A key function of human intelligence is that people can study to carry out new duties by reasoning utilizing just a few examples. Scaling up language fashions has unlocked a variety of latest purposes and paradigms in machine studying, together with the power to carry out difficult reasoning duties by way of in-context studying. Language fashions, nevertheless, are nonetheless delicate to the best way that prompts are given, indicating that they aren’t reasoning in a sturdy method. As an illustration, language fashions usually require heavy immediate engineering or phrasing duties as directions, and so they exhibit sudden behaviors equivalent to efficiency on duties being unaffected even when proven incorrect labels.
In “Image tuning improves in-context studying in language fashions”, we suggest a easy fine-tuning process that we name image tuning, which may enhance in-context studying by emphasizing enter–label mappings. We experiment with image tuning throughout Flan-PaLM fashions and observe advantages throughout varied settings.
- Image tuning boosts efficiency on unseen in-context studying duties and is way more strong to underspecified prompts, equivalent to these with out directions or with out pure language labels.
- Image-tuned fashions are a lot stronger at algorithmic reasoning duties.
- Lastly, symbol-tuned fashions present giant enhancements in following flipped-labels introduced in-context, which means that they’re extra able to utilizing in-context info to override prior data.
Motivation
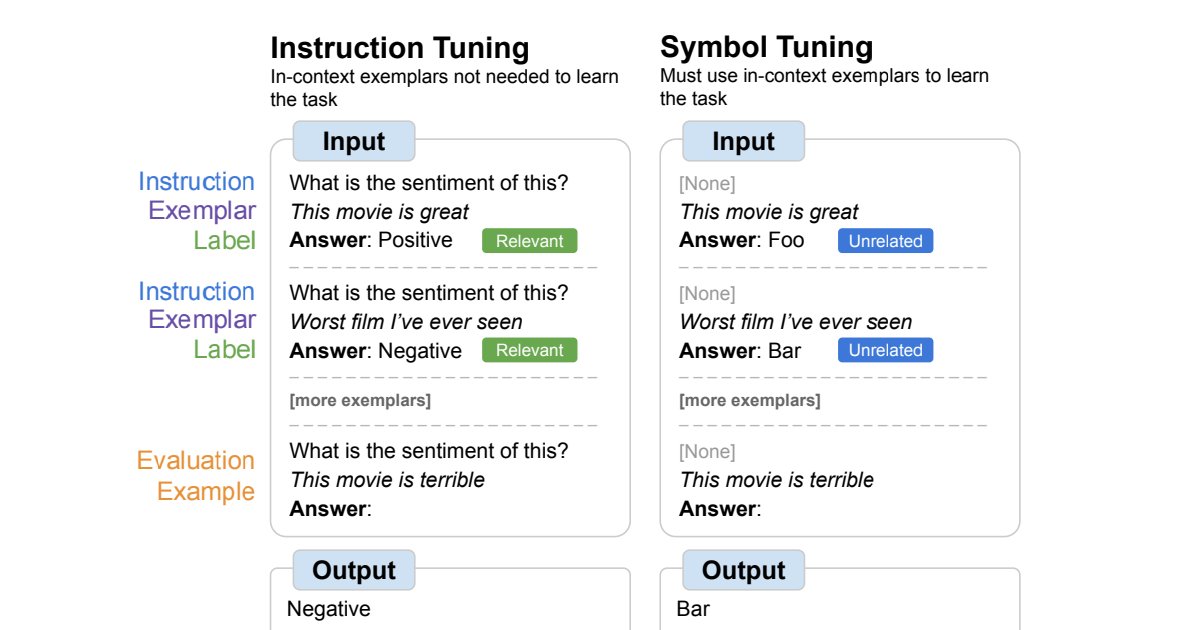
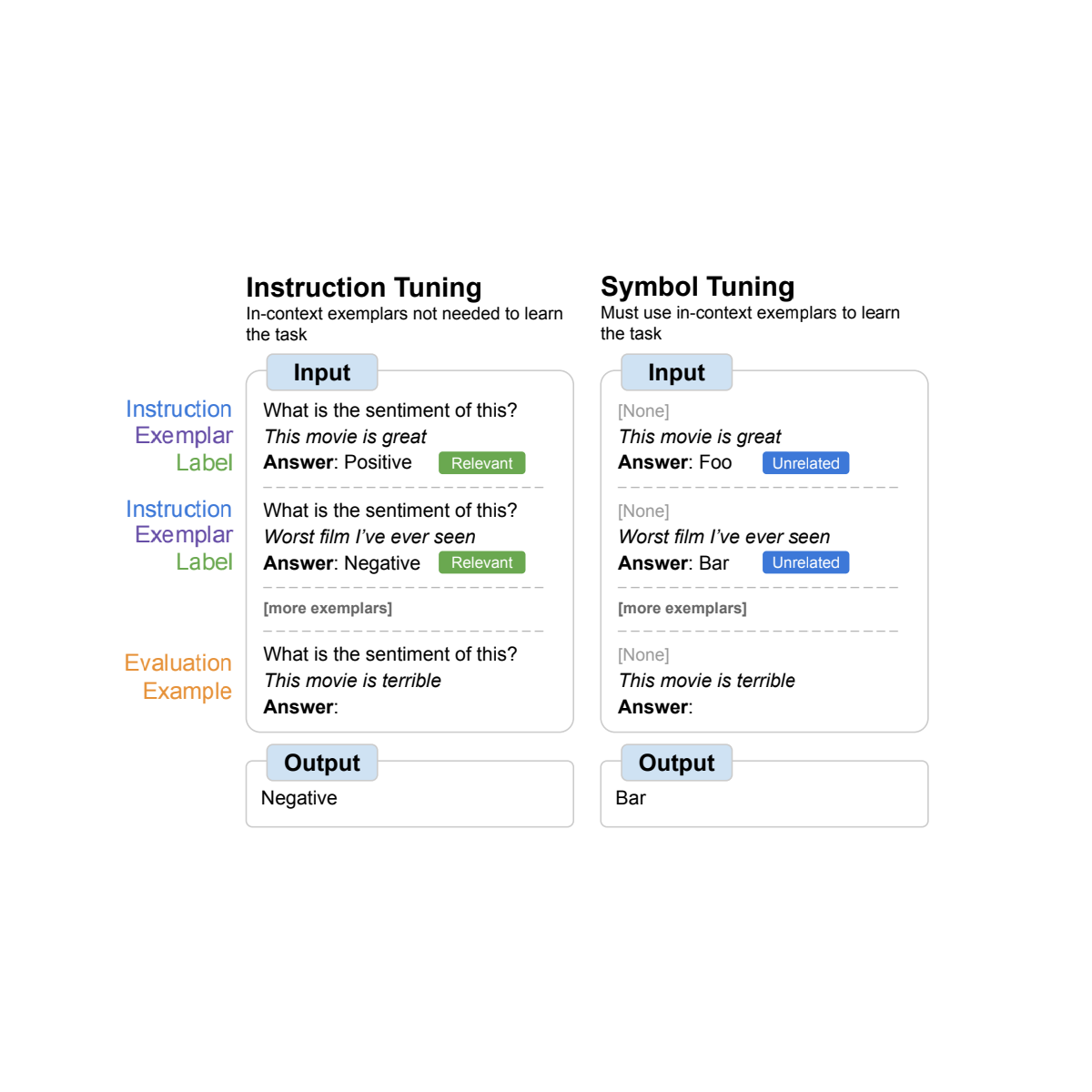
