Visible query answering (VQA) is a machine studying job that requires a mannequin to reply a query about a picture or a set of photos. Standard VQA approaches want a considerable amount of labeled coaching information consisting of 1000’s of human-annotated question-answer pairs related to photos. In recent times, advances in large-scale pre-training have led to the event of VQA strategies that carry out nicely with fewer than fifty coaching examples (few-shot) and with none human-annotated VQA coaching information (zero-shot). Nevertheless, there’s nonetheless a big efficiency hole between these strategies and state-of-the-art totally supervised VQA strategies, reminiscent of MaMMUT and VinVL. Particularly, few-shot strategies battle with spatial reasoning, counting, and multi-hop reasoning. Moreover, few-shot strategies have usually been restricted to answering questions on single photos.
To enhance accuracy on VQA examples that contain advanced reasoning, in “Modular Visible Query Answering by way of Code Technology,” to seem at ACL 2023, we introduce CodeVQA, a framework that solutions visible questions utilizing program synthesis. Particularly, when given a query about a picture or set of photos, CodeVQA generates a Python program (code) with easy visible capabilities that enable it to course of photos, and executes this program to find out the reply. We display that within the few-shot setting, CodeVQA outperforms prior work by roughly 3% on the COVR dataset and a couple of% on the GQA dataset.
CodeVQA
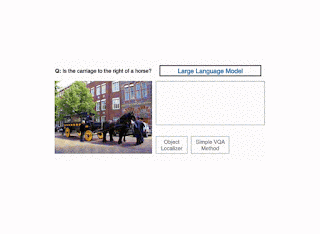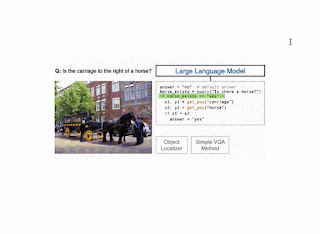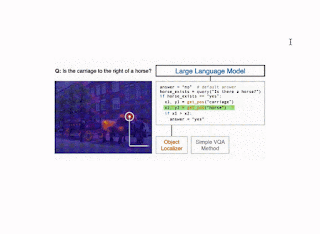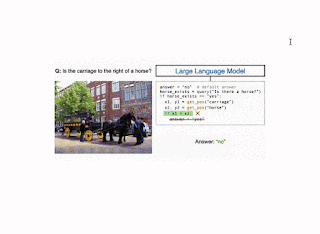
The CodeVQA strategy makes use of a code-writing giant language mannequin (LLM), reminiscent of PALM, to generate Python packages (code). We information the LLM to appropriately use visible capabilities by crafting a immediate consisting of an outline of those capabilities and fewer than fifteen “in-context” examples of visible questions paired with the related Python code for them. To pick these examples, we compute embeddings for the enter query and of the entire questions for which we’ve got annotated packages (a randomly chosen set of fifty). Then, we choose questions which have the best similarity to the enter and use them as in-context examples. Given the immediate and query that we wish to reply, the LLM generates a Python program representing that query.
We instantiate the CodeVQA framework utilizing three visible capabilities: (1) question, (2) get_pos, and (3) find_matching_image.
Question, which solutions a query a couple of single picture, is carried out utilizing the few-shot Plug-and-Play VQA (PnP-VQA) methodology. PnP-VQA generates captions utilizing BLIP — an image-captioning transformer pre-trained on thousands and thousands of image-caption pairs — and feeds these right into a LLM that outputs the solutions to the query.Get_pos, which is an object localizer that takes an outline of an object as enter and returns its place within the picture, is carried out utilizing GradCAM. Particularly, the outline and the picture are handed via the BLIP joint text-image encoder, which predicts an image-text matching rating. GradCAM takes the gradient of this rating with respect to the picture options to search out the area most related to the textual content.Find_matching_image, which is utilized in multi-image questions to search out the picture that greatest matches a given enter phrase, is carried out by utilizing BLIP textual content and picture encoders to compute a textual content embedding for the phrase and a picture embedding for every picture. Then the dot merchandise of the textual content embedding with every picture embedding characterize the relevance of every picture to the phrase, and we decide the picture that maximizes this relevance.
