Constructing fashions that resolve a various set of duties has grow to be a dominant paradigm within the domains of imaginative and prescient and language. In pure language processing, massive pre-trained fashions, equivalent to PaLM, GPT-3 and Gopher, have demonstrated outstanding zero-shot studying of recent language duties. Equally, in pc imaginative and prescient, fashions like CLIP and Flamingo have proven sturdy efficiency on zero-shot classification and object recognition. A pure subsequent step is to make use of such instruments to assemble brokers that may full completely different decision-making duties throughout many environments.
Nevertheless, coaching such brokers faces the inherent problem of environmental variety, since completely different environments function with distinct state motion areas (e.g., the joint area and steady controls in MuJoCo are essentially completely different from the picture area and discrete actions in Atari). This environmental variety hampers data sharing, studying, and generalization throughout duties and environments. Moreover, it’s tough to assemble reward features throughout environments, as completely different duties usually have completely different notions of success.
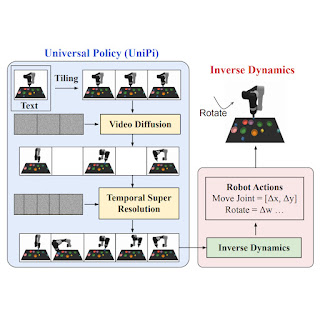
In “Studying Common Insurance policies through Textual content-Guided Video Era”, we suggest a Common Coverage (UniPi) that addresses environmental variety and reward specification challenges. UniPi leverages textual content for expressing activity descriptions and video (i.e., picture sequences) as a common interface for conveying motion and statement habits in numerous environments. Given an enter picture body paired with textual content describing a present objective (i.e., the subsequent high-level step), UniPi makes use of a novel video generator (trajectory planner) to generate video with snippets of what an agent’s trajectory ought to appear to be to attain that objective. The generated video is fed into an inverse dynamics mannequin that extracts underlying low-level management actions, that are then executed in simulation or by an actual robotic agent. We display that UniPi allows using language and video as a common management interface for generalizing to novel objectives and duties throughout various environments.
 |
| Video insurance policies generated by UniPi. |
UniPi implementation
To generate a legitimate and executable plan, a text-to-video mannequin should synthesize a constrained video plan beginning on the present noticed picture. We discovered it simpler to explicitly constrain a video synthesis mannequin throughout coaching (versus solely constraining movies at sampling time) by offering the primary body of every video as specific conditioning context.
At a excessive degree, UniPi has 4 main parts: 1) constant video technology with first-frame tiling, 2) hierarchical planning by means of temporal tremendous decision, 3) versatile habits synthesis, and 4) task-specific motion adaptation. We clarify the implementation and profit of every element intimately under.
Video technology by means of tiling
Current text-to-video fashions like Imagen sometimes generate movies the place the underlying surroundings state adjustments considerably all through the period. To assemble an correct trajectory planner, it’s important that the surroundings stays constant throughout all time factors. We implement surroundings consistency in conditional video synthesis by offering the noticed picture as extra context when denoising every body within the synthesized video. To realize context conditioning, UniPi immediately concatenates every intermediate body sampled from noise with the conditioned noticed picture throughout sampling steps, which serves as a powerful sign to take care of the underlying surroundings state throughout time.
 |
| Textual content-conditional video technology allows UniPi to coach normal function insurance policies on a variety of information sources (simulated, actual robots and YouTube). |
Hierarchical planning
When setting up plans in high-dimensional environments with very long time horizons, immediately producing a set of actions to achieve a objective state rapidly turns into intractable as a result of exponential development of the underlying search area because the plan will get longer. Planning strategies usually circumvent this situation by leveraging a pure hierarchy in planning. Particularly, planning strategies first assemble coarse plans (the intermediate key frames unfold out throughout time) working on low-dimensional states and actions, that are then refined into plans within the underlying state and motion areas.
Just like planning, our conditional video technology process reveals a pure temporal hierarchy. UniPi first generates movies at a rough degree by sparsely sampling movies (“abstractions”) of desired agent habits alongside the time axis. UniPi then refines the movies to signify legitimate habits within the surroundings by super-resolving movies throughout time. In the meantime, coarse-to-fine super-resolution additional improves consistency through interpolation between frames.
