Almost a decade in the past, mini-brains shot onto the neuroscience scene with a hefty promise: understanding the growing mind and restoring injured brains.
Often called mind organoids, these tiny clumps of mind tissue—roughly the scale of a lentil—look nothing just like the three-pound organ piloting our lives. But underneath the floor, they behave eerily just like the mind of a human fetus. Their neurons spark with electrical exercise. They readily combine with—and subsequently management—muscle groups, no less than in a dish. Much like full-blown brains, they offer delivery to new neurons. Some even develop the six-layered construction of the human cortex—the wrinkly, outermost layer of the mind that helps thought, reasoning, judgment, speech, and maybe even consciousness.
But a crucial query haunts neuroscientists: can these Frankenstein bits of mind tissue truly restore an injured mind?
A examine printed in Cell Stem Cell this month concluded that they’ll. Utilizing mind organoids produced from human cells, a workforce led by Dr. Han-Chiao Isaac Chen on the College of Pennsylvania transplanted the mini-brains into grownup rats with substantial harm to their visible cortex—the realm that helps imaginative and prescient.
In simply three months, the mini-brains merged with the rats’ brains. When the workforce shone flashing lights for the animals, the organoids spiked with electrical exercise. In different phrases, the human mini-brain acquired indicators from the rats’ eyes.
It’s not simply random noise. Much like our visible cortex, a few of the mini-brain’s neurons regularly developed a desire for gentle shone at a specific orientation. Think about a black and white windmill blow toy as your eyes regulate to the completely different shifting stripes. It sounds easy, however the capacity of your eyes to regulate—dubbed “orientation choice”—is a classy stage of visible processing that’s crucial to how we understand the world.
The examine is without doubt one of the first to point out that mini-brain tissue can combine with an injured grownup host and carry out its supposed operate. In comparison with earlier makes an attempt at stem cell transplants, the factitious tissues may substitute an injured or degenerating piece of the mind sooner or later—however many caveats stay.
“Neural tissues have the potential to rebuild areas of the injured mind,” stated Chen. “We haven’t labored every little thing out, however this can be a very stable first step.”
A Mini-Mind’s Mini-Life
Mind organoids have had a hell of a journey. First engineered in 2014, they instantly captured the curiosity of neuroscientists as an unprecedented mannequin of the mind.
The quasi-brains are produced from a number of sources to imitate completely different areas of the mind. One fast use was to mix the expertise with iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells) to review neurodevelopmental issues, similar to schizophrenia or autism.
Right here, a affected person’s pores and skin cells are reworked again right into a stem-cell-like state, which might be additional grown right into a 3D tissue of their mind. As a result of the individual and the mini-brain share the identical genes, it’s attainable to partially duplicate the individual’s mind throughout growth—and doubtlessly search out new cures.
Since their delivery, mini-brains have now expanded in dimension, age, and class. One main leap was a constant blood provide. Our brains are intimately intertwined with blood vessels, feeding our neurons and neural networks with oxygen and vitamins to provide vitality. The breakthrough got here in 2017, when a number of groups confirmed that transplanting human organoids into rodent brains triggered the host’s blood vessels to combine and “feed” the structured mind tissue, permitting it to additional grow to be the intricate mind structure contained in the host. The research sparked a firestorm of debate throughout the area, with bioethicists and researchers alike questioning if human organoids may change a rodent’s notion or conduct.
Chen had a special, if more difficult thought. Most earlier research transplanted mini-brains into toddler rodents to nurture the organoids and ease their merger with the growing mind.
Grownup brains, in distinction, are much more ridged. Extremely intertwined neural circuits—together with their signaling and features—are already established. Even when injured, when the mind is prepared for restore, shoving in further bits of human organoid grafts like a Band-Support may assist damaged neural circuits—or intervene with established ones.
Chen’s new examine put the speculation to the take a look at.
An Sudden Merger
To start out, the workforce cultivated mind organoids with a renewable human stem cell line. Utilizing a beforehand validated chemical recipe, the cells have been coaxed into mini-brains that mimic the frontal components of the cortex (across the brow).
