As digital assistants grow to be ubiquitous, customers more and more work together with them to study new matters or get hold of suggestions and anticipate them to ship capabilities past slender dialogues of 1 or two turns. Dynamic planning, specifically the aptitude to look forward and replan based mostly on the move of the dialog, is a necessary ingredient for the making of partaking conversations with the deeper, open-ended interactions that customers anticipate.
Whereas massive language fashions (LLMs) at the moment are beating state-of-the-art approaches in lots of pure language processing benchmarks, they’re sometimes skilled to output the subsequent finest response, fairly than planning forward, which is required for multi-turn interactions. Nevertheless, up to now few years, reinforcement studying (RL) has delivered unimaginable outcomes addressing particular issues that contain dynamic planning, resembling successful video games and protein folding.
At present, we’re sharing our current advances in dynamic planning for human-to-assistant conversations, during which we allow an assistant to plan a multi-turn dialog in the direction of a purpose and adapt that plan in real-time by adopting an RL-based method. Right here we take a look at methods to enhance lengthy interactions by making use of RL to compose solutions based mostly on data extracted from respected sources, fairly than counting on content material generated by a language mannequin. We anticipate that future variations of this work might mix LLMs and RL in multi-turn dialogues. The deployment of RL “within the wild” in a large-scale dialogue system proved a formidable problem as a result of modeling complexity, tremendously massive state and motion areas, and important subtlety in designing reward features.
What’s dynamic planning?
Many sorts of conversations, from gathering data to providing suggestions, require a versatile method and the flexibility to change the unique plan for the dialog based mostly on its move. This capability to shift gears in the midst of a dialog is named dynamic planning, versus static planning, which refers to a extra fastened method. Within the dialog beneath, for instance, the purpose is to interact the consumer by sharing fascinating info about cool animals. To start, the assistant steers the dialog to sharks by way of a sound quiz. Given the consumer’s lack of curiosity in sharks, the assistant then develops an up to date plan and pivots the dialog to sea lions, lions, after which cheetahs.
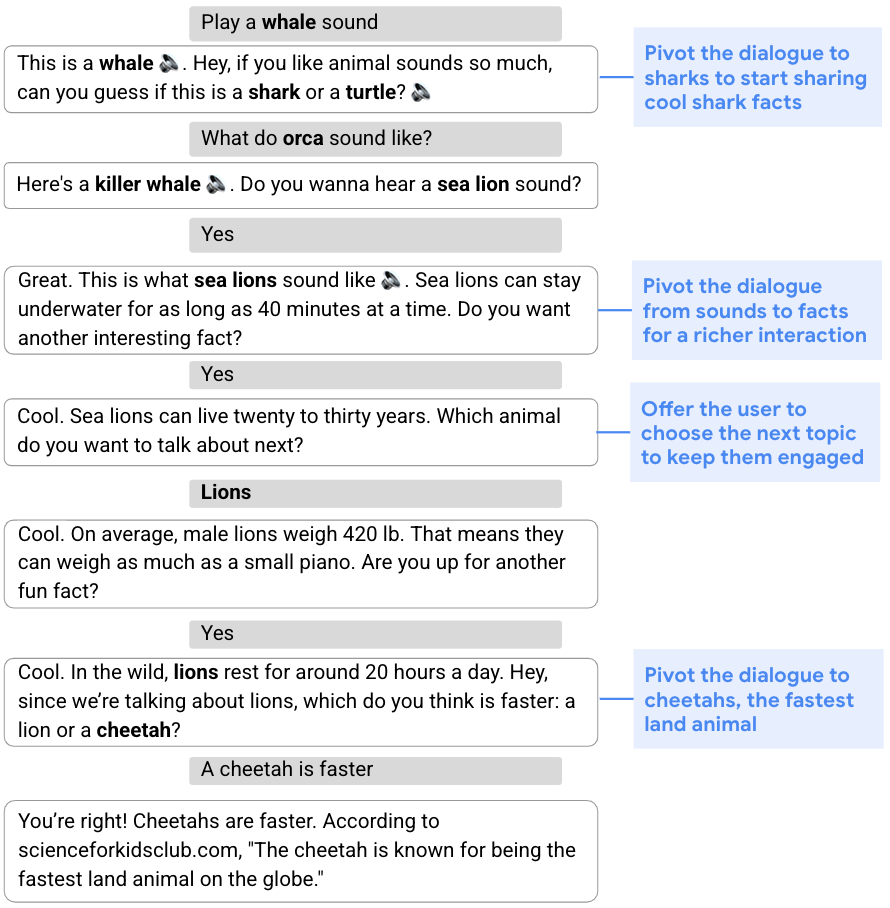 |