Instruction tuning is a typical fine-tuning methodology that has been proven to enhance efficiency and permit fashions to higher comply with in-context examples. One shortcoming, nevertheless, is that fashions will not be compelled to study to make use of the examples as a result of the duty is redundantly outlined within the analysis instance by way of directions and pure language labels. For instance, on the left within the determine above, though the examples can assist the mannequin perceive the duty (sentiment evaluation), they aren’t strictly crucial because the mannequin might ignore the examples and simply learn the instruction that signifies what the duty is.
In image tuning, the mannequin is fine-tuned on examples the place the directions are eliminated and pure language labels are changed with semantically-unrelated labels (e.g., “Foo,” “Bar,” and so on.). On this setup, the duty is unclear with out wanting on the in-context examples. For instance, on the fitting within the determine above, a number of in-context examples could be wanted to determine the duty. As a result of image tuning teaches the mannequin to motive over the in-context examples, symbol-tuned fashions ought to have higher efficiency on duties that require reasoning between in-context examples and their labels.
 |
| Datasets and process varieties used for image tuning. |
Image-tuning process
We chosen 22 publicly-available pure language processing (NLP) datasets that we use for our symbol-tuning process. These duties have been broadly used prior to now, and we solely selected classification-type duties since our methodology requires discrete labels. We then remap labels to a random label from a set of ~30K arbitrary labels chosen from certainly one of three classes: integers, character combos, and phrases.