The three capabilities may be carried out utilizing fashions that require little or no annotation (e.g., textual content and image-text pairs collected from the online and a small variety of VQA examples). Moreover, the CodeVQA framework may be simply generalized past these capabilities to others {that a} consumer would possibly implement (e.g., object detection, picture segmentation, or information base retrieval).
Outcomes
The CodeVQA framework appropriately generates and executes Python packages not just for single-image questions, but in addition for multi-image questions. For instance, if given two photos, every exhibiting two pandas, a query one would possibly ask is, “Is it true that there are 4 pandas?” On this case, the LLM converts the counting query in regards to the pair of photos right into a program through which an object rely is obtained for every picture (utilizing the question perform). Then the counts for each photos are added to compute a complete rely, which is then in comparison with the quantity within the unique query to yield a sure or no reply.
 |
We consider CodeVQA on three visible reasoning datasets: GQA (single-image), COVR (multi-image), and NLVR2 (multi-image). For GQA, we offer 12 in-context examples to every methodology, and for COVR and NLVR2, we offer six in-context examples to every methodology. The desk beneath reveals that CodeVQA improves constantly over the baseline few-shot VQA methodology on all three datasets.
| Methodology | GQA | COVR | NLVR2 | ||||||||
| Few-shot PnP-VQA | 46.56 | 49.06 | 63.37 | ||||||||
| CodeVQA | 49.03 | 54.11 | 64.04 |
| Outcomes on the GQA, COVR, and NLVR2 datasets, exhibiting that CodeVQA constantly improves over few-shot PnP-VQA. The metric is exact-match accuracy, i.e., the share of examples through which the anticipated reply precisely matches the ground-truth reply. |
We discover that in GQA, CodeVQA’s accuracy is roughly 30% increased than the baseline on spatial reasoning questions, 4% increased on “and” questions, and three% increased on “or” questions. The third class contains multi-hop questions reminiscent of “Are there salt shakers or skateboards within the image?”, for which the generated program is proven beneath.
img = open_image("Image13.jpg")
salt_shakers_exist = question(img, "Are there any salt shakers?")
skateboards_exist = question(img, "Are there any skateboards?")
if salt_shakers_exist == "sure" or skateboards_exist == "sure":
reply = "sure"
else:
reply = "no"
In COVR, we discover that CodeVQA’s achieve over the baseline is increased when the variety of enter photos is bigger, as proven within the desk beneath. This development signifies that breaking the issue down into single-image questions is helpful.
| Variety of photos | |||||||||||
| Methodology | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||||
| Few-shot PnP-VQA | 91.7 | 51.5 | 48.3 | 47.0 | 46.9 | ||||||
| CodeVQA | 75.0 | 53.3 | 48.7 | 53.2 | 53.4 | ||||||
Conclusion
We current CodeVQA, a framework for few-shot visible query answering that depends on code era to carry out multi-step visible reasoning. Thrilling instructions for future work embrace increasing the set of modules used and creating an analogous framework for visible duties past VQA. We notice that care needs to be taken when contemplating whether or not to deploy a system reminiscent of CodeVQA, since vision-language fashions like those utilized in our visible capabilities have been proven to exhibit social biases. On the similar time, in comparison with monolithic fashions, CodeVQA gives further interpretability (via the Python program) and controllability (by modifying the prompts or visible capabilities), that are helpful in manufacturing programs.
Acknowledgements
This analysis was a collaboration between UC Berkeley’s Synthetic Intelligence Analysis lab (BAIR) and Google Analysis, and was performed by Sanjay Subramanian, Medhini Narasimhan, Kushal Khangaonkar, Kevin Yang, Arsha Nagrani, Cordelia Schmid, Andy Zeng, Trevor Darrell, and Dan Klein.