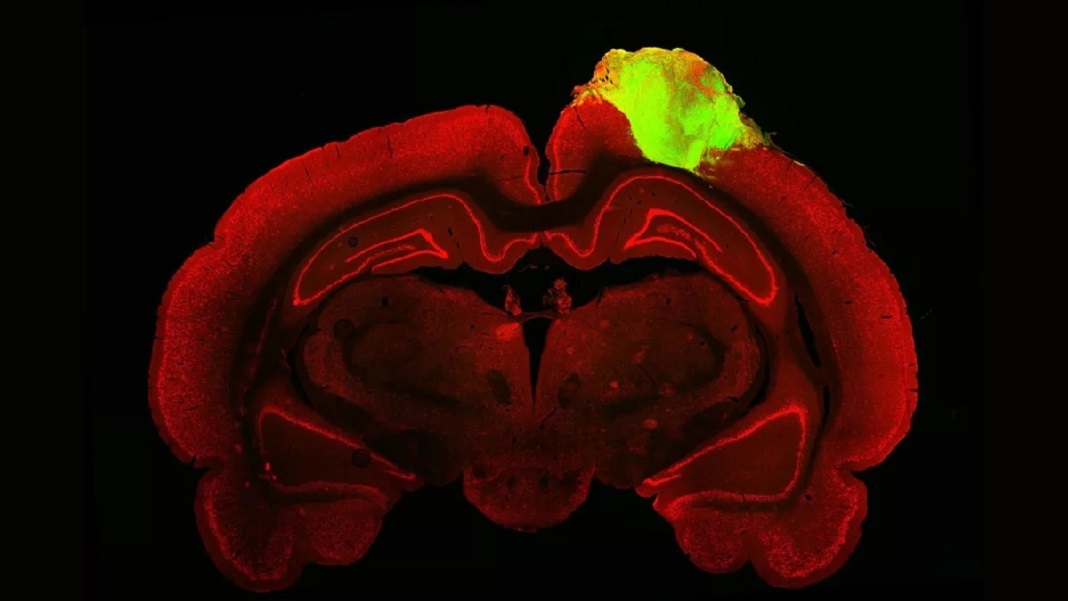
By day 80, the workforce noticed rudimentary cortical layers within the organoid, together with cells organized in a approach that resembled a growing mind. They then transplanted the organoids into the broken visible cortex of younger grownup rats.
Only one month after transplant, the host’s blood vessels merged with the human tissue, supplying it with much-needed oxygen and vitamins and permitting it to additional develop and mature. The mini-brains developed a myriad of various mind cells—not simply neurons, but additionally “supporting” mind cells similar to astrocytes and specialised immune cells dubbed microglia. The latter two are removed from dispensable: they’ve been implicated in mind getting old, Alzheimer’s illness, irritation, and cognition.
However can the transplanted human mini-brain operate inside a rat?
In a primary take a look at, the workforce used a preferred tracer to map the connections between the organoid and the animal’s eye. Much like a dye, the tracer is a virus that hops between neural connections—dubbed synapses—whereas carrying a protein that glows a brilliant inexperienced underneath a fluorescent microscope. Like a highlighted route on Google Maps, the sunshine stream clearly linked all the best way to the transplanted mini-brain, which means that its circuitry linked up, by a number of synapses, to the rats’ eyes.
Second query: may the transplanted tissue assist the rat “see”? In six out of eight animals, turning the lights on or off triggered {an electrical} response, suggesting the human neurons responded to outdoors stimulation. The sample of {the electrical} exercise resembled pure ones seen within the visible cortex, “suggesting that organoid neurons have a comparable potential for gentle responsiveness to visible cortex neuron,” the authors stated.
In one other take a look at, the grafts developed “choosy” neurons that most popular a particular orientation selectivity for gentle—a quirk embedded inside our capacity to understand the world. When examined with completely different gentle gratings that glinted from black to white, the grafted neurons’ general desire mimicked that of regular, wholesome neurons.
“We noticed {that a} good variety of neurons throughout the organoid responded to particular orientations of sunshine, which provides us proof that these organoid neurons have been in a position to not simply combine with the visible system, however they have been in a position to undertake very particular features of the visible cortex,” stated Chen.
Plug-and-Play Mind Tissue?
The examine reveals that mini-brains can quickly set up neural networks with the host’s mind, at a price far quicker than transplanting particular person stem cells. It suggests a strong use for the expertise: repairing broken brains at unprecedented pace.
Many questions stay. For one, the examine was carried out in rats dosed with immunosuppressants to inhibit rejection. The hope for mini-brains is that they’ll be cultured from a affected person’s personal cells, eliminating the necessity for immunosuppressant medicine—a hope but to be absolutely examined. One other drawback is how one can greatest match the mini-brain’s “age” to its host’s, in order to not disrupt the individual’s intrinsic neural indicators.
The workforce’s subsequent step is to assist different broken mind areas utilizing mini-brains, significantly harm as a result of degeneration from age or illness. Including non-invasive applied sciences, similar to neuromodulation or visible “rehabilitation” of the neurons, may additional assist the transplant combine into the host’s circuit and doubtlessly elevate their operate.
“Now, we wish to perceive how organoids could possibly be utilized in different areas of the cortex, not simply the visible cortex, and we wish to perceive the foundations that information how organoid neurons combine with the mind in order that we are able to higher management that course of and make it occur quicker,” stated Chen.
Picture Credit score: Jgamadze et al.