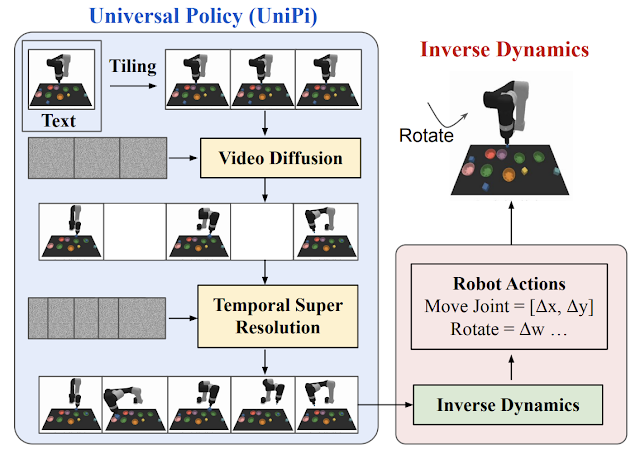 |
| Given an enter statement and textual content instruction, we plan a set of pictures representing agent habits. Photographs are transformed to actions utilizing an inverse dynamics mannequin. |
Versatile behavioral modulation
When planning a sequence of actions for a given sub-goal, one can readily incorporate exterior constraints to modulate a generated plan. Such test-time adaptability might be carried out by composing a probabilistic prior incorporating properties of the specified plan to specify desired constraints throughout the synthesized motion trajectory, which can be appropriate with UniPi. Particularly, the prior might be specified utilizing a discovered classifier on pictures to optimize a selected activity, or as a Dirac delta distribution on a selected picture to information a plan in direction of a selected set of states. To coach the text-conditioned video technology mannequin, we make the most of the video diffusion algorithm, the place pre-trained language options from the Textual content-To-Textual content Switch Transformer (T5) are encoded.
Activity-specific motion adaptation
Given a set of synthesized movies, we prepare a small task-specific inverse dynamics mannequin to translate frames right into a set of low-level management actions. That is unbiased from the planner and might be finished on a separate, smaller and doubtlessly suboptimal dataset generated by a simulator.