For our experiments, we image tune Flan-PaLM, the instruction-tuned variants of PaLM. We use three totally different sizes of Flan-PaLM fashions: Flan-PaLM-8B, Flan-PaLM-62B, and Flan-PaLM-540B. We additionally examined Flan-cont-PaLM-62B (Flan-PaLM-62B at 1.3T tokens as a substitute of 780B tokens), which we abbreviate as 62B-c.
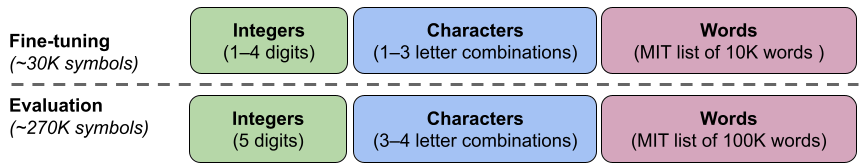 |
| We use a set of ∼300K arbitrary symbols from three classes (integers, character combos, and phrases). ∼30K symbols are used throughout tuning and the remaining are held out for analysis. |
Experimental setup
We wish to consider a mannequin’s capability to carry out unseen duties, so we can’t consider on duties utilized in image tuning (22 datasets) or used throughout instruction tuning (1.8K duties). Therefore, we select 11 NLP datasets that weren’t used throughout fine-tuning.
In-context studying
Within the symbol-tuning process, fashions should study to motive with in-context examples with the intention to efficiently carry out duties as a result of prompts are modified to make sure that duties can’t merely be discovered from related labels or directions. Image-tuned fashions ought to carry out higher in settings the place duties are unclear and require reasoning between in-context examples and their labels. To discover these settings, we outline 4 in-context studying settings that modify the quantity of reasoning required between inputs and labels with the intention to study the duty (primarily based on the provision of directions/related labels)
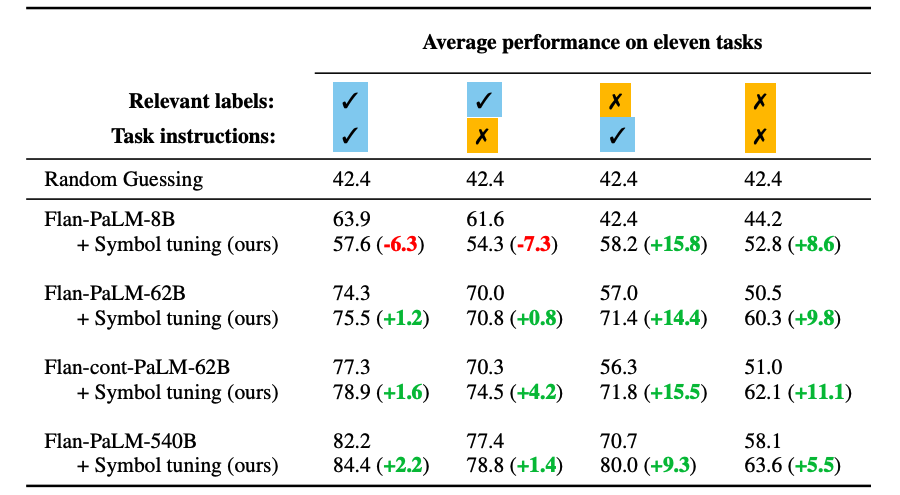
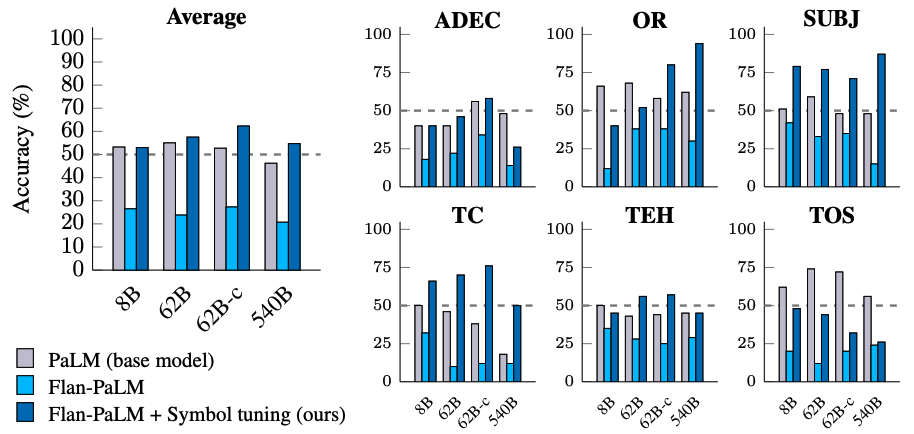
Image tuning improves efficiency throughout all settings for fashions 62B and bigger, with small enhancements in settings with related pure language labels (+0.8% to +4.2%) and substantial enhancements in settings with out related pure language labels (+5.5% to +15.5%). Strikingly, when related labels are unavailable, symbol-tuned Flan-PaLM-8B outperforms FlanPaLM-62B, and symbol-tuned Flan-PaLM-62B outperforms Flan-PaLM-540B. This efficiency distinction means that image tuning can enable a lot smaller fashions to carry out in addition to giant fashions on these duties (successfully saving ∼10X inference compute).
