The widespread availability of cell phones has enabled non-profits to ship important well being info to their beneficiaries in a well timed method. Whereas superior functions on smartphones enable for richer multimedia content material and two-way communication between beneficiaries and well being coaches, less complicated textual content and voice messaging providers will be efficient in disseminating info to giant communities, notably these which might be underserved with restricted entry to info and smartphones. ARMMAN1, one non-profit doing simply this, is predicated in India with the mission of enhancing maternal and youngster well being outcomes in underserved communities.
 |
| Overview of ARMMAN |
One of many packages run by them is mMitra, which employs automated voice messaging to ship well timed preventive care info to anticipating and new moms throughout being pregnant and till one yr after beginning. These messages are tailor-made based on the gestational age of the beneficiary. Common listenership to those messages has been proven to have a excessive correlation with improved behavioral and well being outcomes, similar to a 17% enhance in infants with tripled beginning weight at finish of yr and a 36% enhance in girls realizing the significance of taking iron tablets.
Nonetheless, a key problem ARMMAN confronted was that about 40% of ladies steadily stopped partaking with this system. Whereas it’s potential to mitigate this with stay service calls to girls to elucidate the benefit of listening to the messages, it’s infeasible to name all of the low listeners in this system due to restricted assist workers — this highlights the significance of successfully prioritizing who receives such service calls.