| The assistant dynamically modifies its unique plan to speak about sharks and shares info about different animals. |
Dynamic composition
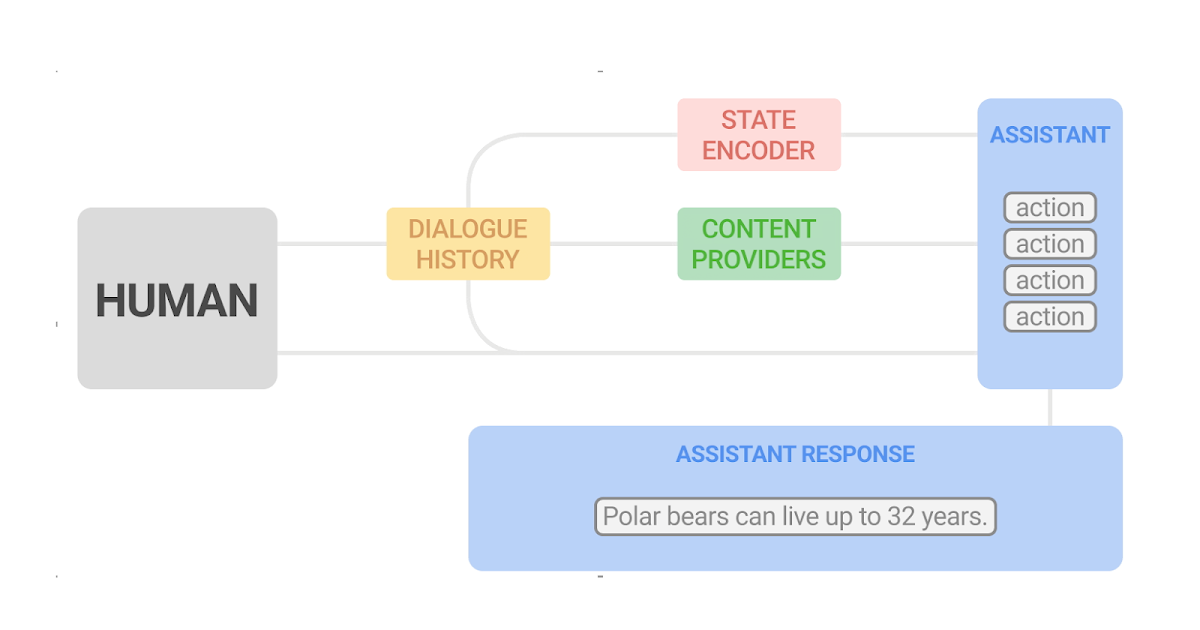
To deal with the problem of conversational exploration, we separate the technology of assistant responses into two elements: 1) content material technology, which extracts related data from respected sources, and a pair of) versatile composition of such content material into assistant responses. We confer with this two-part method as dynamic composition. In contrast to LLM strategies, this method provides the assistant the flexibility to completely management the supply, correctness, and high quality of the content material that it might provide. On the similar time, it may obtain flexibility by way of a realized dialogue supervisor that selects and combines essentially the most applicable content material.
In an earlier paper, “Dynamic Composition for Conversational Area Exploration”, we describe a novel method which consists of: (1) a group of content material suppliers, which provide candidates from totally different sources, resembling information snippets, data graph info, and questions; (2) a dialogue supervisor; and (3) a sentence fusion module. Every assistant response is incrementally constructed by the dialogue supervisor, which selects candidates proposed by the content material suppliers. The chosen sequence of utterances is then fused right into a cohesive response.
Dynamic planning utilizing RL
On the core of the assistant response composition loop is a dialogue supervisor skilled utilizing off-policy RL, specifically an algorithm that evaluates and improves a coverage that’s totally different from the coverage utilized by the agent (in our case, the latter is predicated on a supervised mannequin). Making use of RL to dialogue administration presents a number of challenges, together with a big state house (because the state represents the dialog state, which must account for the entire dialog historical past) and an successfully unbounded motion house (that will embrace all present phrases or sentences in pure language).
We tackle these challenges utilizing a novel RL development. First, we leverage highly effective supervised fashions — particularly, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers — to supply a succinct and efficient dialogue state illustration. These state encoders are fed with the dialogue historical past, composed of a sequence of consumer and assistant turns, and output a illustration of the dialogue state within the type of a latent vector.