Given the enter body and textual content description of the present objective, the inverse dynamics mannequin synthesizes picture frames and generates a management motion sequence that predicts the corresponding future actions. An agent then executes inferred low-level management actions through closed-loop management.
Capabilities and analysis of UniPi
We measure the duty success charge on novel language-based objectives, and discover that UniPi generalizes nicely to each seen and novel combos of language prompts, in comparison with baselines equivalent to Transformer BC, Trajectory Transformer (TT), and Diffuser.
 |
| UniPi generalizes nicely to each seen and novel combos of language prompts in Place (e.g., “place X in Y”) and Relation (e.g., “place X to the left of Y”) duties. |
Under, we illustrate generated movies on unseen combos of objectives. UniPi is ready to synthesize a various set of behaviors that fulfill unseen language subgoals:
 |
| Generated movies for unseen language objectives at check time. |
Multi-environment switch
We measure the duty success charge of UniPi and baselines on novel duties not seen throughout coaching. UniPi once more outperforms the baselines by a big margin:
 |
| UniPi generalizes nicely to new environments when skilled on a set of various multi-task environments. |
Under, we illustrate generated movies on unseen duties. UniPi is additional capable of synthesize a various set of behaviors that fulfill unseen language duties:
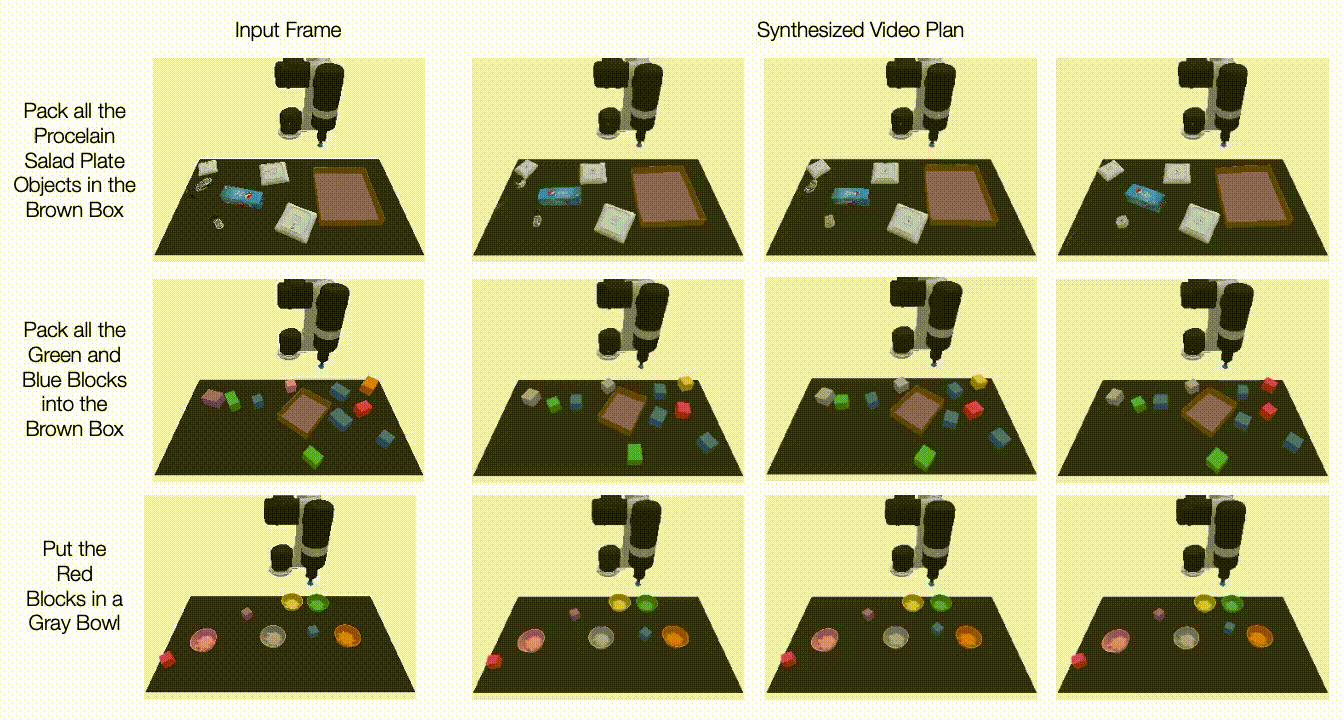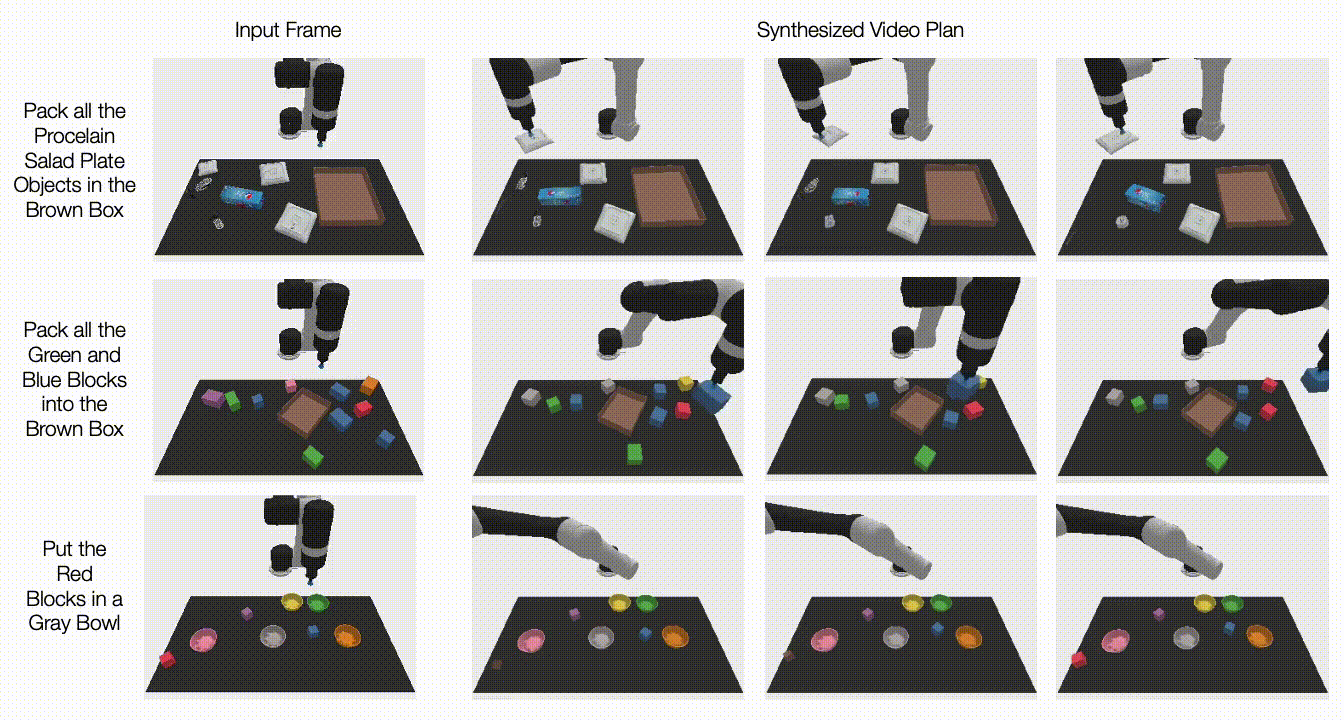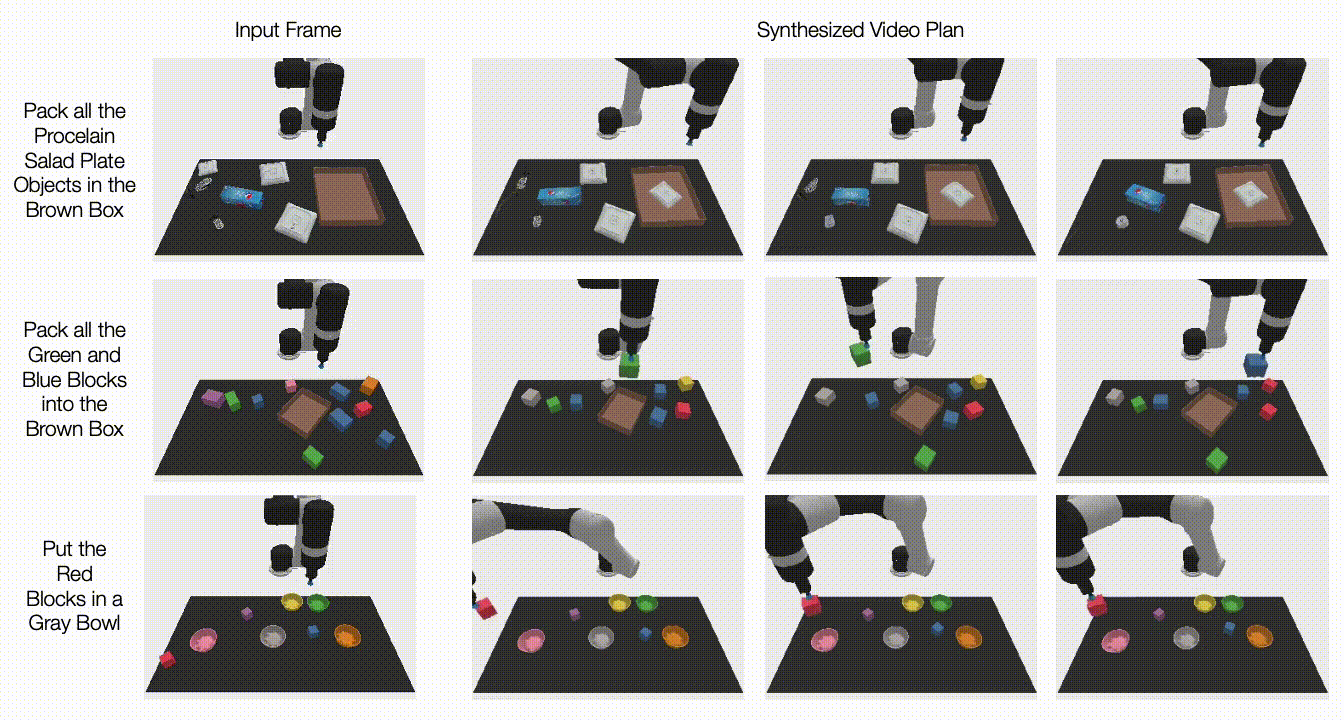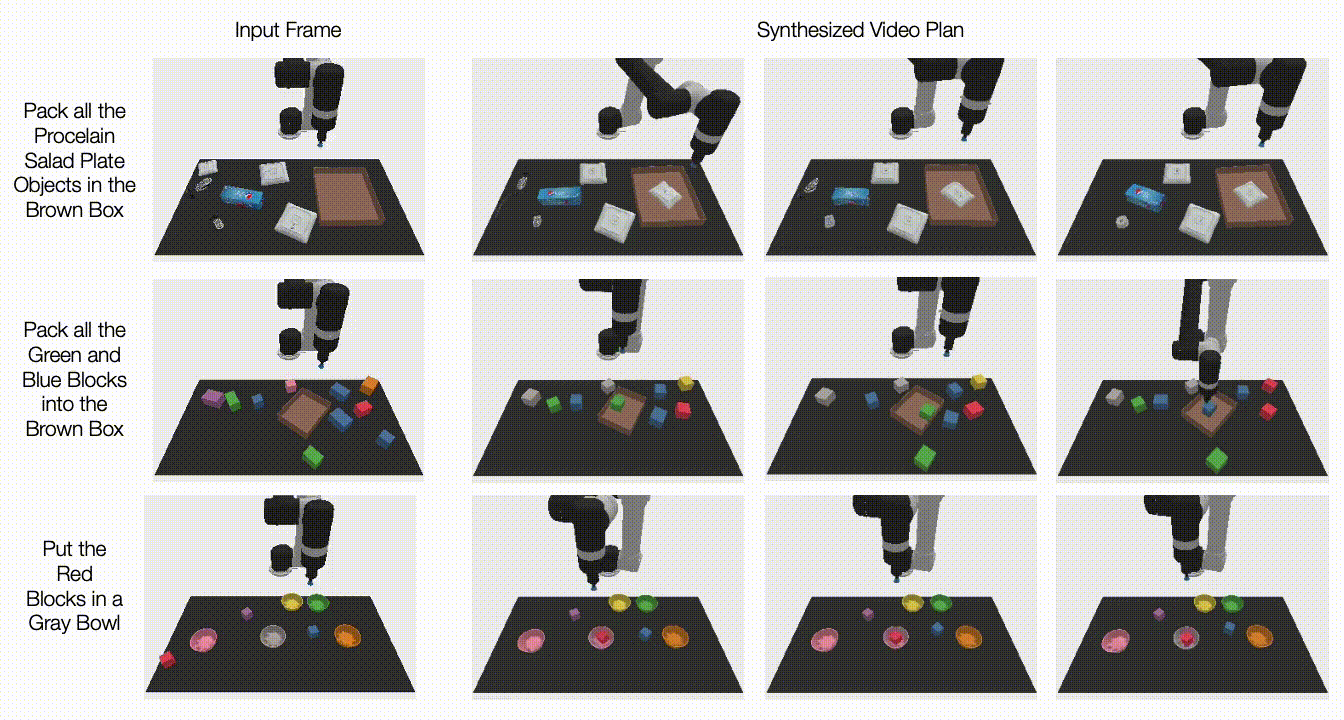 |
| Generated video plans on completely different new check duties within the multitask setting. |
Actual world switch
Under, we additional illustrate generated movies given language directions on unseen actual pictures. Our method is ready to synthesize a various set of various behaviors which fulfill language directions:
 |
Utilizing web pre-training allows UniPi to synthesize movies of duties not seen throughout coaching. In distinction, a mannequin skilled from scratch incorrectly generates plans of various duties:
 |
To judge the standard of movies generated by UniPi when pre-trained on non-robot knowledge, we use the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) and Fréchet Video Distance (FVD) metrics. We used Contrastive Language-Picture Pre-training scores (CLIPScores) to measure the language-image alignment. We display that pre-trained UniPi achieves considerably greater FID and FVD scores and a greater CLIPScore in comparison with UniPi with out pre-training, suggesting that pre-training on non-robot knowledge helps with producing plans for robots. We report the CLIPScore, FID, and VID scores for UniPi skilled on Bridge knowledge, with and with out pre-training:
| Mannequin (24×40) | CLIPScore ↑ | FID ↓ | FVD ↓ | ||||||||