In “Area Research in Deploying Stressed Multi-Armed Bandits: Helping Non-Income in Bettering Maternal and Baby Well being”, printed in AAAI 2022, we describe an ML-based answer that makes use of historic information from the NGO to foretell which beneficiaries will profit most from service calls. We tackle the challenges that include a large-scale actual world deployment of such a system and present the usefulness of deploying this mannequin in an actual research involving over 23,000 individuals. The mannequin confirmed a rise in listenership of 30% in comparison with the present customary of care group.
Background
We mannequin this useful resource optimization downside utilizing stressed multi-armed bandits (RMABs), which have been effectively studied for utility to such issues in a myriad of domains, together with healthcare. An RMAB consists of n arms the place every arm (representing a beneficiary) is related to a two-state Markov determination course of (MDP). Every MDP is modeled as a two-state (good or dangerous state, the place the great state corresponds to excessive listenership within the earlier week), two-action (corresponding as to whether the beneficiary was chosen to obtain a service name or not) downside. Additional, every MDP has an related reward operate (i.e., the reward gathered at a given state and motion) and a transition operate indicating the likelihood of transferring from one state to the following underneath a given motion, underneath the Markov situation that the following state relies upon solely on the earlier state and the motion taken on that arm in that point step. The time period stressed signifies that each one arms can change state regardless of the motion.
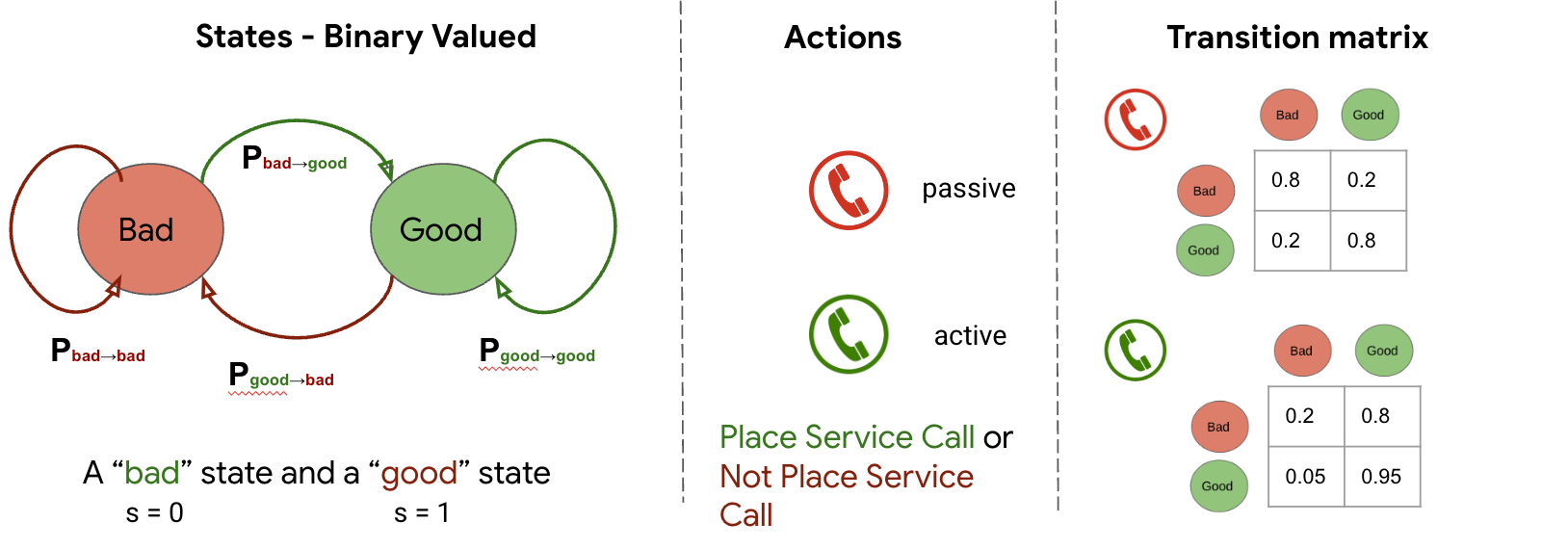 |
| State of a beneficiary could transition from good (excessive engagement) to dangerous (low engagement) with instance passive and lively transition chances proven within the transition matrix. |
Mannequin Improvement
Lastly, the RMAB downside is modeled such that at any time step, given n complete arms, which okay arms needs to be acted on (i.e., chosen to obtain a service name), to maximise reward (engagement with this system).
