu and different profit-driven tech corporations, IDEA is one in every of a handful of establishments backed by native governments lately to work on cutting-edge applied sciences. Meaning the middle in all probability enjoys extra analysis freedom with out the stress to drive industrial success. Primarily based within the tech hub of Shenzhen and supported by one in every of China’s wealthiest cities, it’s an up-and-coming outfit price watching.
Guidelines of AI
China’s generative AI instruments aren’t simply characterised by the home knowledge they be taught from; they’re additionally formed by native legal guidelines. As MIT Expertise Assessment identified, Baidu’s text-to-image mannequin filters out politically delicate key phrases. That’s anticipated, given censorship has lengthy been a common apply on the Chinese language web.
What’s extra important to the way forward for the fledgling subject is the brand new set of regulatory measures focusing on what the federal government dubs “deep synthesis tech”, which denotes “expertise that makes use of deep studying, digital actuality, and different synthesis algorithms to generate textual content, pictures, audio, video, and digital scenes.”As with different forms of web providers in China, from video games to social media, customers are requested to confirm their names earlier than utilizing generative AI apps. The truth that prompts may be traced to at least one’s actual id inevitably has a restrictive affect on consumer habits.
However on the intense facet, these guidelines may result in extra accountable use of generative AI, which is already being abused elsewhere to churn out NSFW and sexist content material. The Chinese language regulation, for instance, explicitly bans folks from producing and spreading AI-created faux information. How that will probably be carried out, although, lies with the service suppliers.
“It’s attention-grabbing that China is on the forefront of attempting to manage [generative AI] as a rustic,” stated Yoav Shoham, founding father of AI21 Labs, an Israel-based OpenAI rival, in an interview. “There are numerous corporations which can be placing limits to AI… Each nation I do know of has efforts to manage AI or to someway ensure that the authorized system, or the social system, is maintaining with the expertise, particularly about regulating the automated technology of content material.”
However there’s no consensus as to how the fast-changing subject must be ruled, but. “I believe it’s an space we’re all studying collectively,” Shoham admitted. “It needs to be a collaborative effort. It has to contain technologists who really perceive the expertise and what it does and what it doesn’t do, the general public sector, social scientists, and people who find themselves impacted by the expertise in addition to the federal government, together with the kind of industrial and authorized side of the regulation.”
Monetizing AI
As artists fret over being changed by highly effective AI, many in China are leveraging machine studying algorithms to earn money in a plethora of the way. They aren’t from probably the most tech-savvy crowd. Relatively, they’re opportunists or stay-home mums in search of an additional supply of earnings. They notice that by enhancing their prompts, they will trick AI into making inventive emojis or beautiful wallpapers, which they will publish on social media to drive advert revenues or instantly cost for downloads. The actually expert ones are additionally promoting their prompts to others who need to be a part of the money-making recreation — and even practice them for a payment.
Others in China are utilizing AI of their formal jobs like the remainder of the world. Mild fiction writers, as an example, can cheaply churn out illustrations for his or her works, a style that’s shorter than novels and sometimes options illustrations. An intriguing use case that may doubtlessly disrupt realms of producing is utilizing AI to design T-shirts, press-on nails, and prints for different client items. By producing giant batches of prototypes shortly, producers save on design prices and shorten their manufacturing cycle.
It’s too early to know the way in another way generative AI is creating in China and the West. However entrepreneurs have made selections primarily based on their early commentary. Just a few founders advised me that companies and professionals are usually blissful to pay for AI as a result of they see a direct return on funding, so startups are desirous to carve out business use instances. One intelligent software got here from Sequoia China-backed Surreal (later renamed to Movio) and Hillhouse-backed ZMO.ai, which found throughout the pandemic that e-commerce sellers have been struggling to search out overseas fashions as China saved its borders shut. The answer? The 2 corporations labored on algorithms that generated vogue fashions of all shapes, colours, and races.
However some entrepreneurs don’t imagine their AI-powered SaaS will see the kind of skyrocketing valuation and meteoric progress their Western counterparts, like Jasper and Stability AI, are having fun with. Over time, quite a few Chinese language startups have advised me they’ve the identical concern: China’s enterprise clients are usually much less keen to pay for SaaS than these in developed economies, which is why lots of them begin increasing abroad.
Competitors in China’s SaaS house can also be dog-eat-dog. “Within the U.S., you are able to do pretty properly by constructing product-led software program, which doesn’t depend on human providers to amass or retain customers. However in China, even in case you have an important product, your rival may steal your supply code in a single day and rent dozens of buyer assist employees, which don’t price that a lot, to outrace you,” stated a founding father of a Chinese language generative AI startup, requesting anonymity.
Shi Yi, founder and CEO of gross sales intelligence startup FlashCloud, agreed that Chinese language corporations typically prioritize short-term returns over long-term innovation. “In regard to expertise improvement, Chinese language tech corporations are usually extra centered on getting expert at purposes and producing fast cash,” he stated. One Shanghai-based investor, who declined to be named, stated he was “a bit dissatisfied that main breakthroughs in generative AI this yr are all occurring exterior China.”
Roadblocks forward
Even when Chinese language tech corporations need to spend money on coaching giant neural networks, they could lack the most effective instruments. In September, the U.S. authorities slapped China with export controls on high-end AI chips. Whereas many Chinese language AI startups are centered on the applying entrance and don’t want high-performance semiconductors that deal with seas of knowledge, for these doing fundamental analysis, utilizing much less highly effective chips means computing will take longer and price extra, stated an enterprise software program investor at a high Chinese language VC agency, requesting anonymity. The excellent news is, he argued, such sanctions are pushing China to spend money on superior applied sciences over the long term.
As an organization that payments itself as a pacesetter in China’s AI subject, Baidu believes the affect of U.S. chip sanction on its AI enterprise is “restricted” each within the brief and long run, stated the agency’s govt vp and head of AI Cloud Group, Dou Shen, on its Q3 earnings name. That’s as a result of “a big portion” of Baidu’s AI cloud enterprise “doesn’t rely an excessive amount of on the extremely superior chips.” And in instances the place it does want high-end chips, it has “already stocked sufficient in hand, really, to assist our enterprise within the close to time period.”
What in regards to the future? “After we have a look at it at a mid- to a longer-term, we even have our personal developed AI chip, so named Kunlun,” the chief stated confidently. “Through the use of our Kunlun chips [Inaudible] in giant language fashions, the effectivity to carry out textual content and picture recognition duties on our AI platform has been improved by 40% and the whole price has been diminished by 20% to 30%.”
Time will inform if Kunlun and different indigenous AI chips will give China an edge within the generative AI race.

