As scorching warmth grips giant swaths of the Earth, lots of people try to place the acute temperatures into context and asking: When was it ever this scorching earlier than?
Globally, 2023 has seen a few of the hottest days in fashionable measurements, however what about farther again, earlier than climate stations and satellites?
Some information retailers have reported that every day temperatures hit a 100,000-year excessive.
As a paleoclimate scientist who research temperatures of the previous, I see the place this declare comes from, however I cringe on the inexact headlines. Whereas this declare might be appropriate, there aren’t any detailed temperature information extending again 100,000 years, so we don’t know for positive.
Right here’s what we will confidently say about when Earth was final this scorching.
This Is a New Local weather State
Scientists concluded just a few years in the past that Earth had entered a brand new local weather state not seen in additional than 100,000 years. As fellow local weather scientist Nick McKay and I lately mentioned in a scientific journal article, that conclusion was a part of a local weather evaluation report revealed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC) in 2021.
Earth was already greater than 1 diploma Celsius (1.8 Fahrenheit) hotter than preindustrial instances, and the degrees of greenhouse gases within the ambiance had been excessive sufficient to guarantee temperatures would keep elevated for a very long time.
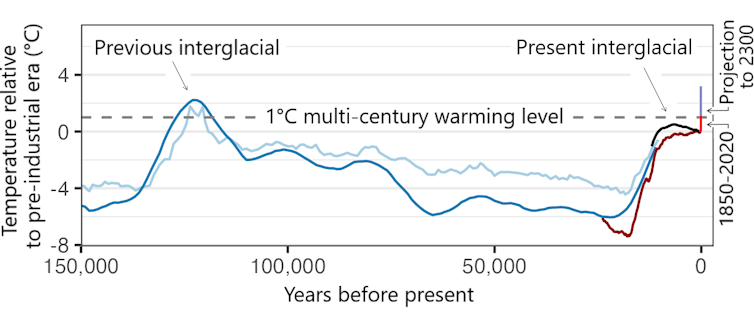
Even beneath probably the most optimistic situations of the long run—during which people cease burning fossil fuels and cut back different greenhouse gasoline emissions—common world temperature will very probably stay no less than one diploma Celsius (1 C) above preindustrial temperatures, and presumably a lot increased, for a number of centuries.
This new local weather state, characterised by a multi-century world warming degree of 1 C and better, may be reliably in contrast with temperature reconstructions from the very distant previous.
How We Estimate Previous Temperature
To reconstruct temperatures from instances earlier than thermometers, paleoclimate scientists depend on data saved in a number of pure archives.
Essentially the most widespread archive going again many 1000’s of years is on the backside of lakes and oceans, the place an assortment of organic, chemical, and bodily proof presents clues to the previous. These supplies construct up repeatedly over time and may be analyzed by extracting a sediment core from the lake mattress or ocean ground.
These sediment-based information are wealthy sources of knowledge which have enabled paleoclimate scientists to reconstruct previous world temperatures, however they’ve necessary limitations.
For one, backside currents and burrowing organisms can combine the sediment, blurring any short-term temperature spikes. For one more, the timeline for every document isn’t recognized exactly, so when a number of information are averaged collectively to estimate previous world temperature, fine-scale fluctuations may be canceled out.
Due to this, paleoclimate scientists are reluctant to check the long-term document of previous temperature with short-term extremes.
Trying Again Tens of 1000’s of Years
Earth’s common world temperature has fluctuated between glacial and interglacial situations in cycles lasting round 100,000 years, pushed largely by gradual and predictable modifications in Earth’s orbit with attendant modifications in greenhouse gasoline concentrations within the ambiance. We’re at present in an interglacial interval that started round 12,000 years in the past as ice sheets retreated and greenhouse gases rose.
that 12,000-year interglacial interval, world temperature averaged over a number of centuries might need peaked roughly round 6,000 years in the past, however in all probability didn’t exceed the 1 C world warming degree at that time, in accordance with the IPCC report. One other examine discovered that world common temperatures continued to extend throughout the interglacial interval. It is a subject of energetic analysis.
Which means we have now to look farther again to discover a time that may have been as heat as at this time.
The final glacial episode lasted practically 100,000 years. There isn’t any proof that long-term world temperatures reached the preindustrial baseline anytime throughout that interval.
If we glance even farther again, to the earlier interglacial interval, which peaked round 125,000 years in the past, we do discover proof of hotter temperatures. The proof suggests the long-term common temperature was in all probability not more than 1.5 C (2.7 F) above preindustrial ranges—not way more than the present world warming degree.
Now What?
With out speedy and sustained reductions in greenhouse gasoline emissions, the Earth is at present heading in the right direction to achieve temperatures of roughly 3 C (5.4 F) above preindustrial ranges by the top of the century, and presumably fairly a bit increased.
At that time, we would want to look again hundreds of thousands of years to discover a local weather state with temperatures as scorching. That may take us again to the earlier geologic epoch, the Pliocene, when the Earth’s local weather was a distant relative of the one which sustained the rise of agriculture and civilization.![]()
This text is republished from The Dialog beneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.
Picture Credit score: dannymoore1973