The likelihood of transitioning from one state to a different with (lively likelihood) or with out (passive likelihood) receiving a service name are due to this fact the underlying mannequin parameters which might be important to fixing the above optimization. To estimate these parameters, we use the demographic information of the beneficiaries collected at time of enrolment by the NGO, similar to age, revenue, training, variety of youngsters, and so forth., in addition to previous listenership information, all in-line with the NGO’s information privateness requirements (extra under).
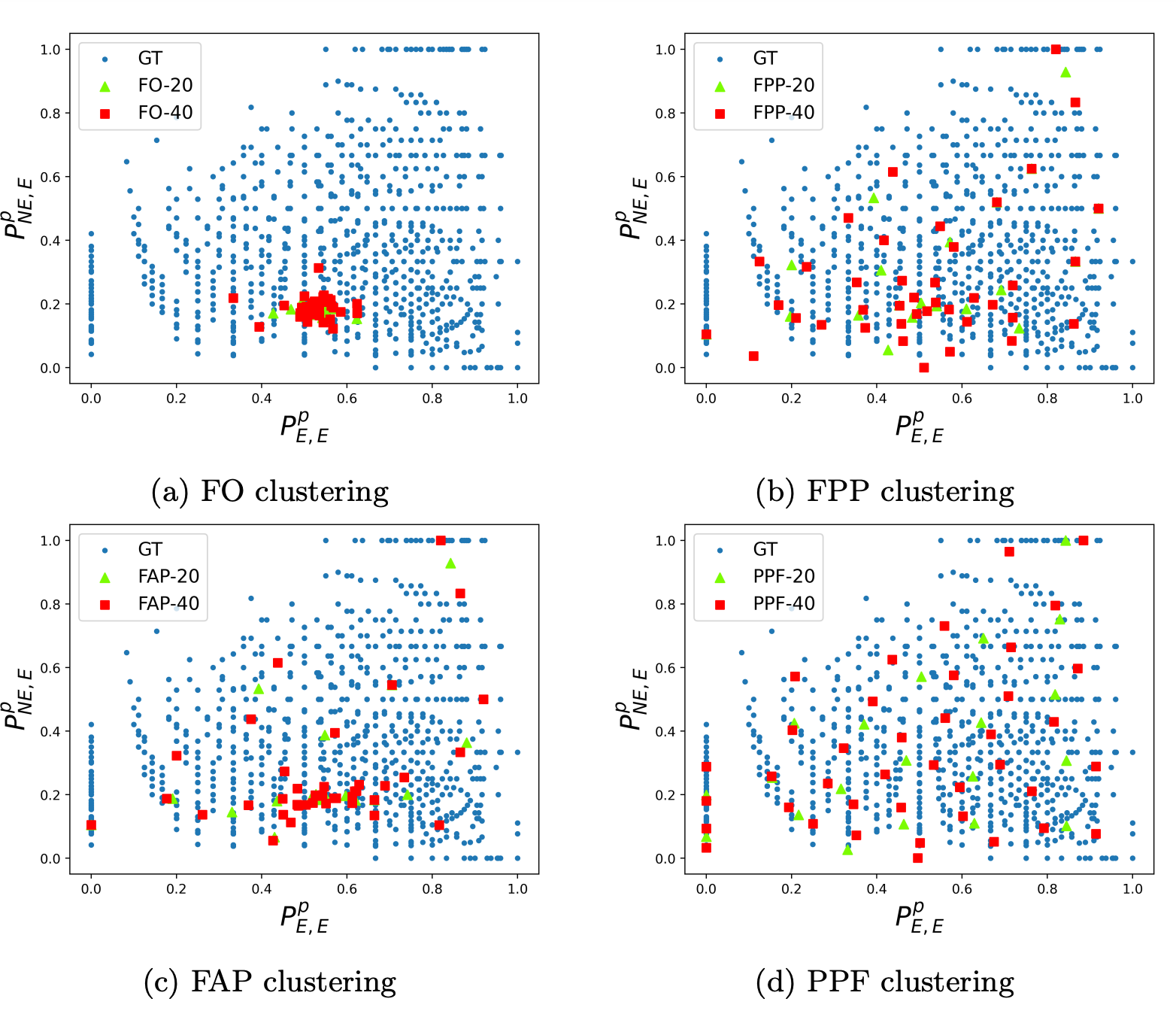
Nonetheless, the restricted quantity of service calls limits the info equivalent to receiving a service name. To mitigate this, we use clustering methods to be taught from the collective observations of beneficiaries inside a cluster and allow overcoming the problem of restricted samples per particular person beneficiary.
Particularly, we carry out clustering on listenership behaviors, after which compute a mapping from the demographic options to every cluster.
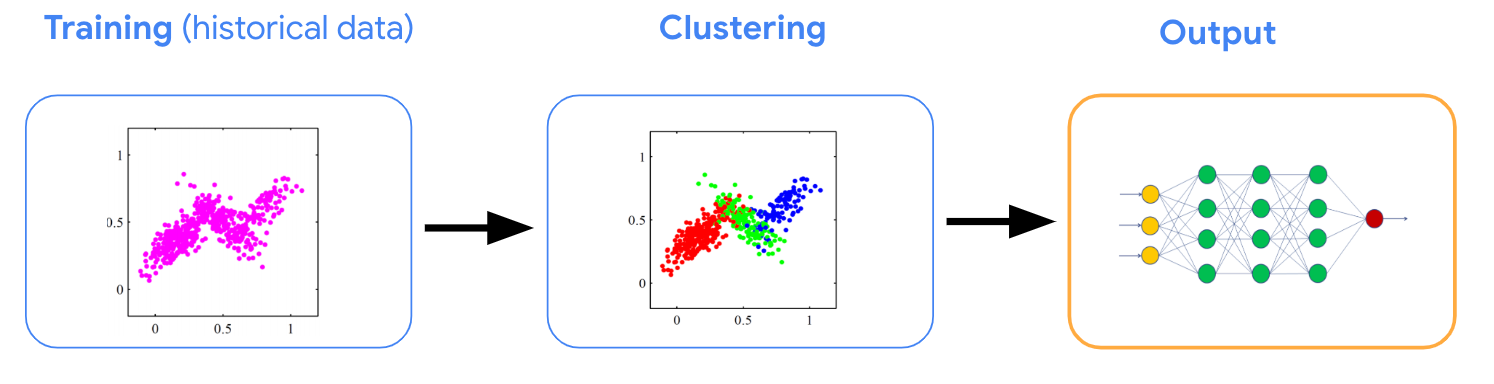 |
| Clustering on previous listenership information reveals clusters with beneficiaries that behave equally. We then infer a mapping from demographic options to clusters. |
This mapping is helpful as a result of when a brand new beneficiary is enrolled, we solely have entry to their demographic info and haven’t any data of their listenership patterns, since they haven’t had an opportunity to pay attention but. Utilizing the mapping, we are able to infer transition chances for any new beneficiary that enrolls into the system.
We used a number of qualitative and quantitative metrics to deduce the optimum set of of clusters and explored totally different mixtures of coaching information (demographic options solely, options plus passive chances, options plus all chances, passive chances solely) to attain essentially the most significant clusters, which might be consultant of the underlying information distribution and have a low variance in particular person cluster sizes.