Second, we use the truth that a comparatively small set of cheap candidate utterances or actions could be generated by content material suppliers at every dialog flip, and restrict the motion house to those. Whereas the motion house is often fastened in RL settings, as a result of all states share the identical motion house, ours is a non-standard house during which the candidate actions could differ with every state, since content material suppliers generate totally different actions relying on the dialogue context. This places us within the realm of stochastic motion units, a framework that formalizes circumstances the place the set of actions obtainable in every state is ruled by an exogenous stochastic course of, which we tackle utilizing Stochastic Motion Q-Studying, a variant of the Q-learning method. Q-learning is a well-liked off-policy RL algorithm, which doesn’t require a mannequin of the surroundings to guage and enhance the coverage. We skilled our mannequin on a corpus of crowd-compute–rated conversations obtained utilizing a supervised dialogue supervisor.
Reinforcement studying mannequin analysis
We in contrast our RL dialogue supervisor with a launched supervised transformer mannequin in an experiment utilizing Google Assistant, which conversed with customers about animals. A dialog begins when a consumer triggers the expertise by asking an animal-related question (e.g., “How does a lion sound?”). The experiment was carried out utilizing an A/B testing protocol, during which a small proportion of Assistant customers have been randomly sampled to work together with our RL-based assistant whereas different customers interacted with the usual assistant.
We discovered that the RL dialogue supervisor conducts longer, extra partaking conversations. It will increase dialog size by 30% whereas bettering consumer engagement metrics. We see a rise of 8% in cooperative responses to the assistant’s questions — e.g., “Inform me about lions,” in response to “Which animal do you need to hear about subsequent?” Though there’s additionally a big enhance in nominally “non-cooperative” responses (e.g., “No,” as a reply to a query proposing extra content material, resembling “Do you need to hear extra?”), that is anticipated because the RL agent takes extra dangers by asking pivoting questions. Whereas a consumer might not be within the conversational route proposed by the assistant (e.g., pivoting to a different animal), the consumer will usually proceed to interact in a dialogue about animals.
As well as, some consumer queries comprise express optimistic (e.g., “Thanks, Google,” or “I’m pleased.”) or adverse (e.g., “Shut up,” or “Cease.”) suggestions. Whereas an order of magnitude fewer than different queries, they provide a direct measure of consumer (dis)satisfaction. The RL mannequin will increase express optimistic suggestions by 32% and reduces adverse suggestions by 18%.
Realized dynamic planning traits and methods
We observe a number of traits of the (unseen) RL plan to enhance consumer engagement whereas conducting longer conversations. First, the RL-based assistant ends 20% extra turns in questions, prompting the consumer to decide on extra content material. It additionally higher harnesses content material range, together with info, sounds, quizzes, sure/no questions, open questions, and so forth. On common, the RL assistant makes use of 26% extra distinct content material suppliers per dialog than the supervised mannequin.
Two noticed RL planning methods are associated to the existence of sub-dialogues with totally different traits. Sub-dialogues about animal sounds are poorer in content material and exhibit entity pivoting at each flip (i.e., after enjoying the sound of a given animal, we will both recommend the sound of a distinct animal or quiz the consumer about different animal sounds). In distinction, sub-dialogues involving animal info sometimes comprise richer content material and have better dialog depth. We observe that RL favors the richer expertise of the latter, choosing 31% extra fact-related content material. Lastly, when limiting evaluation to fact-related dialogues, the RL assistant displays 60% extra focus-pivoting turns, that’s, conversational turns that change the main focus of the dialogue.
Beneath, we present two instance conversations, one carried out by the supervised mannequin (left) and the second by the RL mannequin (proper), during which the primary three consumer turns are an identical. With a supervised dialogue supervisor, after the consumer declined to listen to about “at this time’s animal”, the assistant pivots again to animal sounds to maximise the quick consumer satisfaction. Whereas the dialog carried out by the RL mannequin begins identically, it displays a distinct planning technique to optimize the general consumer engagement, introducing extra various content material, resembling enjoyable info.
Future analysis and challenges
Up to now few years, LLMs skilled for language understanding and technology have demonstrated spectacular outcomes throughout a number of duties, together with dialogue. We at the moment are exploring the usage of an RL framework to empower LLMs with the aptitude of dynamic planning in order that they’ll dynamically plan forward and delight customers with a extra partaking expertise.
Acknowledgements
The work described is co-authored by: Moonkyung Ryu, Yinlam Chow, Orgad Keller, Ido Greenberg, Avinatan Hassidim, Michael Fink, Yossi Matias, Idan Szpektor and Gal Elidan. We want to thank: Roee Aharoni, Moran Ambar, John Anderson, Ido Cohn, Mohammad Ghavamzadeh, Lotem Golany, Ziv Hodak, Adva Levin, Fernando Pereira, Shimi Salant, Shachar Shimoni, Ronit Slyper, Ariel Stolovich, Hagai Taitelbaum, Noam Velan, Avital Zipori and the CrowdCompute workforce led by Ashwin Kakarla. We thank Sophie Allweis for her suggestions on this blogpost and Tom Small for the visualization.