| No pre-training | 24.43 ± 0.04 | 17.75 ± 0.56 | 288.02 ± 10.45 | ||||||||
| Pre-trained | 24.54 ± 0.03 | 14.54 ± 0.57 | 264.66 ± 13.64 |
| Utilizing current web knowledge improves video plan predictions below all metrics thought of. |
The way forward for large-scale generative fashions for choice making
The optimistic outcomes of UniPi level to the broader route of utilizing generative fashions and the wealth of information on the web as highly effective instruments to be taught general-purpose choice making programs. UniPi is just one step in direction of what generative fashions can carry to choice making. Different examples embrace utilizing generative basis fashions to offer photorealistic or linguistic simulators of the world during which synthetic brokers might be skilled indefinitely. Generative fashions as brokers can even be taught to work together with complicated environments such because the web, in order that a lot broader and extra complicated duties can ultimately be automated. We stay up for future analysis in making use of internet-scale basis fashions to multi-environment and multi-embodiment settings.
Acknowledgements
We’d wish to thank all remaining authors of the paper together with Bo Dai, Hanjun Dai, Ofir Nachum, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Dale Schuurmans, and Pieter Abbeel. We wish to thank George Tucker, Douglas Eck, and Vincent Vanhoucke for the suggestions on this put up and on the unique paper.