Clustering has the added benefit of decreasing computational price for resource-limited NGOs, because the optimization must be solved at a cluster degree quite than a person degree. Lastly, fixing RMAB’s is thought to be P-space exhausting, so we select to resolve the optimization utilizing the favored Whittle index method, which finally supplies a rating of beneficiaries primarily based on their possible advantage of receiving a service name.
Outcomes
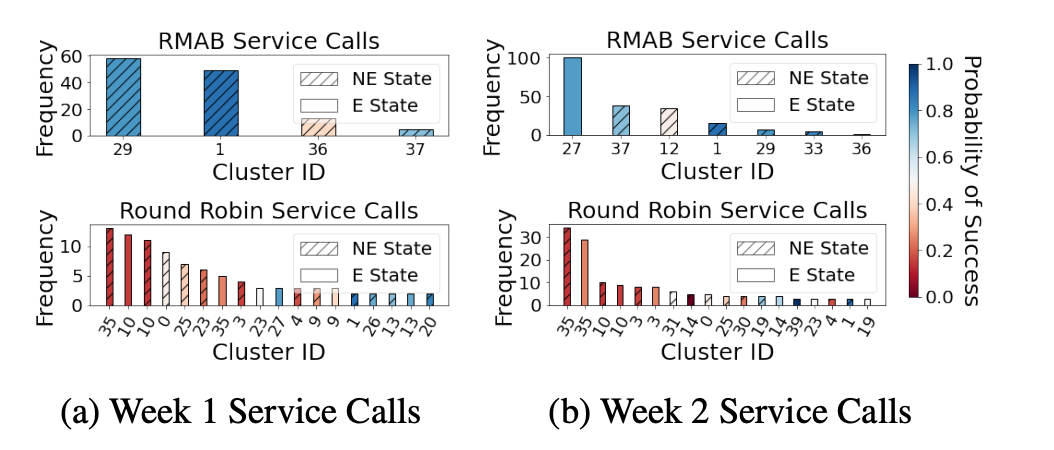
We evaluated the mannequin in an actual world research consisting of roughly 23,000 beneficiaries who had been divided into three teams: the present customary of care (CSOC) group, the “spherical robin” (RR) group, and the RMAB group. The beneficiaries within the CSOC group comply with the unique customary of care, the place there are not any NGO initiated service calls. The RR group represents the situation the place the NGO usually conducts service calls utilizing some systematic set order — the concept right here is to have an simply executable coverage that providers sufficient of a cross-section of beneficiaries and will be scaled up or down per week primarily based on obtainable sources (that is the method utilized by the NGO on this specific case, however the method could differ for various NGOs). The RMAB group receives service calls as predicted by the RMAB mannequin. All of the beneficiaries throughout the three teams proceed to obtain the automated voice messages impartial of the service calls.
On the finish of seven weeks, RMAB-based service calls resulted within the highest (and statistically important) discount in cumulative engagement drops (32%) in comparison with the CSOC group.
 |
| The plot reveals cumulative engagement drops prevented in comparison with the management group. |
| RMAB vs CSOC | RR vs CSOC | RMAB vs RR | |
| % discount in cumulative engagement drops | 32.0% | 5.2% | 28.3% |
| p-value | 0.044 | 0.740 | 0.098 |
Moral Concerns
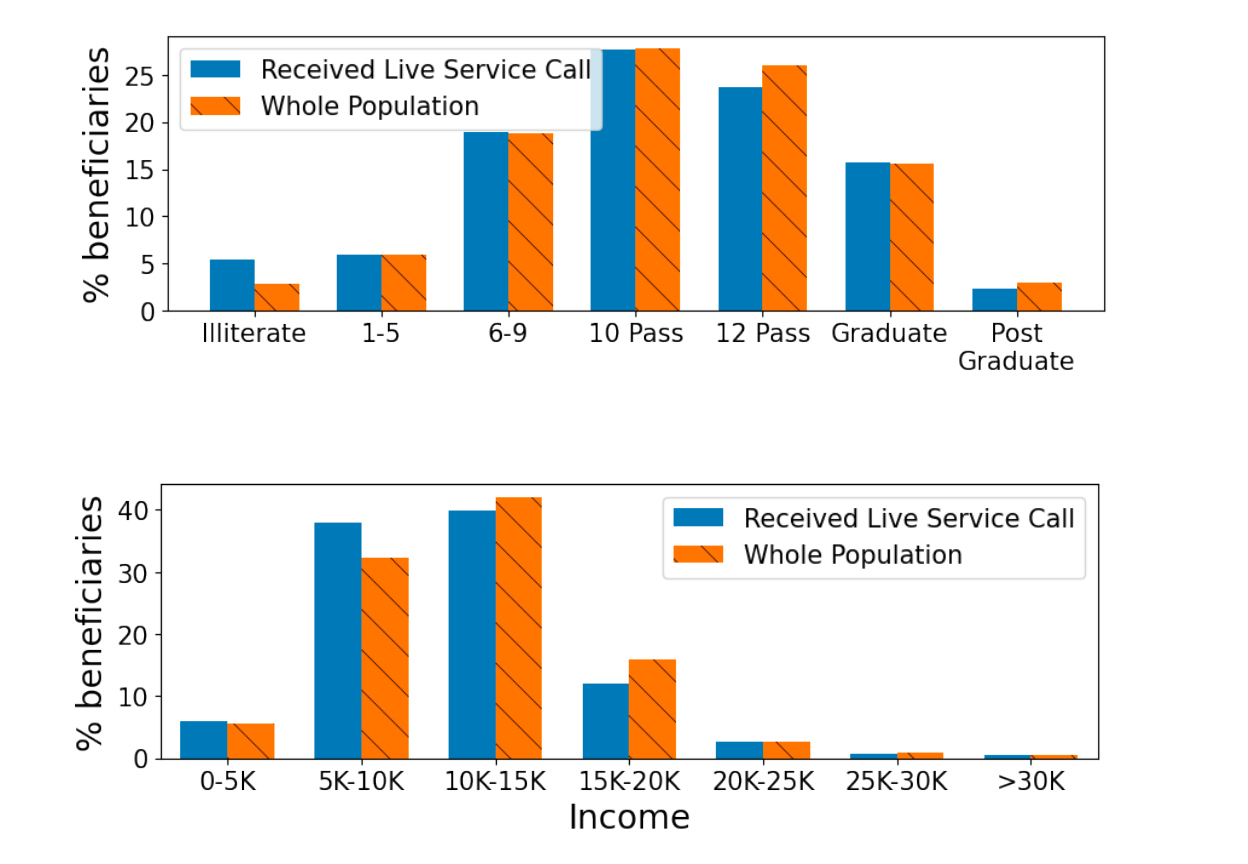