Algorithmic reasoning
We additionally experiment on algorithmic reasoning duties from BIG-Bench. There are two most important teams of duties: 1) Listing features — establish a change operate (e.g., take away the final component in a listing) between enter and output lists containing non-negative integers; and a couple of) easy turing ideas — motive with binary strings to study the idea that maps an enter to an output (e.g., swapping 0s and 1s in a string).
On the record operate and easy turing idea duties, image tuning ends in a median efficiency enchancment of 18.2% and 15.3%, respectively. Moreover, Flan-cont-PaLM-62B with image tuning outperforms Flan-PaLM-540B on the record operate duties on common, which is equal to a ∼10x discount in inference compute. These enhancements counsel that image tuning strengthens the mannequin’s capability to study in-context for unseen process varieties, as image tuning didn’t embrace any algorithmic knowledge.
 |
| Image-tuned fashions obtain increased efficiency on record operate duties and easy turing idea duties. (A–E): classes of record features duties. (F): easy turing ideas process. |
Flipped labels
Within the flipped-label experiment, labels of in-context and analysis examples are flipped, which means that prior data and input-label mappings disagree (e.g., sentences containing optimistic sentiment labeled as “adverse sentiment”), thereby permitting us to check whether or not fashions can override prior data. Earlier work has proven that whereas pre-trained fashions (with out instruction tuning) can, to some extent, comply with flipped labels introduced in-context, instruction tuning degraded this capability.
We see that there’s a related pattern throughout all mannequin sizes — symbol-tuned fashions are way more able to following flipped labels than instruction-tuned fashions. We discovered that after image tuning, Flan-PaLM-8B sees a median enchancment throughout all datasets of 26.5%, Flan-PaLM-62B sees an enchancment of 33.7%, and Flan-PaLM-540B sees an enchancment of 34.0%. Moreover, symbol-tuned fashions obtain related or higher than common efficiency as pre-training–solely fashions.
 |
| Image-tuned fashions are a lot better at following flipped labels introduced in-context than instruction-tuned fashions are. |
Conclusion
We introduced image tuning, a brand new methodology of tuning fashions on duties the place pure language labels are remapped to arbitrary symbols. Image tuning relies off of the instinct that when fashions can’t use directions or related labels to find out a introduced process, it should achieve this by as a substitute studying from in-context examples. We tuned 4 language fashions utilizing our symbol-tuning process, using a tuning combination of twenty-two datasets and roughly 30K arbitrary symbols as labels.
We first confirmed that image tuning improves efficiency on unseen in-context studying duties, particularly when prompts don’t comprise directions or related labels. We additionally discovered that symbol-tuned fashions had been a lot better at algorithmic reasoning duties, regardless of the dearth of numerical or algorithmic knowledge within the symbol-tuning process. Lastly, in an in-context studying setting the place inputs have flipped labels, image tuning (for some datasets) restores the power to comply with flipped labels that was misplaced throughout instruction tuning.
Future work
By image tuning, we purpose to extend the diploma to which fashions can look at and study from enter–label mappings throughout in-context studying. We hope that our outcomes encourage additional work in the direction of enhancing language fashions’ capability to motive over symbols introduced in-context.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this publish at the moment are a part of Google DeepMind. This work was performed by Jerry Wei, Le Hou, Andrew Lampinen, Xiangning Chen, Da Huang, Yi Tay, Xinyun Chen, Yifeng Lu, Denny Zhou, Tengyu Ma, and Quoc V. Le. We want to thank our colleagues at Google Analysis and Google DeepMind for his or her recommendation and useful discussions.