An ethics board on the NGO reviewed the research. We took important measures to make sure participant consent is known and recorded in a language of the neighborhood’s selection at every stage of this system. Knowledge stewardship resides within the fingers of the NGO, and solely the NGO is allowed to share information. The code will quickly be obtainable publicly. The pipeline solely makes use of anonymized information and no personally identifiable info (PII) is made obtainable to the fashions. Delicate information, similar to caste, faith, and so forth., should not collected by ARMMAN for mMitra. Subsequently, in pursuit of guaranteeing equity of the mannequin, we labored with public well being and subject specialists to make sure different indicators of socioeconomic standing had been measured and adequately evaluated as proven under.
The proportion of beneficiaries that obtained a stay service name inside every revenue bracket moderately matches the proportion within the total inhabitants. Nonetheless, variations are noticed in decrease revenue classes, the place the RMAB mannequin favors beneficiaries with decrease revenue and beneficiaries with no formal training. Lastly, area specialists at ARMMAN have been deeply concerned within the growth and testing of this technique and have supplied steady enter and oversight in information interpretation, information consumption, and mannequin design.
Conclusions
After thorough testing, the NGO has at the moment deployed this technique for scheduling of service calls on a weekly foundation. We’re hopeful that it will pave the way in which for extra deployments of ML algorithms for social impression in partnerships with non-profits in service of populations which have up to now benefited much less from ML. This work was additionally featured in Google for India 2021.
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of our AI for Social Good efforts and was led by Google Analysis, India. Because of all our collaborators at ARMMAN, Google Analysis India, Google.org, and College Relations: Aparna Hegde, Neha Madhiwalla, Suresh Chaudhary, Aditya Mate, Lovish Madaan, Shresth Verma, Gargi Singh, Divy Thakkar.
1ARMMAN runs a number of packages to supply preventive care info to girls via being pregnant and infancy enabling them to hunt care, in addition to packages to coach and assist well being staff for well timed detection and administration of high-risk situations. ↩